Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2021; 27(11): 990-1005
Published online Mar 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i11.990
Published online Mar 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i11.990
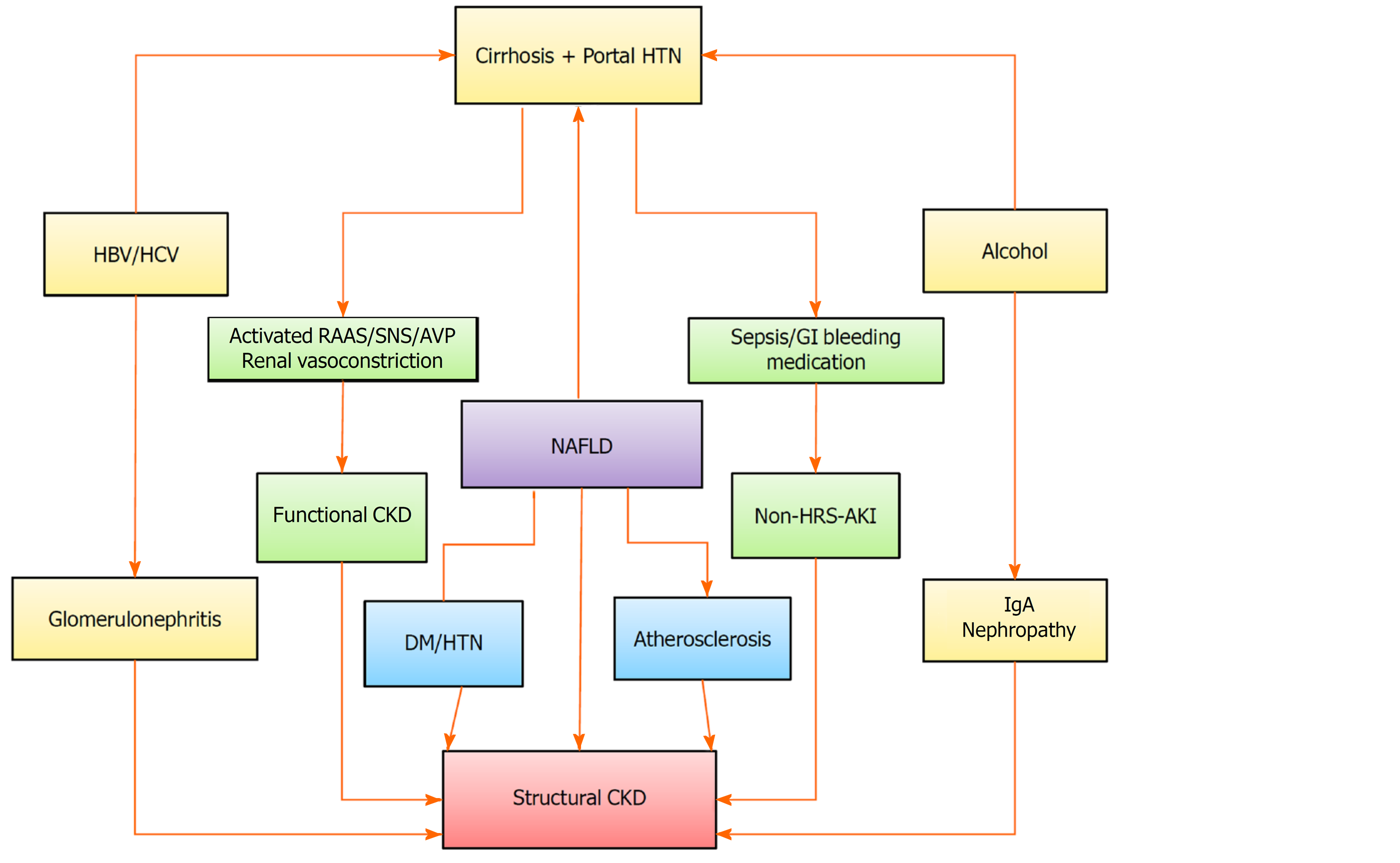
Figure 1 Risk factors associated with chronic kidney disease in patients with liver cirrhosis.
A rising trend in the prevalence of medicine degree, hypertension and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease seem to be the key factors behind the increased prevalence of chronic kidney disease in cirrhosis. The risk of developing de-novo chronic kidney disease remains high for acute kidney injury survivors. CKD: Chronic kidney disease; HTN: Hypertension; HBV: Hepatis B virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; RAAS: Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; SNS: Sympathetic nervous system; AVP: Arginine vasopressin; GI: Gastrointestinal; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; HRS: Hepatorenal syndrome; AKI: Acute kidney injury.
- Citation: Kumar R, Priyadarshi RN, Anand U. Chronic renal dysfunction in cirrhosis: A new frontier in hepatology. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(11): 990-1005
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i11/990.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i11.990