Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2020; 26(9): 883-903
Published online Mar 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i9.883
Published online Mar 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i9.883
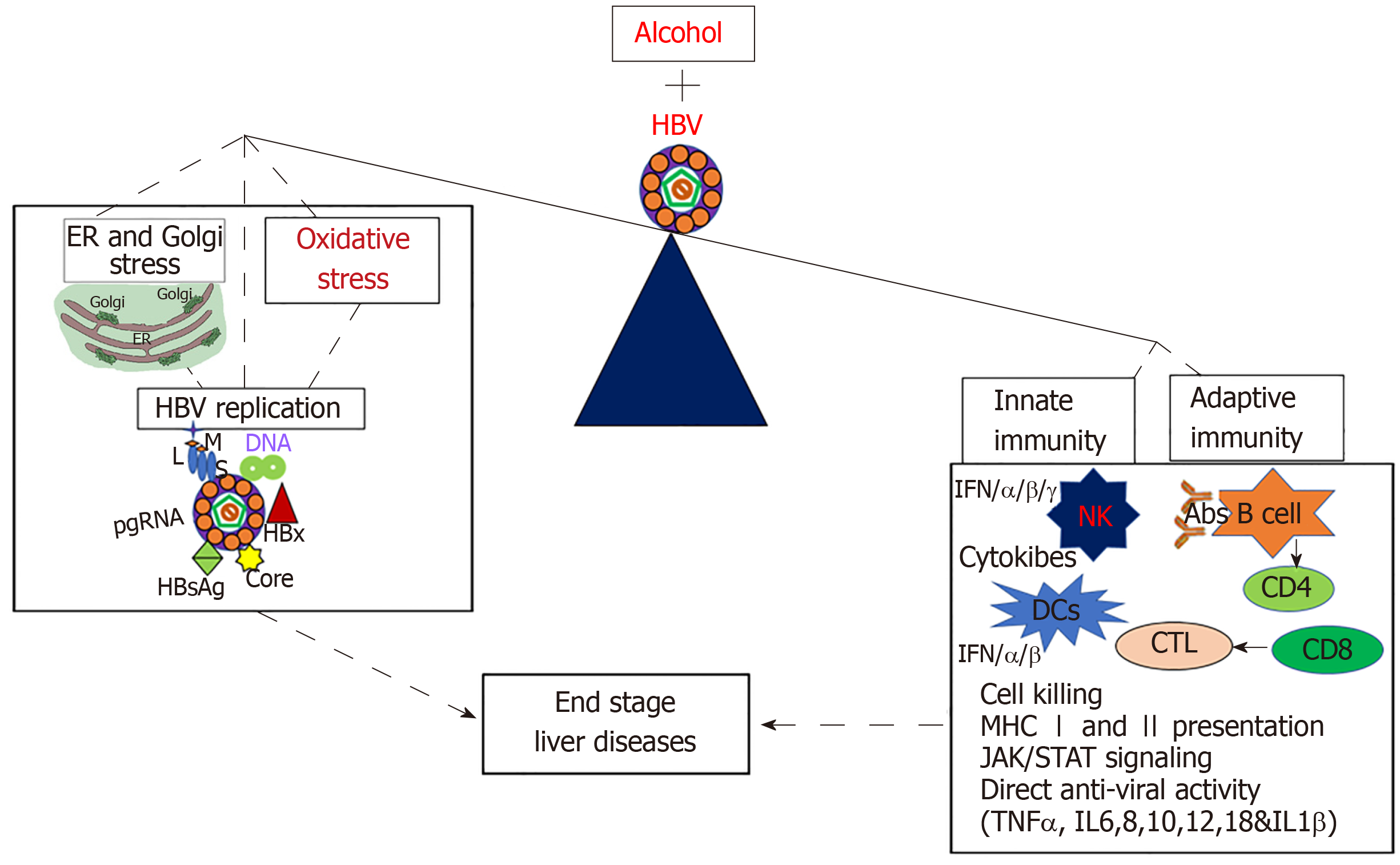
Figure 2 Mechanisms of alcohol and hepatitis B virus-infection induced liver injury.
Alcohol and hepatitis B virus together increase hepatitis B virus replication, oxidative stress, and cell organelle stress (endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi stress) which ultimately suppresses both adaptive and innate immune response, thereby leading to end- stage liver diseases. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; IFN: Interferon; IL: Interleukin; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; NK: Natural killers.
- Citation: Ganesan M, Eikenberry A, Poluektova LY, Kharbanda KK, Osna NA. Role of alcohol in pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(9): 883-903
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i9/883.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i9.883