Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2021; 27(21): 2727-2757
Published online Jun 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i21.2727
Published online Jun 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i21.2727
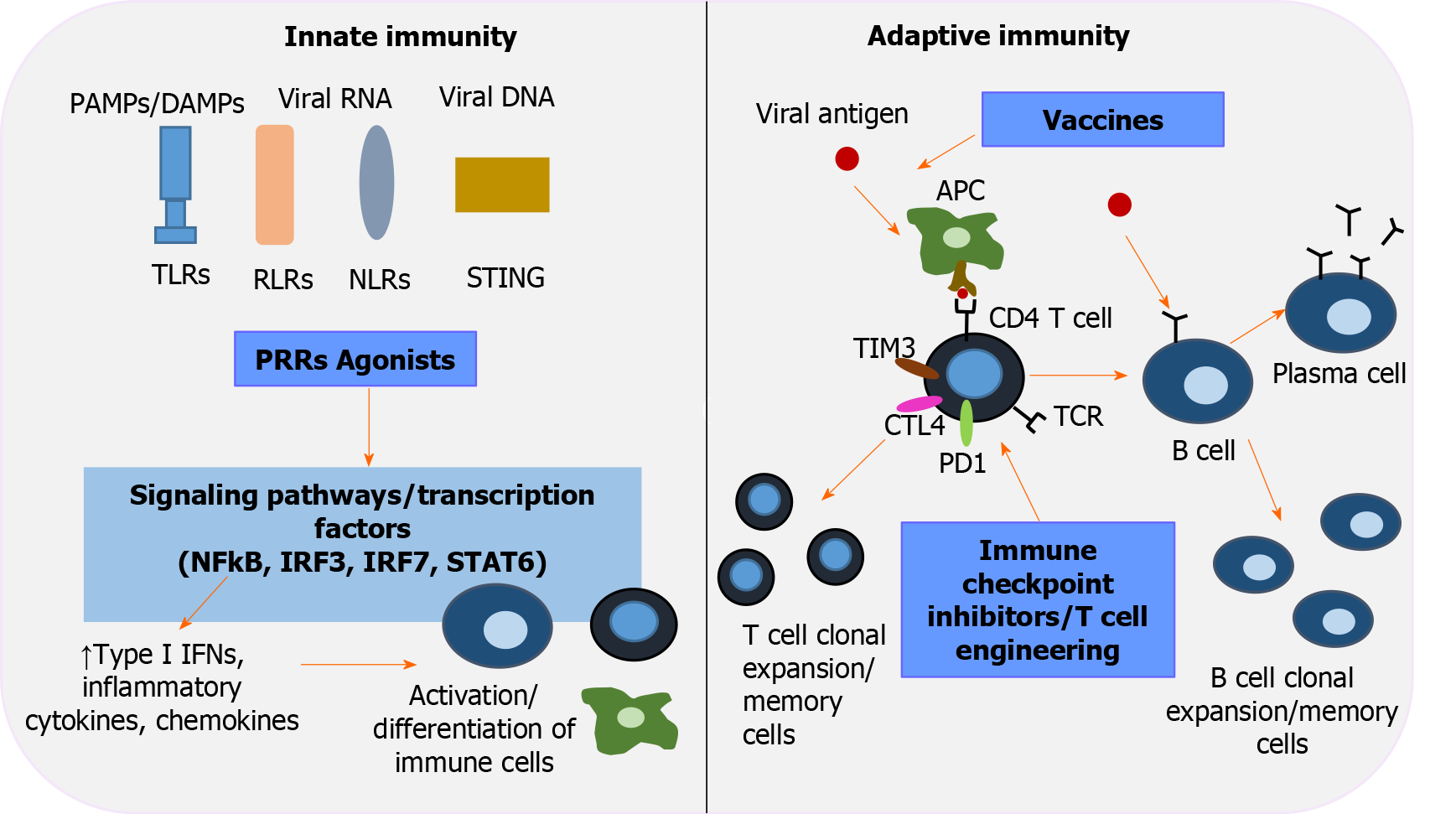
Figure 2 Immunotherapeutic interventions to revive host immunity in chronic hepatitis B virus infection.
Pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs), including toll-like receptors, retinoic acid-inducible gene-I-like receptors, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors, stimulator of interferon genes, are key players in innate immunity and the first line of defense that recognizes pathogen-associated molecular patterns/damage-associated molecular patterns. Activation of PRRs by their corresponding agonists triggers transduction signals and transcription factors [nuclear factor-κB, interferon regulatory factor (IRF) 3, IRF 7, signal transducer and activator of transcription 6], which in turn upregulate type interferons, inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, leading to well-orchestrated immune cell differentiation. Immune checkpoint inhibitors aim to restore T-cell function by inhibiting negative regulators of T-cell activation (programmed cell death protein 1, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4, T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-3). Adoptive transfer of genetically engineered T -cells is an alternative strategy to elicit potent hepatitis B virus - specific T-cell responses. The role of therapeutic vaccination in overcoming exhausted cellular and humoral responses is currently under investigation. An efficient vaccine repairs function and induces antigen- presenting cells to activate the two arms of adaptive immunity: polyclonal and multispecific CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses, and well-regulated B cells that differentiate into plasma cells and secrete neutralizing antibodies. IFNs: Interferons; IRF: Interferon regulatory factor; NF-κΒ: Nuclear factor-κB; NLRs: Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors; PAMPS: Pathogen-associated molecular patterns; PD-1: Programmed cell death protein 1; PRRs: Pattern-recognition receptors; RLRs: Retinoic acid-inducible gene-I-like receptors; STAT6: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 6; STING: Stimulator of interferon genes; TIM3: T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-3; TLRs: Toll-like receptors.
- Citation: Tsounis EP, Tourkochristou E, Mouzaki A, Triantos C. Toward a new era of hepatitis B virus therapeutics: The pursuit of a functional cure. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(21): 2727-2757
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i21/2727.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i21.2727