Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2021; 27(17): 1864-1882
Published online May 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i17.1864
Published online May 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i17.1864
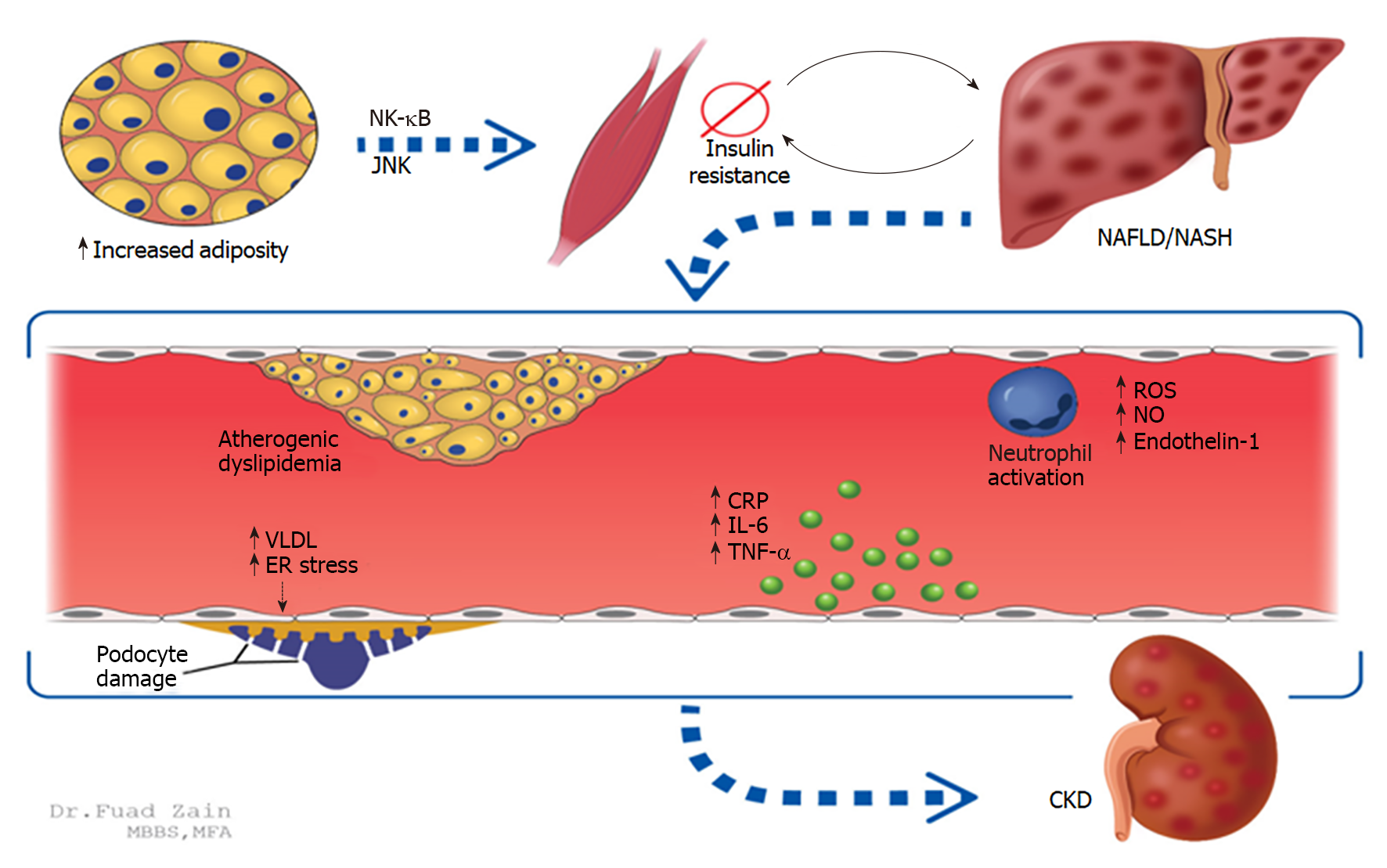
Figure 1 Two established mechanisms between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and the development of chronic kidney disease are increased adiposity and insulin resistance.
NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; JNK: Jun N-terminal kinases; NAFLD/NASH: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; NO: Nitric oxide; CRP: C-reactive protein; IL-6: Interleukin-6; VLDL: Very low-density lipoprotein; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; CKD: Chronic kidney disease
- Citation: Heda R, Yazawa M, Shi M, Bhaskaran M, Aloor FZ, Thuluvath PJ, Satapathy SK. Non-alcoholic fatty liver and chronic kidney disease: Retrospect, introspect, and prospect. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(17): 1864-1882
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i17/1864.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i17.1864