Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2021; 27(21): 2850-2870
Published online Jun 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i21.2850
Published online Jun 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i21.2850
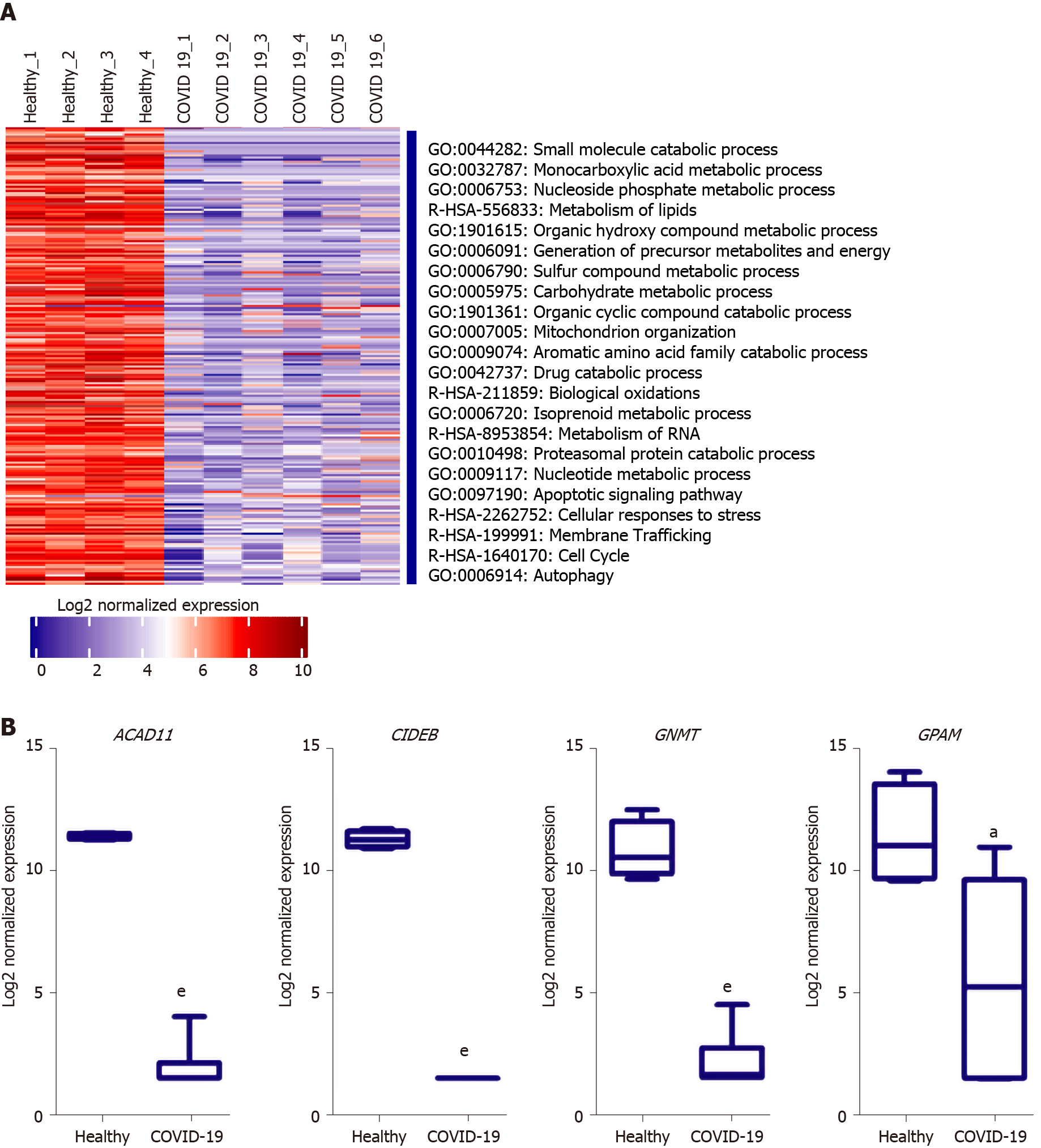
Figure 6 functional clustering analysis of the downregulated transcriptome of severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients liver autopsy tissues.
A: Heatmap representation of the differentially downregulated genes and subsequently enriched pathways and functional clusters in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV2) infected liver samples in comparison to baseline expression in healthy tissue samples; B: box plot representation of some of the top downregulated transcripts in SARS-CoV-2 infected liver tissue samples. Data presented as mean ± SE; aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0005, eP < 0.0001 COVID-19 vs Healthy. ACAD11: acyl-CoA dehydrogenases 11; CIDEB: cell death-inducing DNA fragmentation factor alpha-like effector B; GNMT: glycine N-methyltransferase; GPAM: glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase and metabolism.
- Citation: Hammoudeh SM, Hammoudeh AM, Bhamidimarri PM, Mahboub B, Halwani R, Hamid Q, Rahmani M, Hamoudi R. Insight into molecular mechanisms underlying hepatic dysfunction in severe COVID-19 patients using systems biology. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(21): 2850-2870
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i21/2850.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i21.2850