Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2021; 27(18): 2160-2176
Published online May 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i18.2160
Published online May 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i18.2160
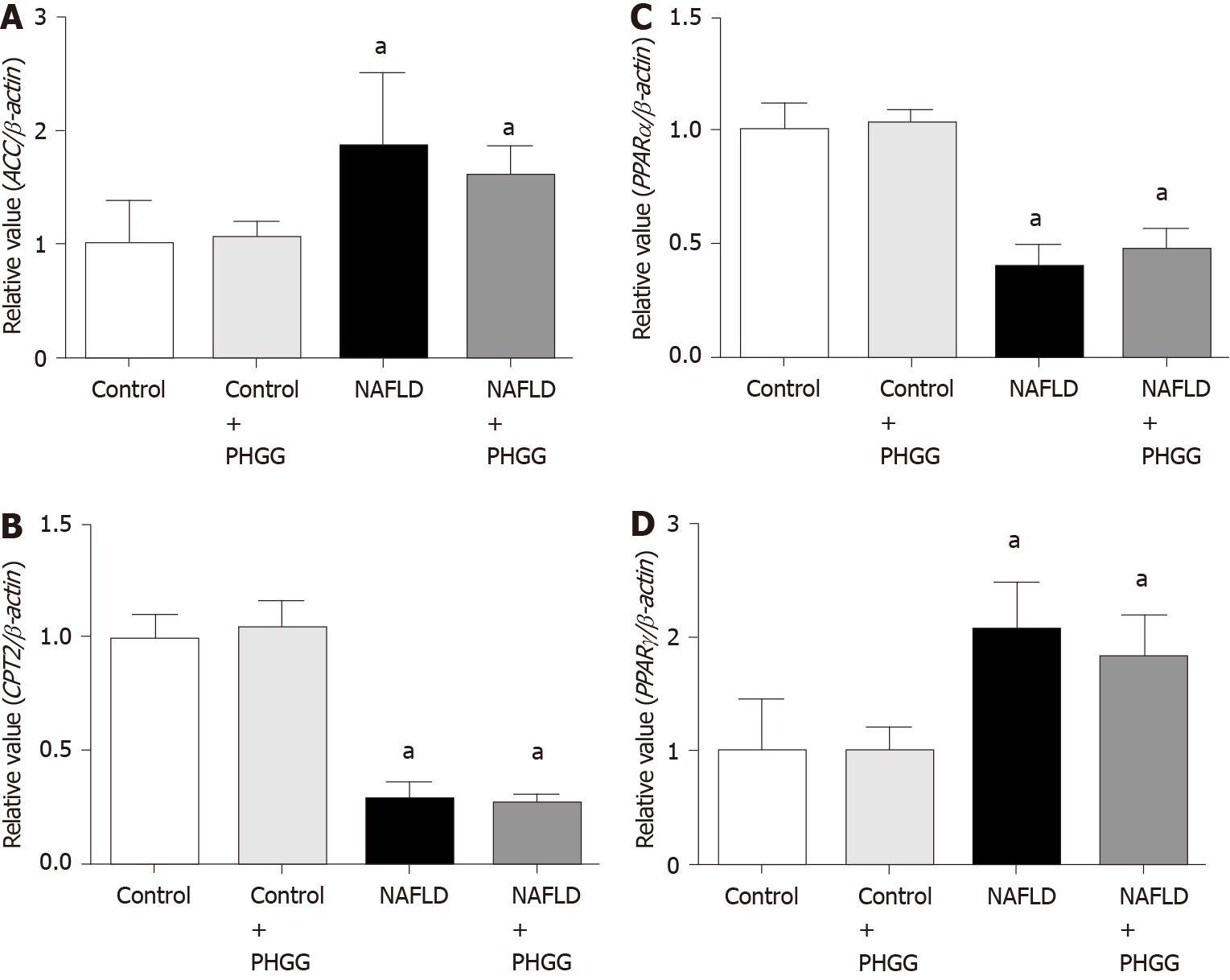
Figure 3 Effects of partially hydrolyzed guar gum on lipid synthesis and degradation in the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease model.
A: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; B: Carnitine O-palmitoyltransferase II; C: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) α; D: PPARγ mRNA expression in the liver. mRNA expression was evaluated using real-time polymerase chain reaction. Data represent the mean ± SD of seven mice. aP < 0.05 significant differences compared to the control group. NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; PHGG: Partially hydrolyzed guar gum; ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; CPT2: Carnitine O-palmitoyltransferase II.
- Citation: Takayama S, Katada K, Takagi T, Iida T, Ueda T, Mizushima K, Higashimura Y, Morita M, Okayama T, Kamada K, Uchiyama K, Handa O, Ishikawa T, Yasukawa Z, Okubo T, Itoh Y, Naito Y. Partially hydrolyzed guar gum attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice through the gut-liver axis. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(18): 2160-2176
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i18/2160.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i18.2160