Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2020; 26(46): 7312-7324
Published online Dec 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i46.7312
Published online Dec 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i46.7312
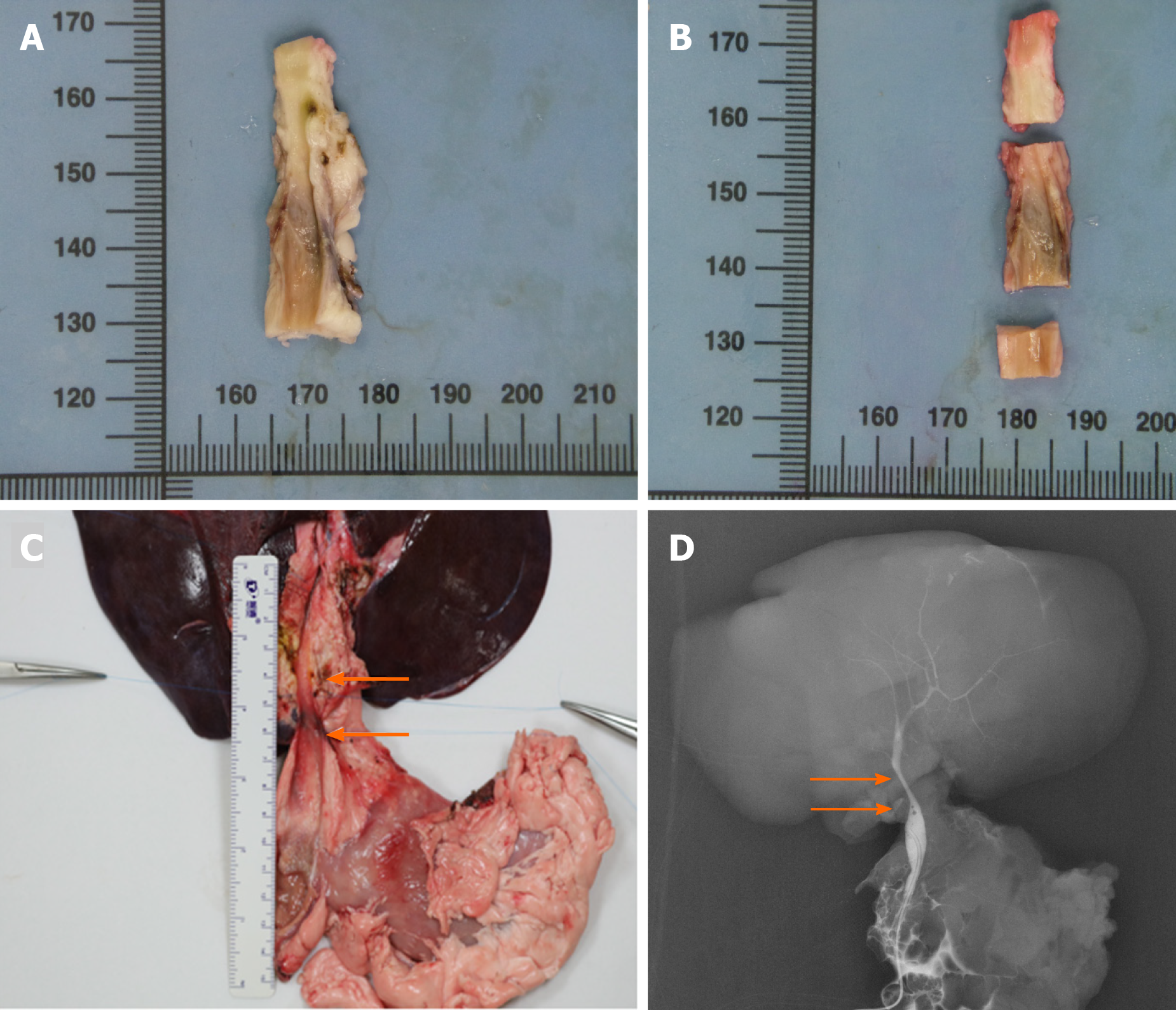
Figure 3 Autopsy and cholangiography.
A: The macroscopic assessment of the extrahepatic bile duct (BD) indicated the inner walls of the anastomoses were smooth without scars or stricture; B: The extrahepatic BD was divided into three segments to perform the microscopic assessment according to the anastomoses; C: The en bloc liver procured was associated with the entire extrahepatic BD including partial duodenum and pancreas after euthanasia. The area of two white arrows denoted the location of the animal-derived artificial bile duct (group B); D: The cholangiography showed patency of the animal-derived artificial bile duct without dilatation of the proximal BD. The area of two white arrows denoted the location of the animal-derived artificial bile duct (group B).
- Citation: Shang H, Zeng JP, Wang SY, Xiao Y, Yang JH, Yu SQ, Liu XC, Jiang N, Shi XL, Jin S. Extrahepatic bile duct reconstruction in pigs with heterogenous animal-derived artificial bile ducts: A preliminary experience. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(46): 7312-7324
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i46/7312.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i46.7312