Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2020; 26(9): 947-959
Published online Mar 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i9.947
Published online Mar 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i9.947
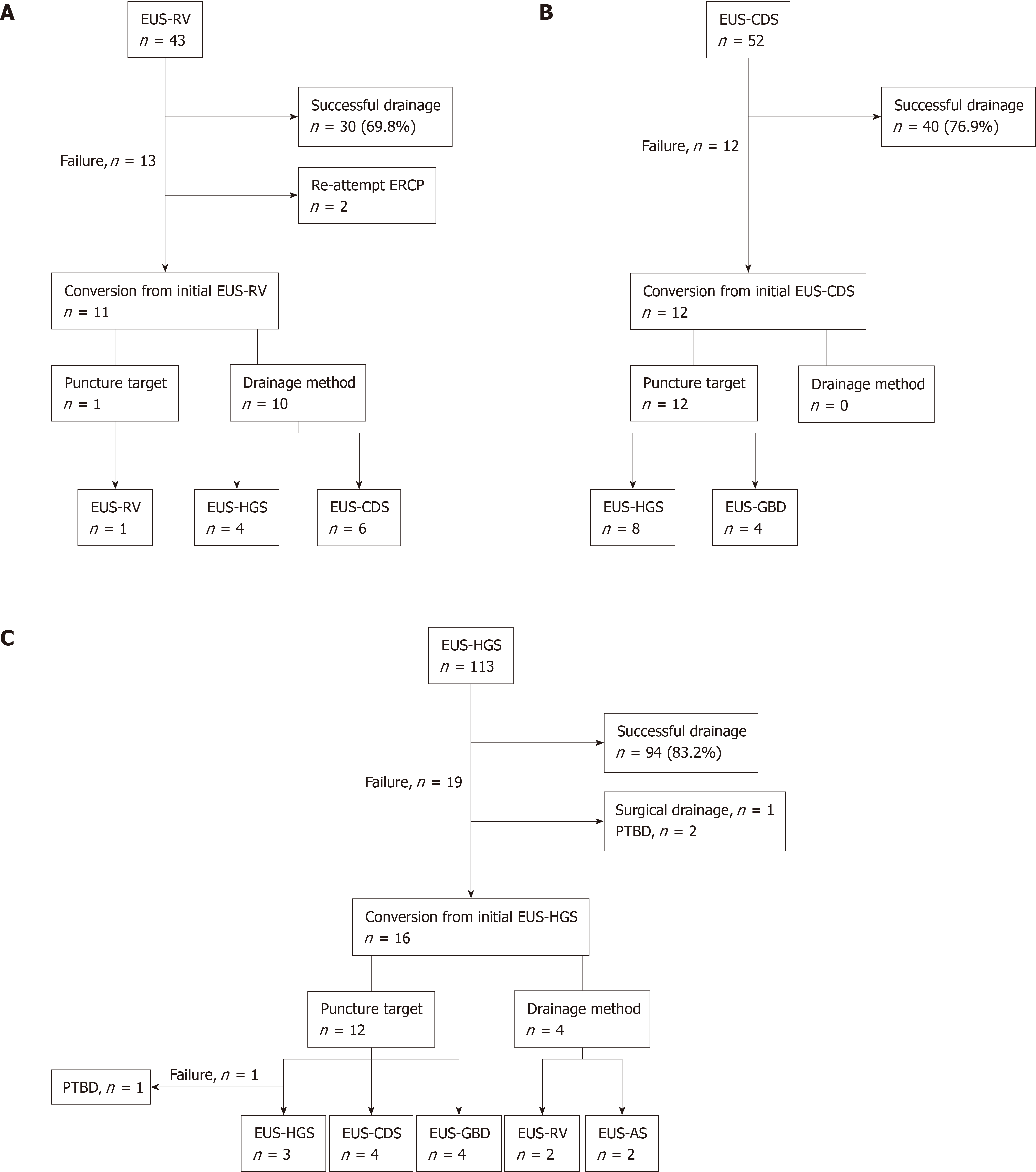
Figure 3 Technical outcomes of each initial endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage technique in this study.
A: EUS-guided rendezvous technique; B: EUS-guided choledochoduodenostomy; C: EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy. EUS-RV: EUS-guided rendezvous technique; EUS-CDS: EUS-guided choledochoduodenostomy; EUS-HGS: EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy; EUS-AS: EUS-guided antegrade stenting; PTBD: Percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage.
- Citation: Minaga K, Takenaka M, Yamao K, Kamata K, Omoto S, Nakai A, Yamazaki T, Okamoto A, Ishikawa R, Yoshikawa T, Chiba Y, Watanabe T, Kudo M. Clinical utility of treatment method conversion during single-session endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(9): 947-959
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i9/947.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i9.947