Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2020; 26(9): 904-917
Published online Mar 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i9.904
Published online Mar 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i9.904
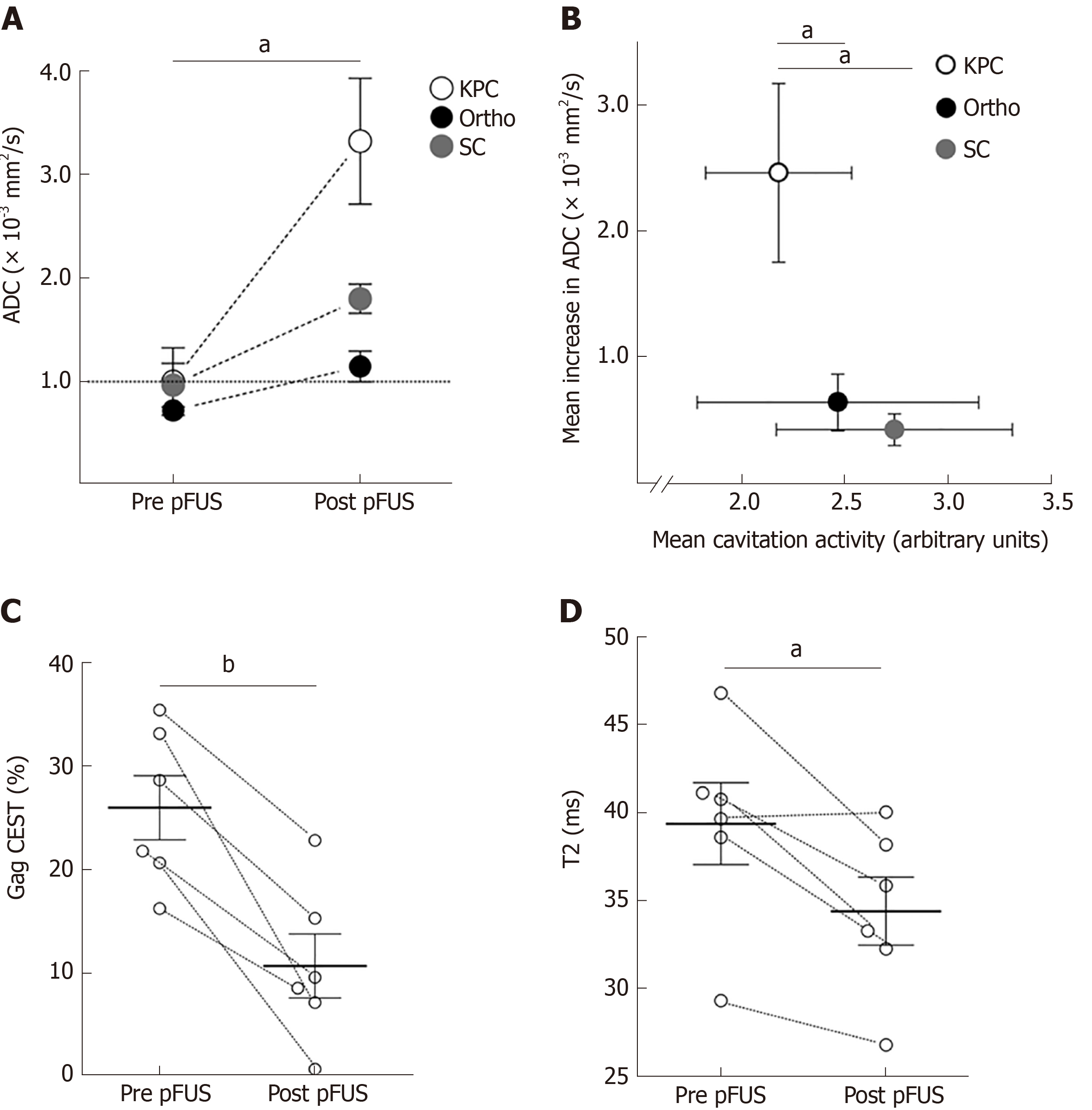
Figure 2 14T magnetic resonance imaging parameter changes due to pulsed focused ultrasound treatments.
A: There was significant increase in mean apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) quantitation for all three murine pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma models (n = 6 in each group). The horizontal dotted line at ADC = 1 demarcates a frequently used clinical threshold for “restricted” diffusion; B: Cavitation was successfully achieved in all treated animals. On average, cavitation activity tended to be lower in the KPC animals, yet the absolute increase in ADC values for these animals was significantly higher than the other two models post-pulsed focused ultrasound (pFUS) treatment; C and D: GagCEST (C) and T2 (D) quantifications in KPC animals revealed significant decrease in mean values (solid horizontal lines) post-pFUS treatment (n = 6). There was no significant change in these parameters in the other tumor models. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. ADC: Apparent diffusion coefficient; pFUS: Pulsed focused ultrasound; Ortho: Orthotopic; KPC: Genetic mouse model; SC: Subcutaneous.
- Citation: Maloney E, Wang YN, Vohra R, Son H, Whang S, Khokhlova T, Park J, Gravelle K, Totten S, Hwang JH, Lee D. Magnetic resonance imaging biomarkers for pulsed focused ultrasound treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(9): 904-917
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i9/904.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i9.904