Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2020; 26(6): 598-613
Published online Feb 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i6.598
Published online Feb 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i6.598
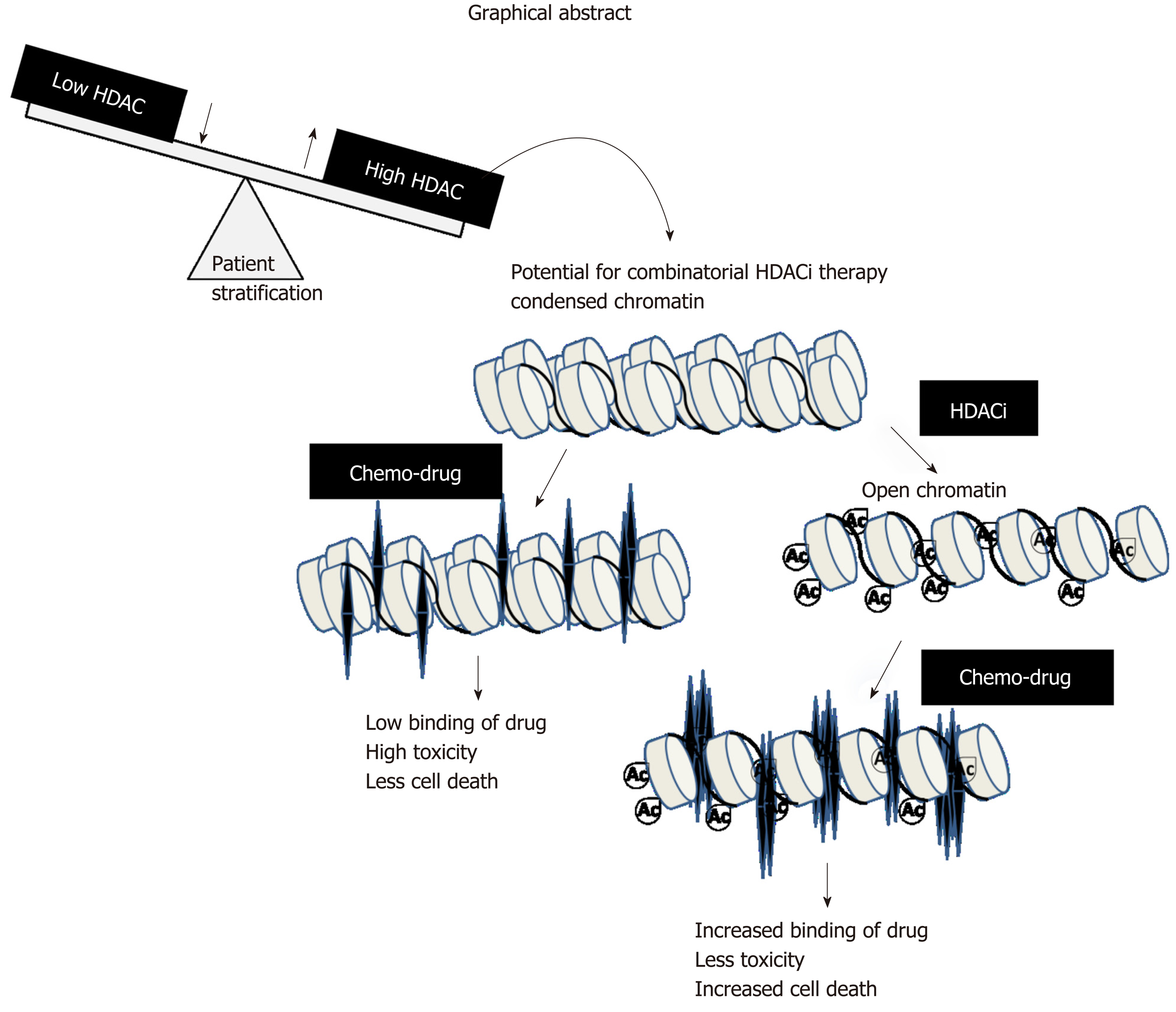
Figure 7 Graphical abstract: Model depicting stratification of patients with high histone deacetylase activity/levels of histone deacetylase inhibitor therapy.
A prior treatment of histone deacetylase inhibitors would relax the condensed chromatin of a stratified patient group, making it more accessible and increasing its interaction with chemotherapeutic drugs compared to only first-line chemo treatment. This would enhance the number of cells killed at lower drug concentrations with a decrease in side-effects and toxicity. HDAC: Histone deacetylase; HAT: Histone acetyl transferase.
- Citation: Amnekar RV, Khan SA, Rashid M, Khade B, Thorat R, Gera P, Shrikhande SV, Smoot DT, Ashktorab H, Gupta S. Histone deacetylase inhibitor pre-treatment enhances the efficacy of DNA-interacting chemotherapeutic drugs in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(6): 598-613
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i6/598.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i6.598