Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2020; 26(9): 904-917
Published online Mar 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i9.904
Published online Mar 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i9.904
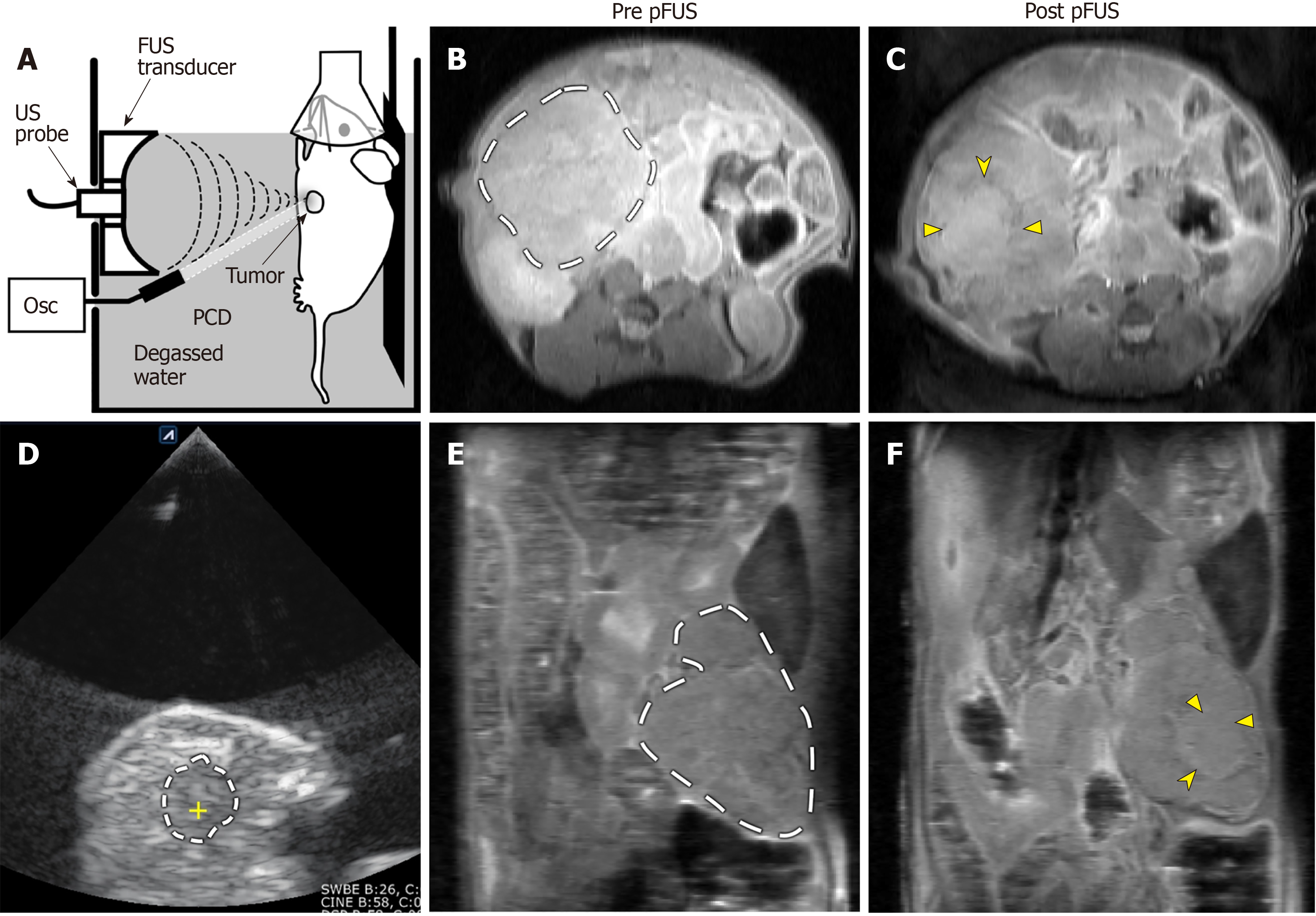
Figure 1 Representative images of pulsed focused ultrasound treatment and 14T magnetic resonance imaging assessment.
(A) Sagittal plane line drawing and (D) axial plane ultrasound (US) image of a pulsed focused ultrasound (pFUS) treatment. Animals were anesthetized, placed on a mobile platform, and partially submerged in degassed water. Tumors were identified using B-mode images from a diagnostic US probe. The KPC mouse tumors generally appear as predominantly hypoechoic masses along the distribution of the pancreas (dashed line in D; the yellow cross within marks the focus of the pFUS transducer). Axial (B and C) and coronal (E and F) pre- and post-treatment proton density weighted anatomic images from a different KPC mouse. Dashed lines in B and E demarcate the pancreatic tumor mass. The treated area demonstrates predominantly isointense signal (solid arrowheads in C and F), with a peripheral ring of hypointense signal (notched arrowheads in C and F), most likely representing sequelae of hyperacute hemorrhage. pFUS: Pulsed focused ultrasound; SC: Subcutaneous; Osc: Oscilloscope; PCD: Passive cavitation detector.
- Citation: Maloney E, Wang YN, Vohra R, Son H, Whang S, Khokhlova T, Park J, Gravelle K, Totten S, Hwang JH, Lee D. Magnetic resonance imaging biomarkers for pulsed focused ultrasound treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(9): 904-917
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i9/904.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i9.904