Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2021; 27(14): 1369-1391
Published online Apr 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i14.1369
Published online Apr 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i14.1369
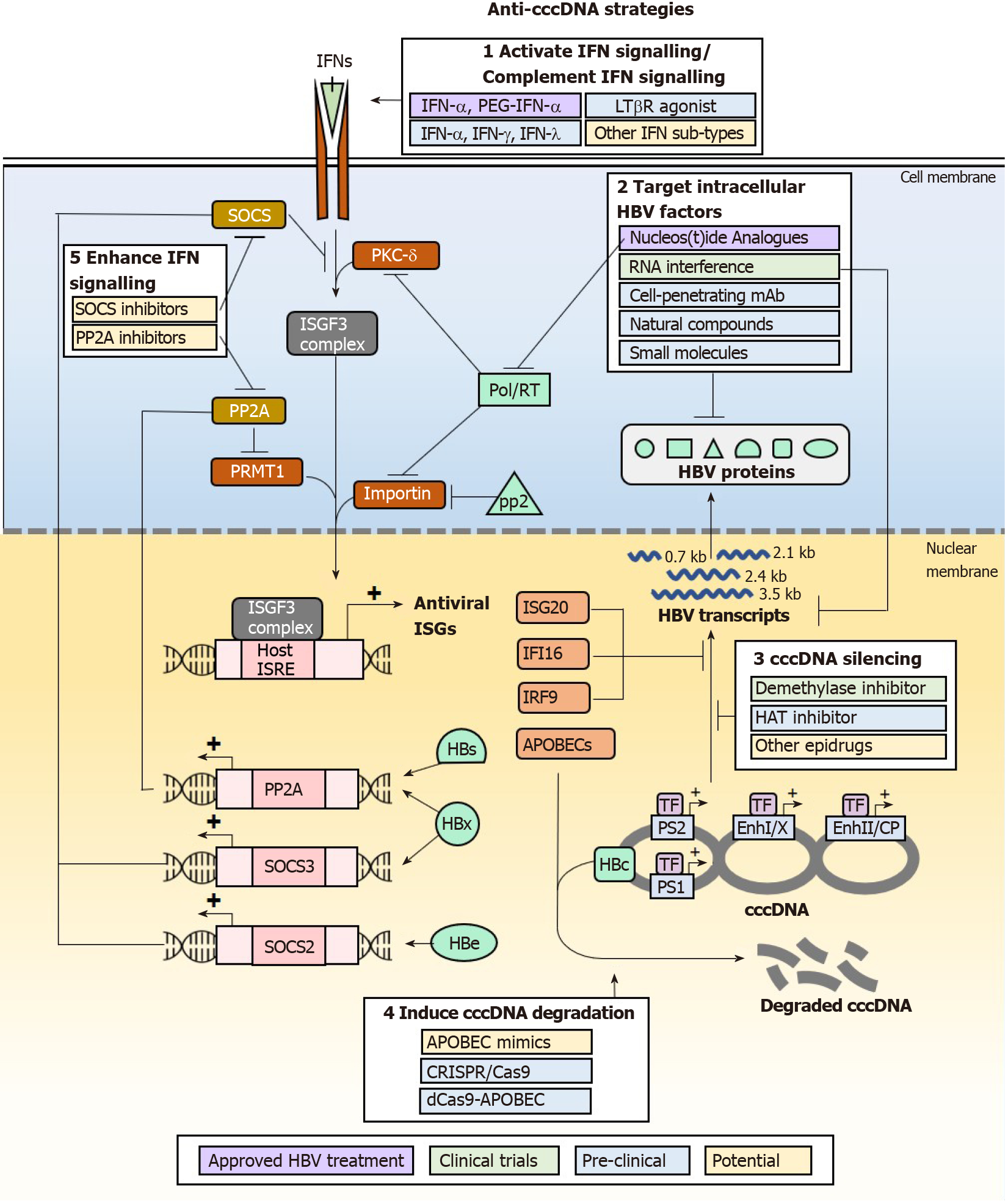
Figure 3 Anti-covalently closed circular DNA strategies and antagonistic hepatitis B virus proteins that modulate the interferon signalling pathway.
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) has developed multiple mechanisms that target different parts of the intracellular interferon (IFN) signalling pathway to avert elimination by IFN treatment. Therapeutic agents that counter HBV anti-IFN signalling activities or enhance the strength of host cell IFN signalling may be beneficial to increase the efficiency of IFN treatment for the elimination or silencing of covalently closed circular DNA. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; IFN: Interferon; PEG: Pegylated form; SOCS: Suppressor of cytokine signalling; PKC-δ: Protein kinase C-delta; IRF: Interferon regulatory factor; JAK: Activate janus kinase; STAT: Signal transducers and activators of transcription; Pol/RT: Polymerase/reverse transcriptase; TNF: Tumour necrosis factor; ISGs: Interferon-stimulated genes; ISRE: Interferon-stimulated response elements; cccDNA: Covalently closed circular DNA.
- Citation: Goh ZY, Ren EC, Ko HL. Intracellular interferon signalling pathways as potential regulators of covalently closed circular DNA in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(14): 1369-1391
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i14/1369.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i14.1369