Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2020; 26(46): 7299-7311
Published online Dec 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i46.7299
Published online Dec 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i46.7299
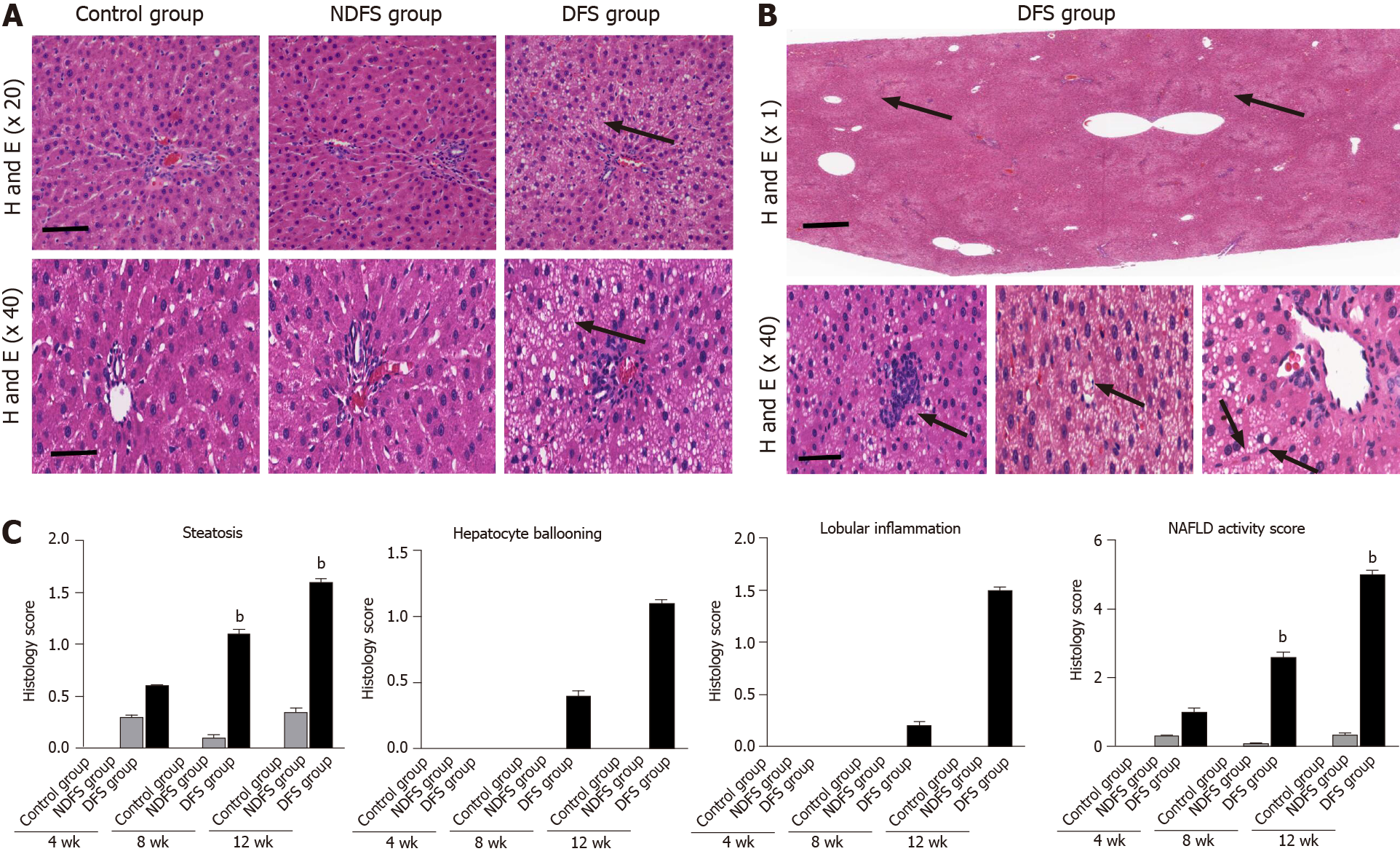
Figure 3 Hematoxylin-eosin staining and histology score of rat liver in the three groups.
A: Steatosis of rat liver in the three groups at week 12. Scale bars = 100 μm (top row). Scale bars = 50 μm (bottom row); B: Special pathological features of rat liver from dry-fried soybeans (DFS) group at week 12 (diffuse steatosis around the portal area, scale bars = 2.5 μm. Inflammation, hepatocyte ballooning and clusters of myofibroblasts, scale bars = 50 μm); C: Histology score of steatosis, hepatocyte ballooning, lobular inflammation and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity score were quantified. Data are shown as mean ± standard deviation (bP < 0.05, DFS group vs control group, nonfried soybeans group [NDFS]). H and E: Hematoxylin-eosin.
- Citation: Xue LJ, Han JQ, Zhou YC, Peng HY, Yin TF, Li KM, Yao SK. Untargeted metabolomics characteristics of nonobese nonalcoholic fatty liver disease induced by high-temperature-processed feed in Sprague-Dawley rats. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(46): 7299-7311
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i46/7299.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i46.7299