Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2020; 26(46): 7312-7324
Published online Dec 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i46.7312
Published online Dec 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i46.7312
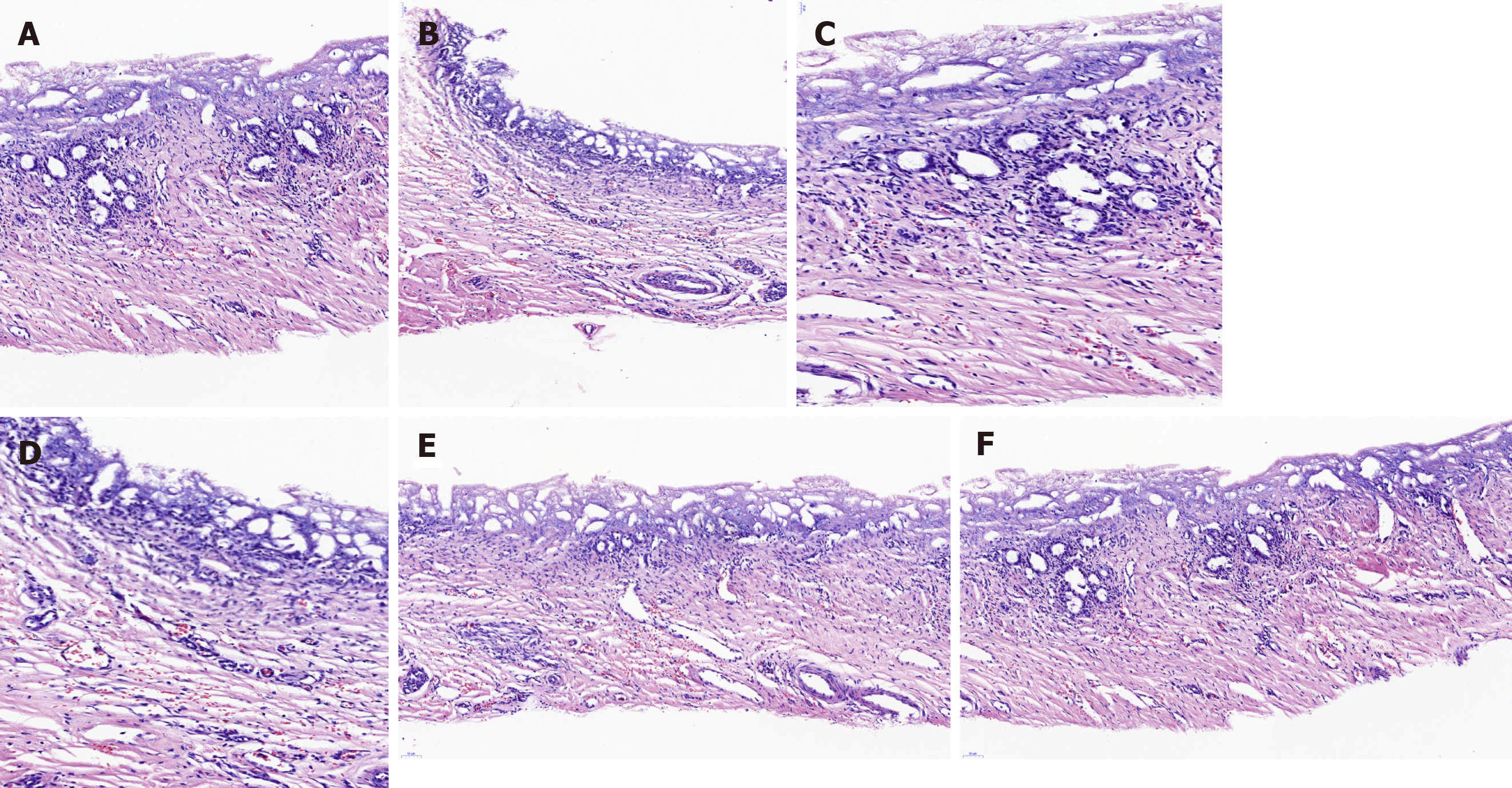
Figure 4 Hematoxylin/eosin staining of the animal-derived artificial bile duct site.
No marked transmural neutrophil and lymphoplasma cell infiltration was observed. A: Hematoxylin/eosin (H/E) staining of a 6 mo survival pig in group A (magnification: 20 ×); B: H/E staining of a 12 mo survival pig in group B (magnification: 20 ×); C: H/E staining of a 6 mo survival pig in group A (magnification: 40 ×); D: H/E staining of a 12 mo survival pig in group B (magnification: 40 ×); E and F: H/E staining result of neovascularization was marked in group A and B (magnification: 20 ×).
- Citation: Shang H, Zeng JP, Wang SY, Xiao Y, Yang JH, Yu SQ, Liu XC, Jiang N, Shi XL, Jin S. Extrahepatic bile duct reconstruction in pigs with heterogenous animal-derived artificial bile ducts: A preliminary experience. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(46): 7312-7324
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i46/7312.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i46.7312