Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2021; 27(1): 55-68
Published online Jan 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i1.55
Published online Jan 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i1.55
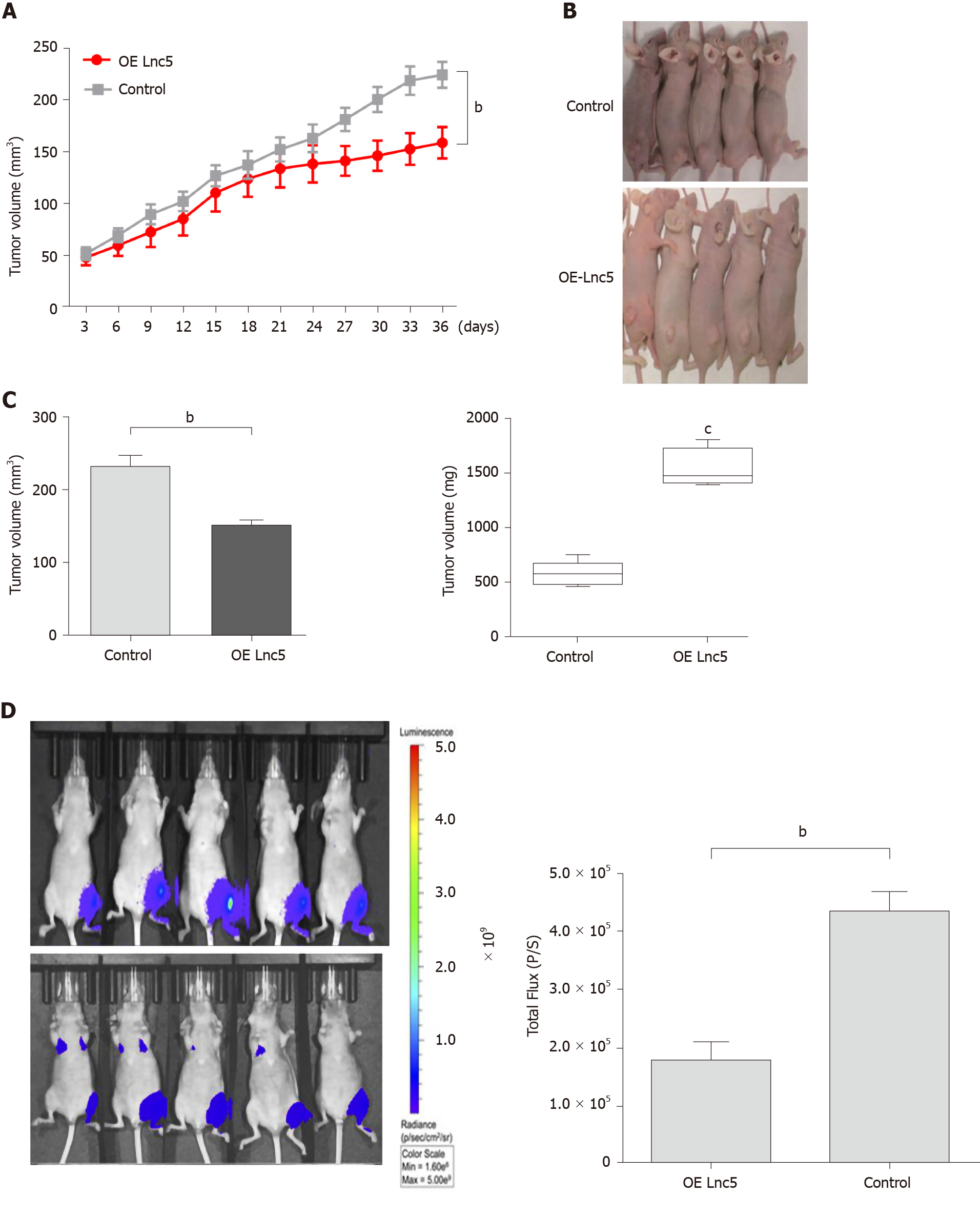
Figure 4 Long non-coding ribonucleic acid W5 inhibits tumor growth in vivo.
A: Huh7 cells (5 × 106) stably expressed with long non-coding ribonucleic acid W5 (lncRNA W5) were subcutaneously injected into the left flank of nude mice, and the effect of lncRNA W5 on hepatocellular carcinoma tumor growth was examined every 3 d during the course of the experiment (n = 5); B: A representative image of the xenograft-bearing mice; C: Tumors were isolated from the nude mice after sacrifice. The effects of lncRNA W5 on hepatocellular carcinoma growth were determined by tumor volume and tumor weight; D: LncRNA W5-overexpressing Huh7 cells which stably expressed luciferase were injected into nude mice (n = 5). The bioluminescence photographs of tumor were recorded with the in vivo 200 Imaging System. A representative luciferase signal was recorded from each group at 6 wk after injection. bP < 0.01.
- Citation: Lei GL, Fan HX, Wang C, Niu Y, Li TL, Yu LX, Hong ZX, Yan J, Wang XL, Zhang SG, Ren MJ, Yang PH. Long non-coding ribonucleic acid W5 inhibits progression and predicts favorable prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(1): 55-68
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i1/55.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i1.55