Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2021; 27(18): 2141-2159
Published online May 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i18.2141
Published online May 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i18.2141
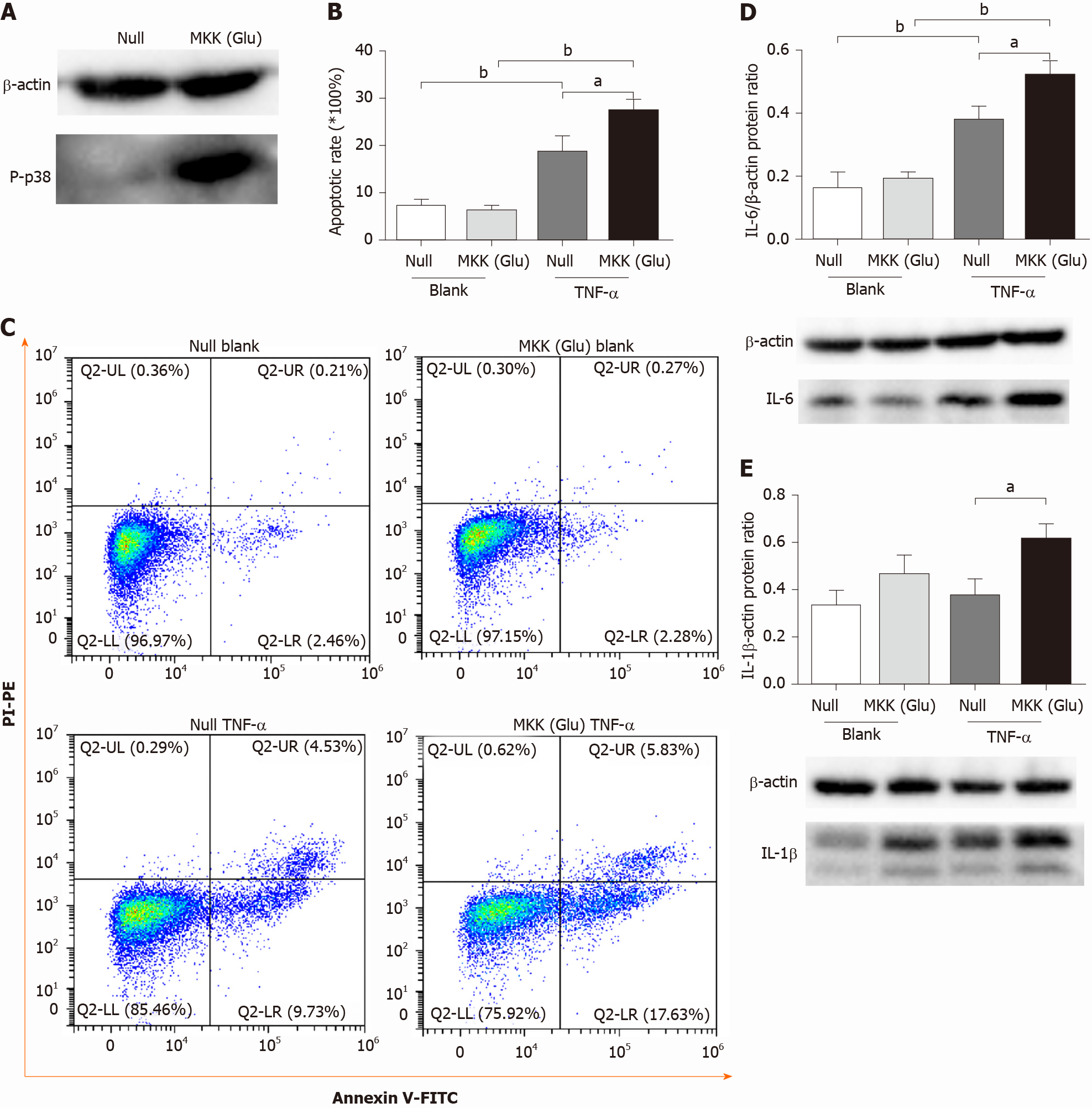
Figure 1 p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase overactivation aggravates tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis and inflammatory cytokine expression in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells.
A: Western blotting confirmed that mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (Glu) transfection constitutively activated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells; B: Apoptotic rate in null and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (Glu) pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells stimulated with or without tumor necrosis factor-alpha for 24 h; C: Representative images of flow cytometry analysis for apoptosis; D: The expression level of interleukin-6 in each group; E: The expression level of interleukin-1β in each group. Data are expressed as mean ± SE of 3-4 samples per group; aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. IL: Interleukin; MKK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
- Citation: Zhang XX, Wang HY, Yang XF, Lin ZQ, Shi N, Chen CJ, Yao LB, Yang XM, Guo J, Xia Q, Xue P. Alleviation of acute pancreatitis-associated lung injury by inhibiting the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(18): 2141-2159
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i18/2141.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i18.2141