Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2020; 26(45): 7131-7152
Published online Dec 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i45.7131
Published online Dec 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i45.7131
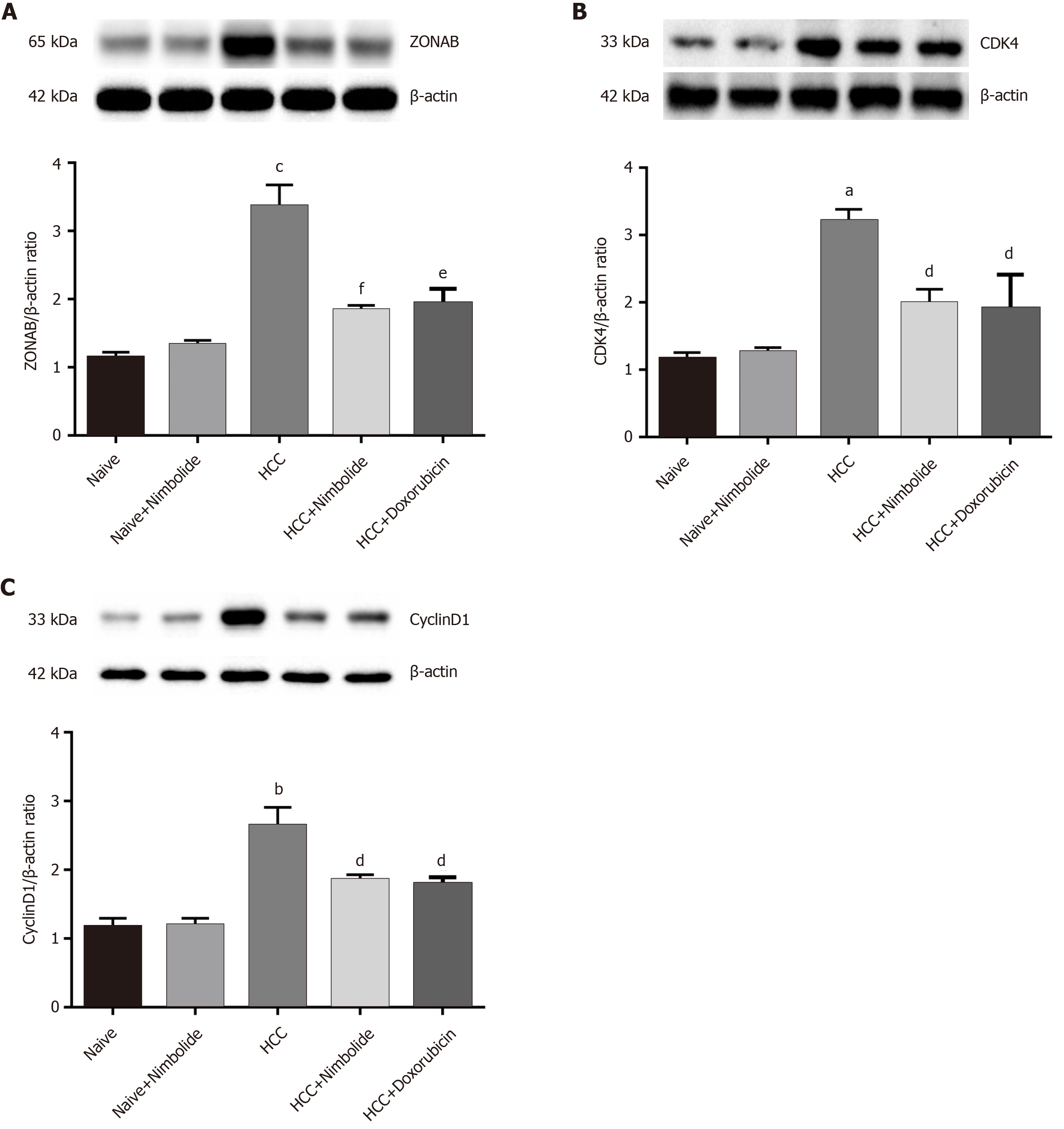
Figure 5 Nimbolide treatment attenuates hepatic zonula occludens 1 associated nucleic acid binding protein and cell cycle markers proteins expression in diethylnitrosamine and N-nitrosomorpholine induced hepatocellular carcinoma mice.
A: Hepatic protein expression levels of zonula occludens 1 associated nucleic acid binding protein by western blot in naive and experimental groups; B: Hepatic protein expression levels of cyclin dependent kinase 4 by western blot in naive and experimental groups; C: Hepatic protein expression levels of CyclinD1 by western blot in naive and experimental groups. All the data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3). The comparison between the groups was analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison post-hoc test or Kruskal-Wallis followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison post-hoc test. aP < 0.01, bP < 0.001, cP < 0.0001 compared to naïve group; dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 compared to HCC group. ZONAB: Zonula occludens 1 associated nucleic acid binding protein; CDK4: Cyclin dependent kinase; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Ram AK, Vairappan B, Srinivas BH. Nimbolide inhibits tumor growth by restoring hepatic tight junction protein expression and reduced inflammation in an experimental hepatocarcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(45): 7131-7152
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i45/7131.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i45.7131