Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2020; 26(47): 7497-7512
Published online Dec 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i47.7497
Published online Dec 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i47.7497
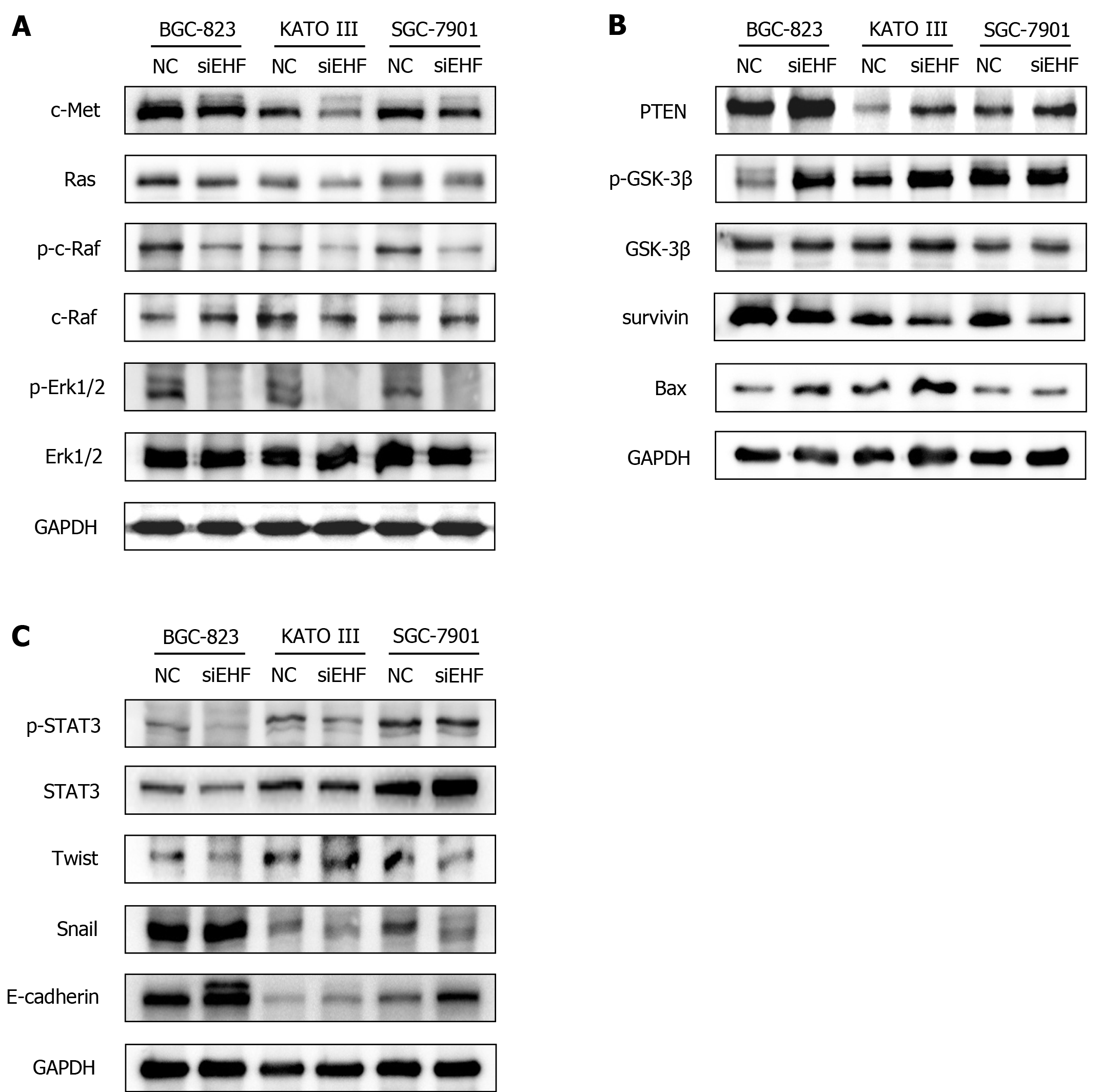
Figure 6 ETS homologous factor promotes the malignant biological behaviors of gastric cancer cells through the c-Met pathway.
Western blotting was conducted to investigate the effects of ETS homologous factor (EHF) silencing on the expression and activities of signaling molecules in the c-Met pathway. A: Alterations in the Ras- extracellular signal-related kinase 1/2 (Erk1/2) cascade after EHF inhibition; B: The molecular changes in phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) and glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK3β) and their potential targets following EHF silencing; C: The altered activities of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and the changed expression of its downstream effectors after EHF downregulation. GC: Gastric cancer; NC: Negative control group.
- Citation: Gu ML, Zhou XX, Ren MT, Shi KD, Yu MS, Jiao WR, Wang YM, Zhong WX, Ji F. Blockage of ETS homologous factor inhibits the proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells through the c-Met pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(47): 7497-7512
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i47/7497.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i47.7497