Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2020; 26(46): 7352-7366
Published online Dec 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i46.7352
Published online Dec 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i46.7352
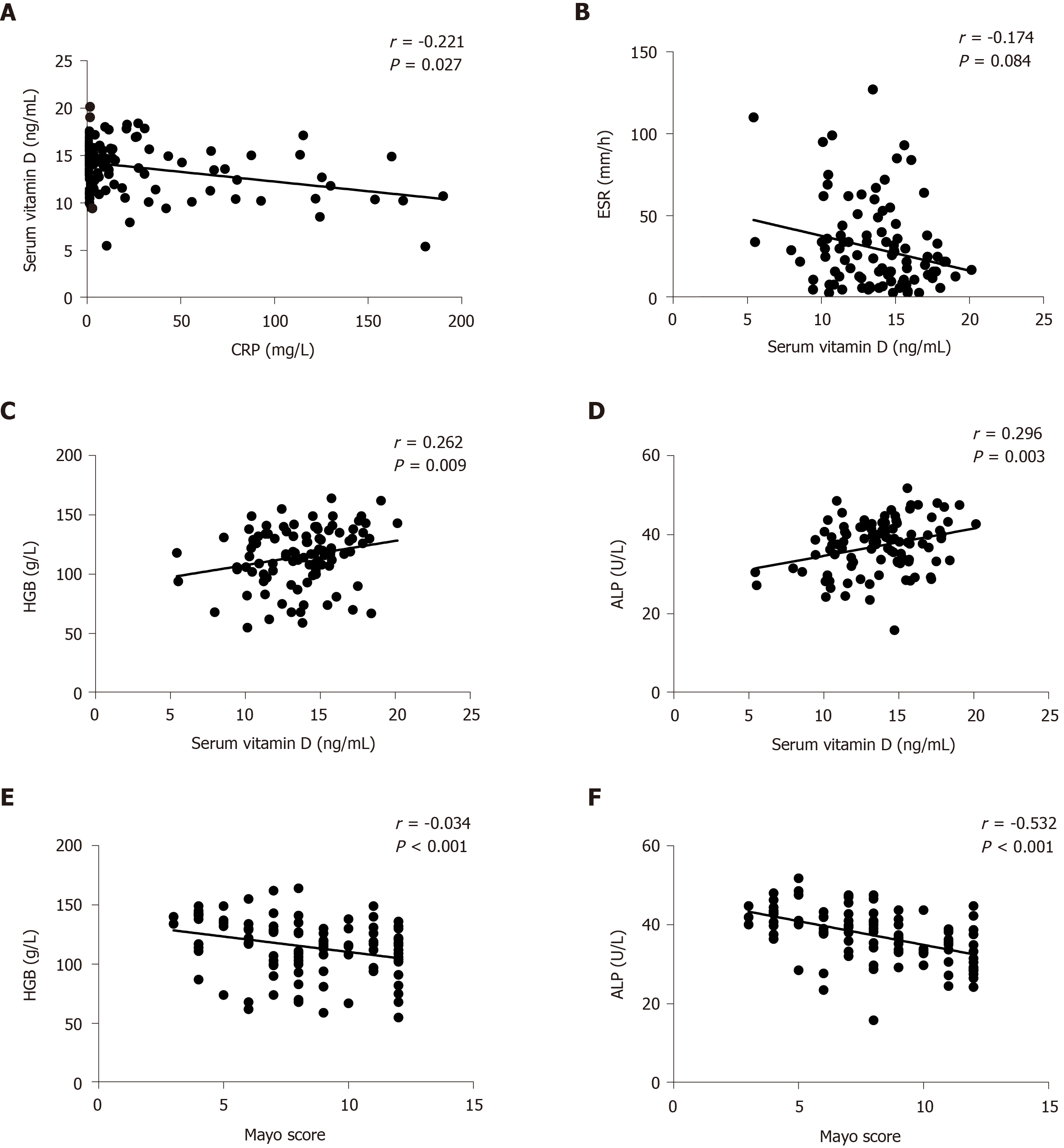
Figure 3 Correlation between vitamin D level and C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, hemoglobin and alkaline phosphatase.
A: Correlation between vitamin D level and C-reactive protein; B: Correlation between vitamin D level and erythrocyte sedimentation rate; C: Correlation between vitamin D level and hemoglobin; D: Correlation between vitamin D level and alkaline phosphatase; E: Correlation between hemoglobin and the Mayo score; and F: Correlation between alkaline phosphatase and the Mayo score. ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; CRP: C-reactive protein; ESR: Erythrocyte sedimentation rate; HGB: Hemoglobin.
- Citation: Wang HQ, Zhang WH, Wang YQ, Geng XP, Wang MW, Fan YY, Guan J, Shen JL, Chen X. Colonic vitamin D receptor expression is inversely associated with disease activity and jumonji domain-containing 3 in active ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(46): 7352-7366
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i46/7352.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i46.7352