Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2021; 27(1): 55-68
Published online Jan 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i1.55
Published online Jan 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i1.55
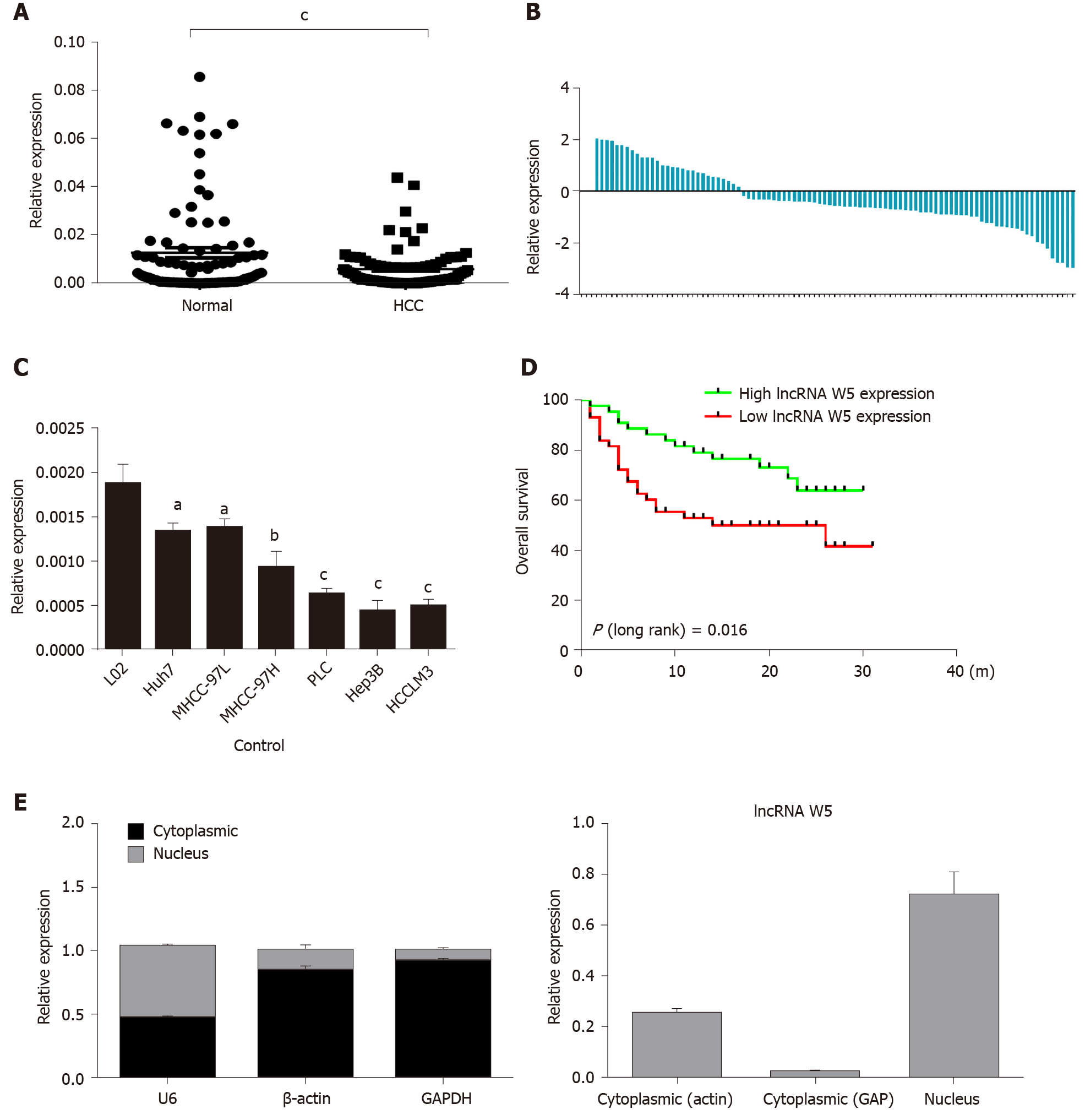
Figure 1 Expression of long non-coding ribonucleic acid W5 is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues and cells.
A: The expression of long non-coding ribonucleic acid (lncRNA) W5 was detected by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) in tumor tissues and non-adjacent normal tissues of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients (n = 86). LncRNA W5 expression was normalized to GAPDH expression; B: The expression of lncRNA W5 was detected by qRT-PCR in tumor tissues and non-adjacent normal tissues of 86 HCC patients; C: The expression levels of lncRNA W5 in a series of HCC cell lines were reduced compared to that in LO2 cells; D: Analysis of overall survival based on lncRNA W5 expression levels is shown in 86 HCC patients; and E: Subcellular localization of lncRNA W5 in Huh7 cells was examined by qRT-PCR. GAPDH, β-actin and U1 were considered as the control markers, respectively. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; lncRNA: Long non-coding ribonucleic acid; qRT-PCR: Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction.
- Citation: Lei GL, Fan HX, Wang C, Niu Y, Li TL, Yu LX, Hong ZX, Yan J, Wang XL, Zhang SG, Ren MJ, Yang PH. Long non-coding ribonucleic acid W5 inhibits progression and predicts favorable prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(1): 55-68
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i1/55.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i1.55