Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2020; 26(6): 598-613
Published online Feb 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i6.598
Published online Feb 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i6.598
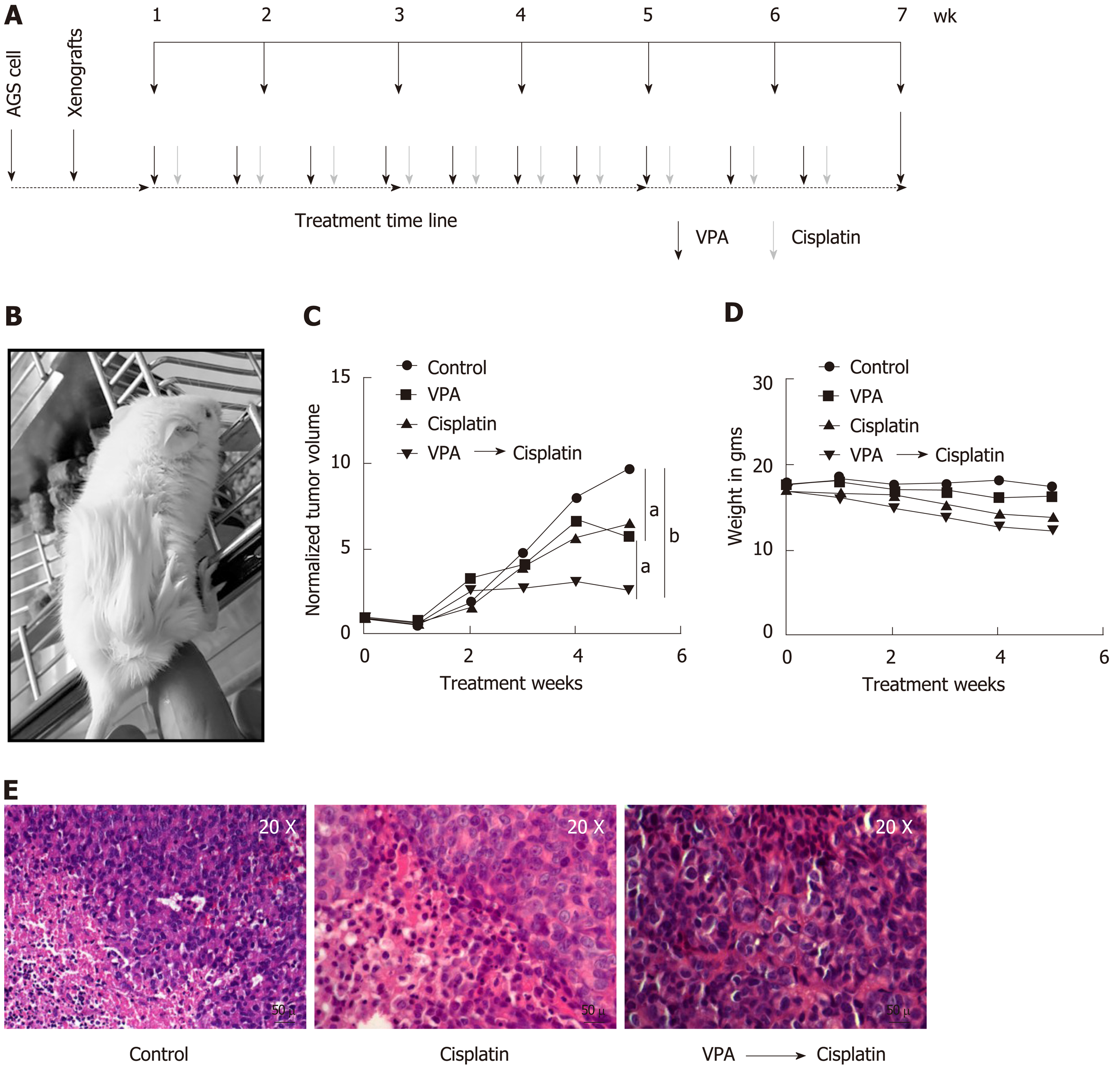
Figure 6 Valproic sensitizes AGS cell xenografts to cisplatin in an in vivo mice model.
A: Schematic diagram depicting timeline of in vivo drug administration. AGS cells were injected into NOD-SCID mice. After tumors reached approximately 100 mm3; B: Mice were divided into four groups (n = 3), (1) control, (2) valproic acid (300 mg/kg/d), (3) cisplatin (2 mg/kg/d), and (4) combinatorial treatment of valproic acid followed by cisplatin at the same dose mentioned above; C: Average tumor volumes of groups normalized to the initial tumor volumes (before treatment) are plotted over a period of 5 wk of drug treatment. The outcome of the different treatment regimens was statistically validated by performing unpaired t-tests (aP < 0.05; bP < 0.005); D: Mean weight of animals in a group measured over the treatment period to assess toxicity; E: Histopathology of tumor sections by hematoxylin and eosin staining of different groups following 5 wk of treatment. VPA: Valproic acid.
- Citation: Amnekar RV, Khan SA, Rashid M, Khade B, Thorat R, Gera P, Shrikhande SV, Smoot DT, Ashktorab H, Gupta S. Histone deacetylase inhibitor pre-treatment enhances the efficacy of DNA-interacting chemotherapeutic drugs in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(6): 598-613
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i6/598.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i6.598