Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2020; 26(6): 598-613
Published online Feb 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i6.598
Published online Feb 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i6.598
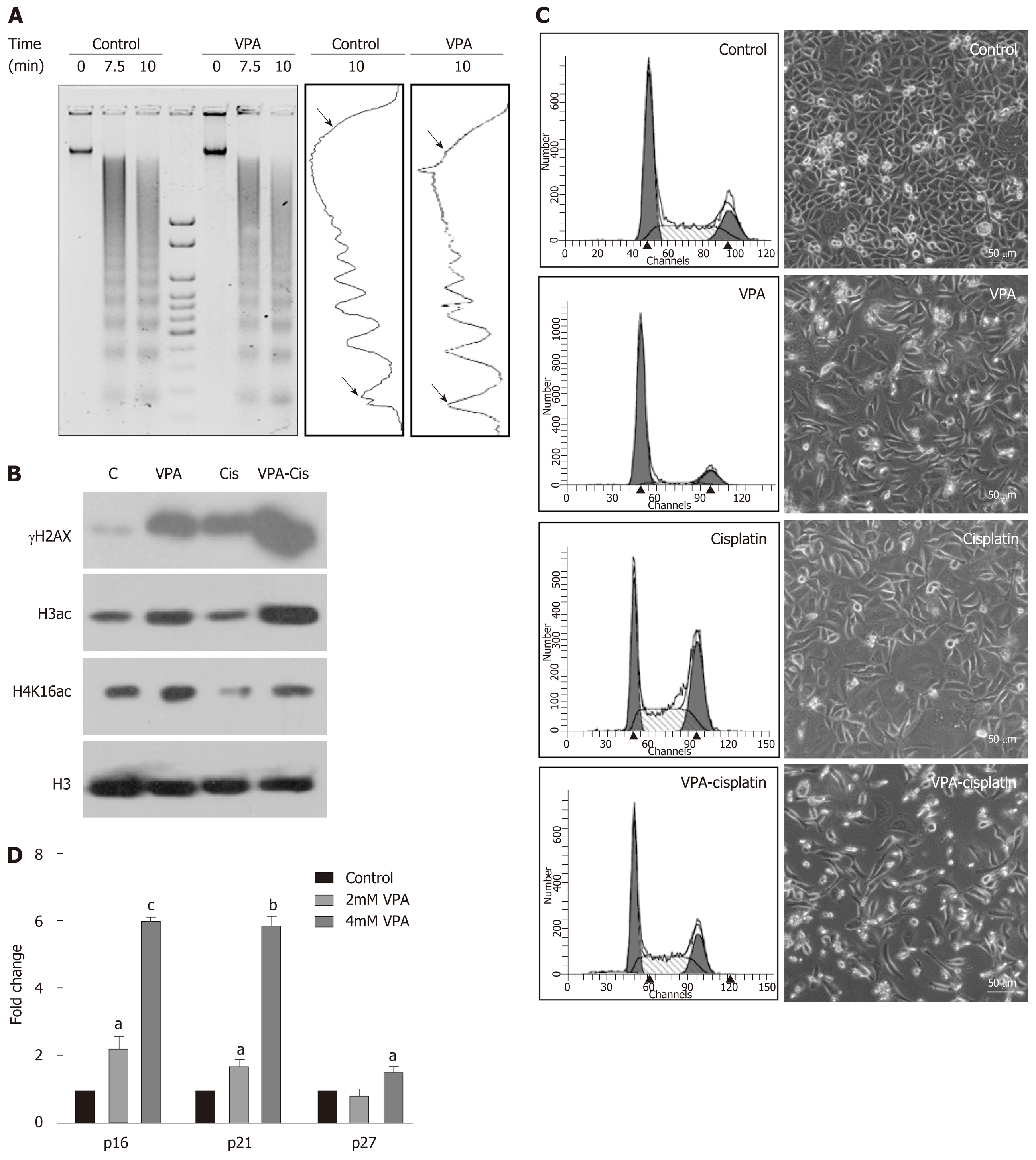
Figure 5 Pretreatment regime is associated with chromatin relaxation, enhanced DNA damage and re-expression of tumor suppressors.
A: Chromatin organization in the AGS cell line by micrococcal nuclease (MNase) assays with time-dependent kinetics was studied following 24 h treatment with valproic acid (VPA) (2 mmol/L). AGS cells were treated with an inhibitory concentration (IC)25 concentration of cisplatin and VPA alone or in combination for 24 h, and the following parameters were analyzed: B: Histone post-translational modifications; C: Cell cycle profile and morphology; and D: Effect of VPA on re-expression of tumor suppressors was studied by treating AGS cells with the IC25 and IC50 concentrations of VPA for 24 h, followed by real time PCR for the p16, p21 and p27 genes (aP < 0.02; bP < 0.0009; cP < 0.0001). MNase: Micrococcal nuclease; HDACi: Histone deacetylase inhibitor; PTMs: Post-translational modifications; VPA: Valproic acid; IC: Inhibitory concentration; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction.
- Citation: Amnekar RV, Khan SA, Rashid M, Khade B, Thorat R, Gera P, Shrikhande SV, Smoot DT, Ashktorab H, Gupta S. Histone deacetylase inhibitor pre-treatment enhances the efficacy of DNA-interacting chemotherapeutic drugs in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(6): 598-613
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i6/598.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i6.598