Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2020; 26(44): 7061-7075
Published online Nov 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i44.7061
Published online Nov 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i44.7061
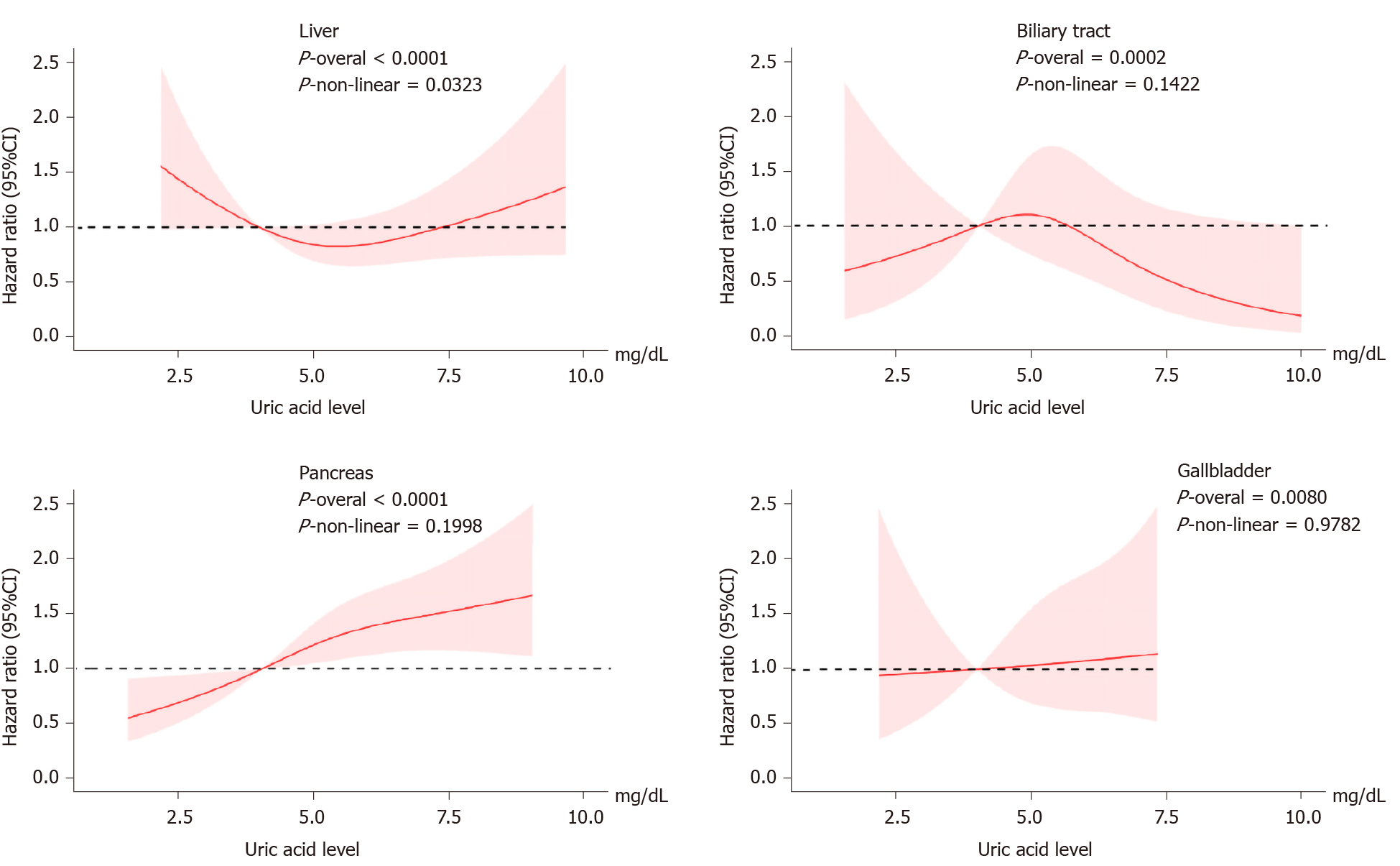
Figure 3 Dose response of uric acid and hepatobiliary-pancreatic cancer risk.
Adjusted for genders, age, education, ethnic, family history of cancer, alcohol intake, smoking status, annual household income, fruit and vegetable intake and physical activity and body mass index. The reference uric acid level for these plots (with hazard ratio fixed as 1.0) was 4.0 mg/dL. CI: Confidence interval.
- Citation: Huang CF, Huang JJ, Mi NN, Lin YY, He QS, Lu YW, Yue P, Bai B, Zhang JD, Zhang C, Cai T, Fu WK, Gao L, Li X, Yuan JQ, Meng WB. Associations between serum uric acid and hepatobiliary-pancreatic cancer: A cohort study. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(44): 7061-7075
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i44/7061.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i44.7061