Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2021; 27(19): 2394-2414
Published online May 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i19.2394
Published online May 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i19.2394
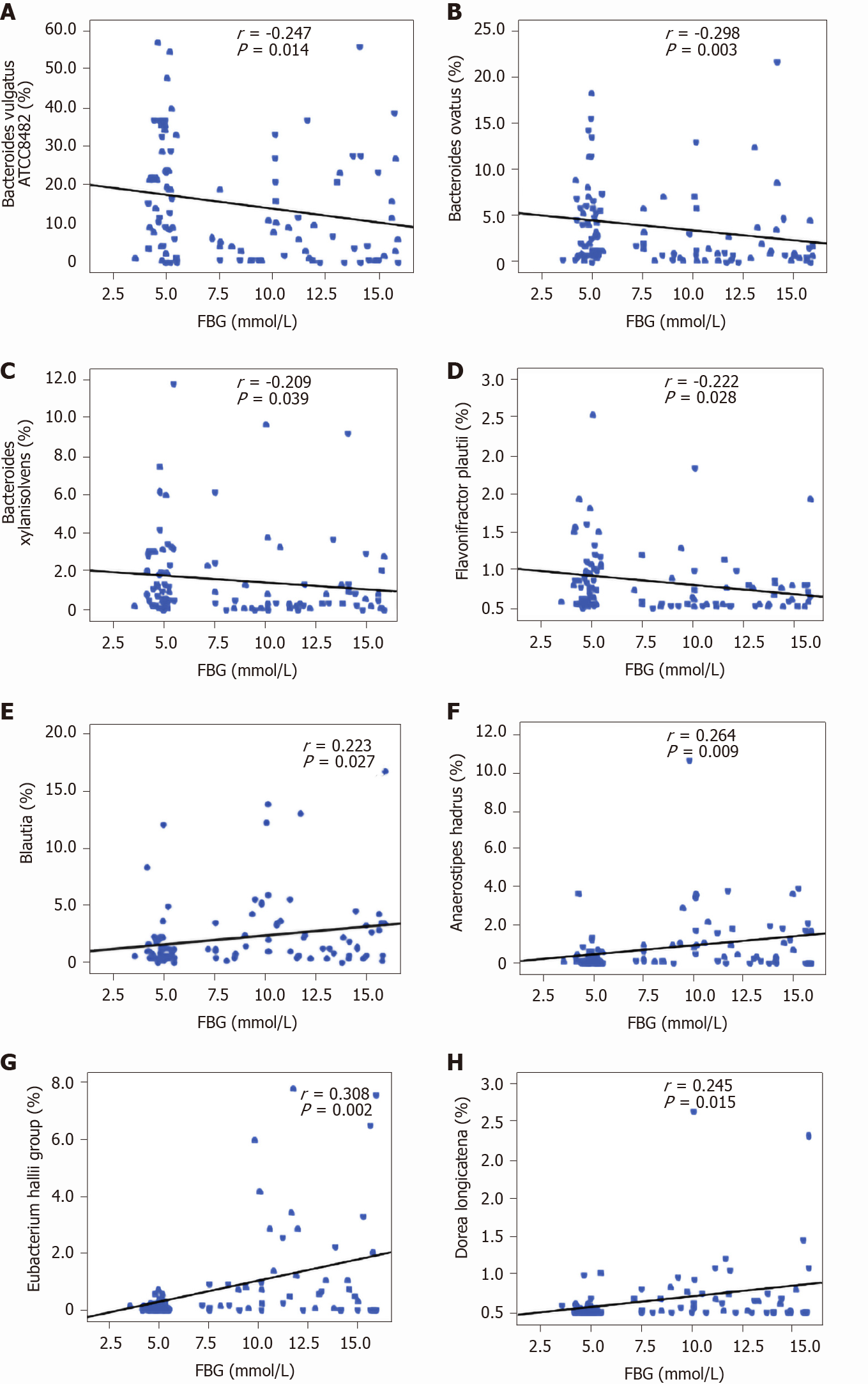
Figure 6 Correlation between key bacteria in type 1 diabetes mellitus-associated fecal microbiota and fasting blood glucose.
The different taxa, including Bacteroides vulgatus ATCC8482, Bacteroides ovatus, Bacteroides xylanisolvens, and Flavonifractor plautii, were negatively correlated with fasting blood glucose (FBG), while Blautia, the Eubacterium hallii group, Anaerostipes hadrus, and Dorea longicatena were positively correlated with FBG. Spearman’s rank correlation and probability were used to evaluate statistical significance. A: Bacteroides vulgatus ATCC8482; B: Bacteroides ovatus; C: Bacteroides xylanisolvens; D: Flavonifractor plautii; E: Blautia; F: Anaerostipes hadrus; G: Eubacterium hallii; H: Dorea longicatena. FBG: Fasting blood glucose.
- Citation: Liu X, Cheng YW, Shao L, Sun SH, Wu J, Song QH, Zou HS, Ling ZX. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in Chinese children with type 1 diabetes mellitus: An observational study . World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(19): 2394-2414
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i19/2394.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i19.2394