Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2020; 26(47): 7470-7484
Published online Dec 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i47.7470
Published online Dec 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i47.7470
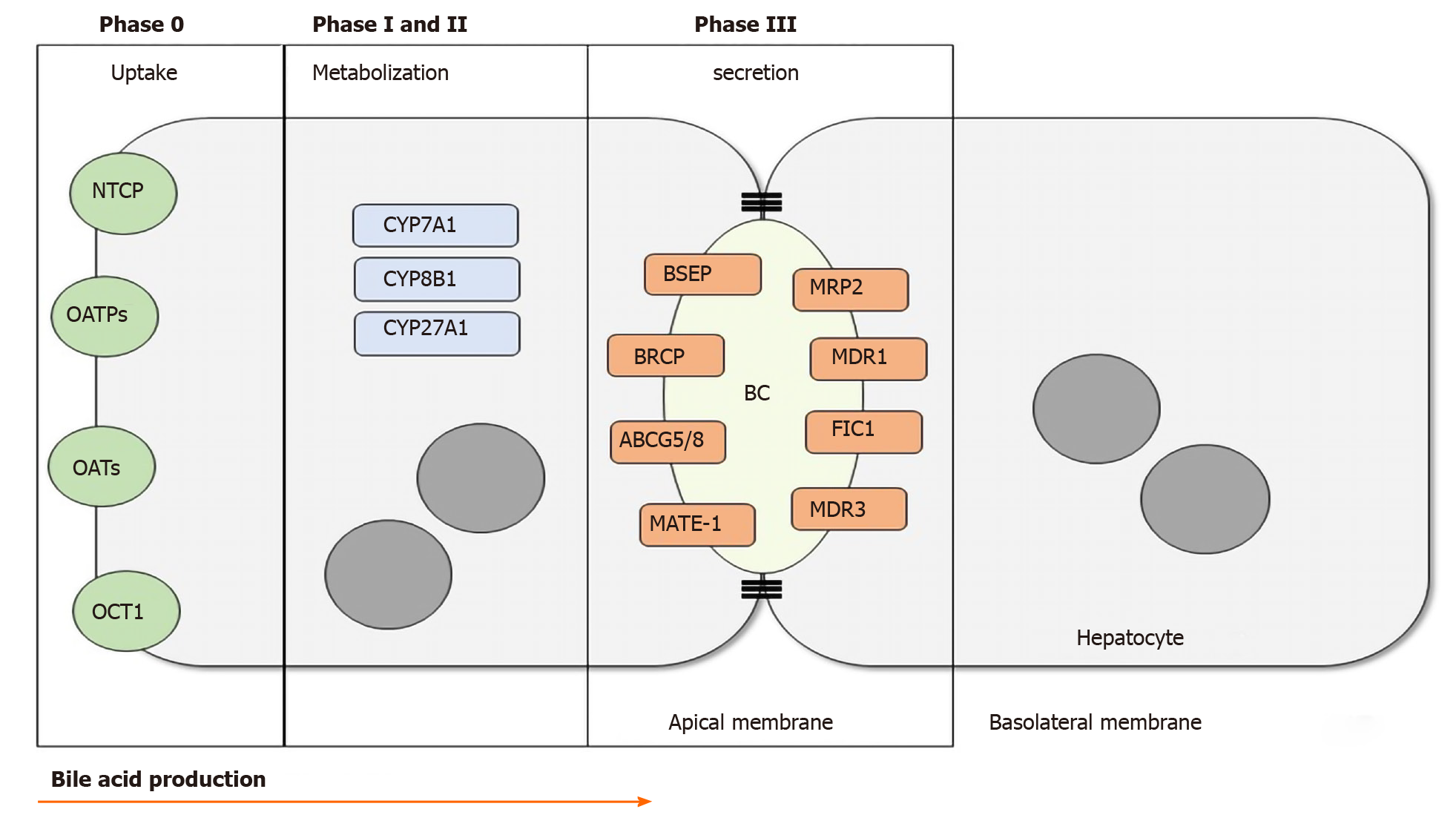
Figure 1 Bile acid production.
In phase 0, bile acids and other organic products are transported through the basolateral membrane of the hepatocyte. Phase I and II take place in the cytoplasm through activation and metabolization of differents CYPs. In phase III the bile acids are secreted into the biliary canalicus by the transmebrane transporters. NTCP: Na+-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide; OATPs: Organic anion transporting polypeptides; OATs: Organic anion transporter; OCT1: Organic cation transporter 1; CYP7A1: Cytochrome P450 Family 7 Subfamily A Member 1; CYP8B1: Cytochrome P450 Family 8 Subfamily b Member 1; CYP27A1: Cytochrome P450 Family 27 Subfamily A Member 1; BSEP: Bile salt export pump; BRCP: Breast cancer resistance protein; ABCG5/8: ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 5/8; MATE-1: Multidrug and toxin extrusion 1; MRP2: Multidrug resistance-associated protein 2; MDR1: Multidrug resistance class 1 glycoprotein; FIC1: Familial intrahepatic cholestasis 1; MDR3: Multidrug resistance class 3 glycoprotein; BC: Biliary canaliculus.
- Citation: Amirneni S, Haep N, Gad MA, Soto-Gutierrez A, Squires JE, Florentino RM. Molecular overview of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(47): 7470-7484
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i47/7470.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i47.7470