Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2020; 26(45): 7131-7152
Published online Dec 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i45.7131
Published online Dec 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i45.7131
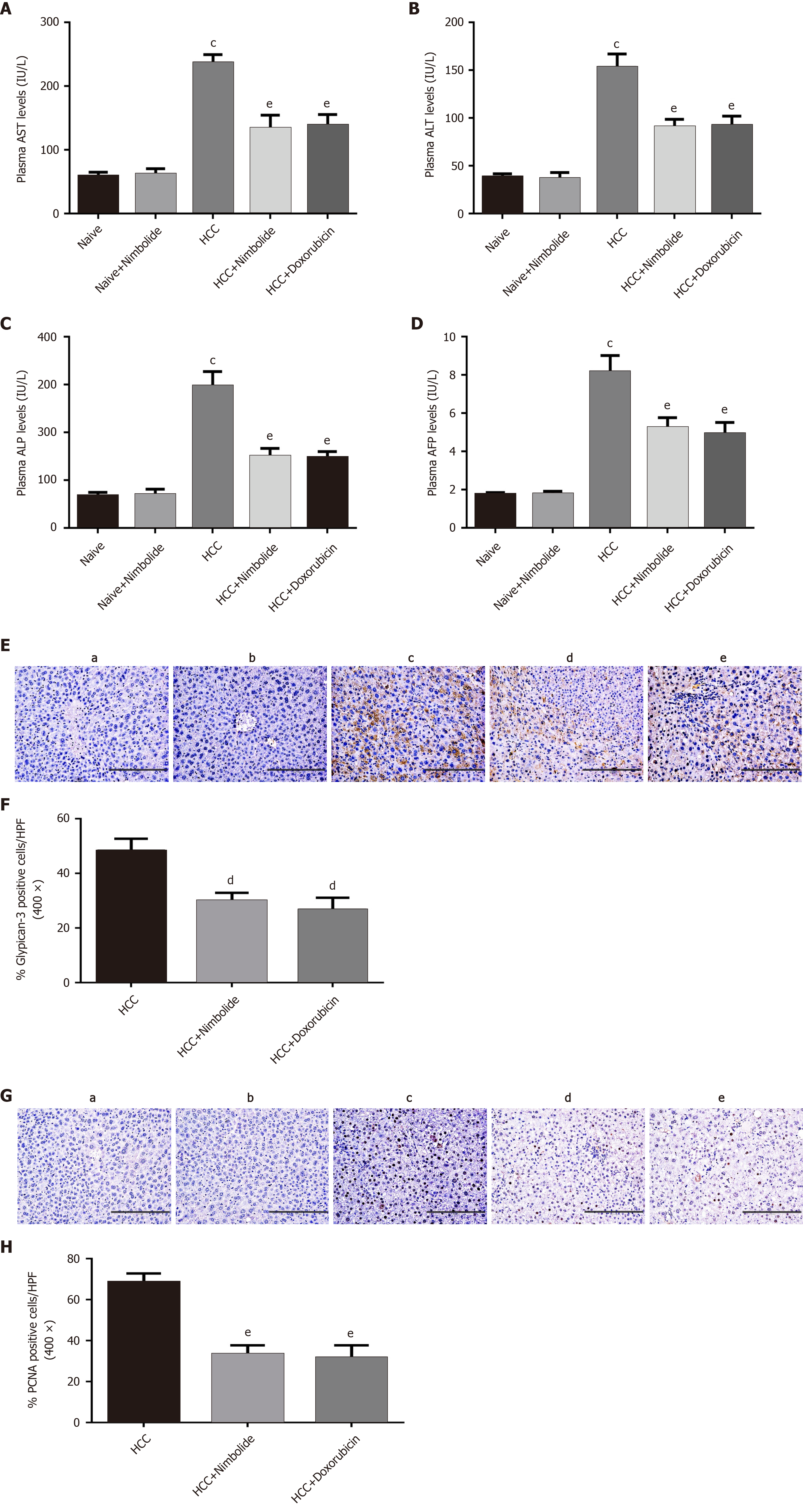
Figure 3 Effect of nimbolide on liver function parameters and tumor and cell proliferation markers in diethylnitrosamine and N-nitrosomorpholine induced hepatocellular carcinoma mice.
A: Plasma aspartate aminotransferase level in naïve and experimental groups; B: Plasma alanine aminotransferase level in naïve and experimental groups; C: Plasma alkaline phosphatase level in naïve and experimental groups; D: Plasma alpha-fetoprotein level in naïve and experimental groups; E: Representative images of glypican-3 immunostaining of mice liver from naive and experimental groups (200 × magnification); F: Quantification of glypican-3 positive cells in experimental groups by counting five 400 × fields of each liver section; G: Representative images of proliferating hepatocytes by proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) immunostaining of mice liver from naive and experimental groups (200 × magnification); H: Quantification of PCNA positive nuclei in experimental groups by counting five 400 × fields of each liver section. Scale bar: 200 μm; all the data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3-6). The comparison between the groups was analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison post-hoc test or Kruskal-Wallis followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison post-hoc test. cP < 0.0001 compared to naïve group; dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01 compared to hepatocellular carcinoma group. AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; HPF: High-power fields; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Ram AK, Vairappan B, Srinivas BH. Nimbolide inhibits tumor growth by restoring hepatic tight junction protein expression and reduced inflammation in an experimental hepatocarcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(45): 7131-7152
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i45/7131.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i45.7131