Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2021; 27(18): 2160-2176
Published online May 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i18.2160
Published online May 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i18.2160
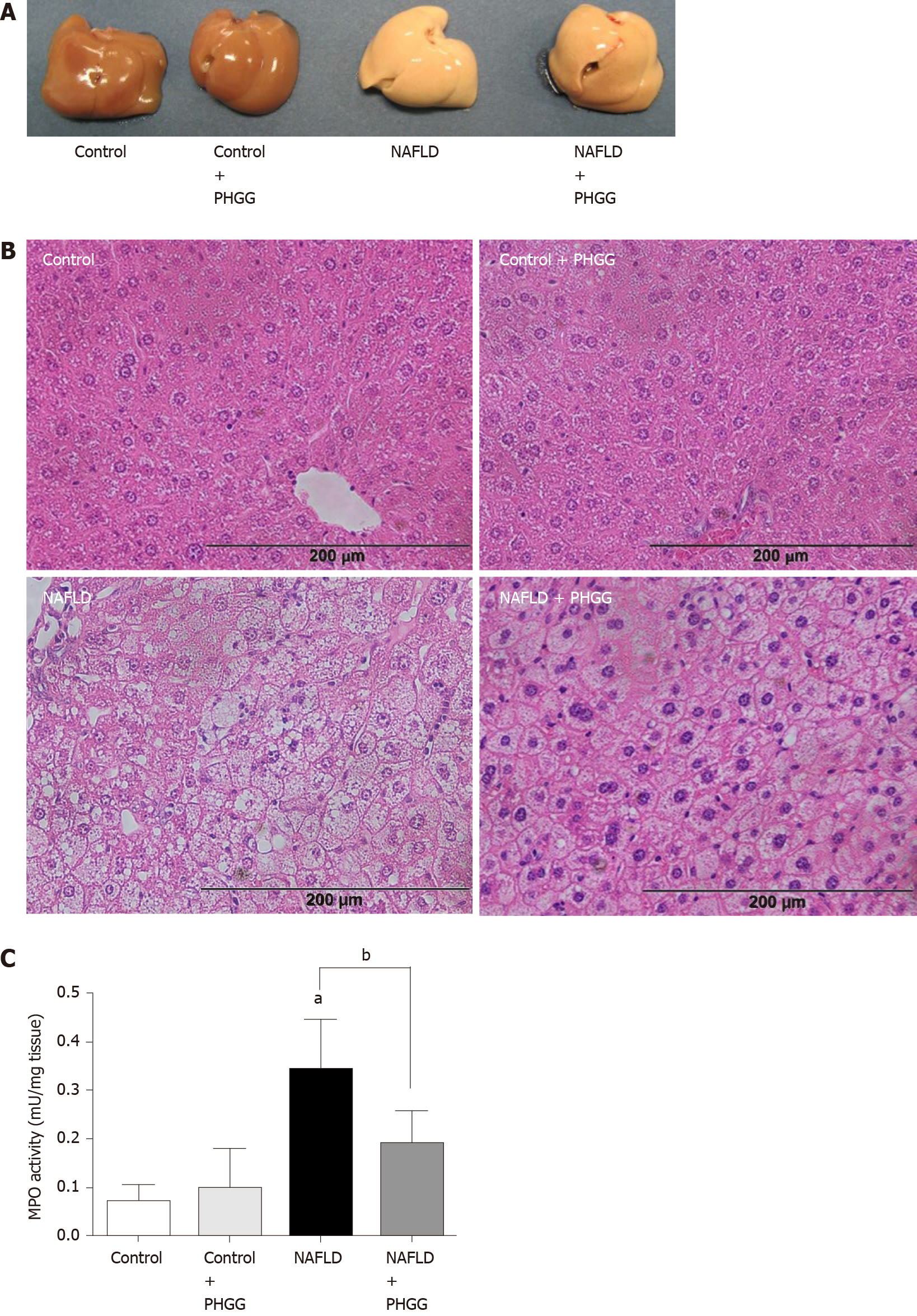
Figure 1 Effects of partially hydrolyzed guar gum on the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease model.
A: Representative macroscopic findings in the liver. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease was induced in mice subjected to the atherogenic diet with increased intestinal permeability for 8 wk; B: Representative histological findings in the liver. Magnification, × 100. Hematoxylin and eosin staining; C: Myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity. The liver was homogenized and MPO activity was determined as an index of neutrophil accumulation in the liver. Data represent the mean ± SD of seven mice. aP < 0.05 significant differences compared to the control group; bP < 0.05 significant differences between the 2 selected groups. NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; PHGG: Partially hydrolyzed guar gum; MPO: Myeloperoxidase.
- Citation: Takayama S, Katada K, Takagi T, Iida T, Ueda T, Mizushima K, Higashimura Y, Morita M, Okayama T, Kamada K, Uchiyama K, Handa O, Ishikawa T, Yasukawa Z, Okubo T, Itoh Y, Naito Y. Partially hydrolyzed guar gum attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice through the gut-liver axis. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(18): 2160-2176
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i18/2160.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i18.2160