Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2020; 26(44): 6945-6962
Published online Nov 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i44.6945
Published online Nov 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i44.6945
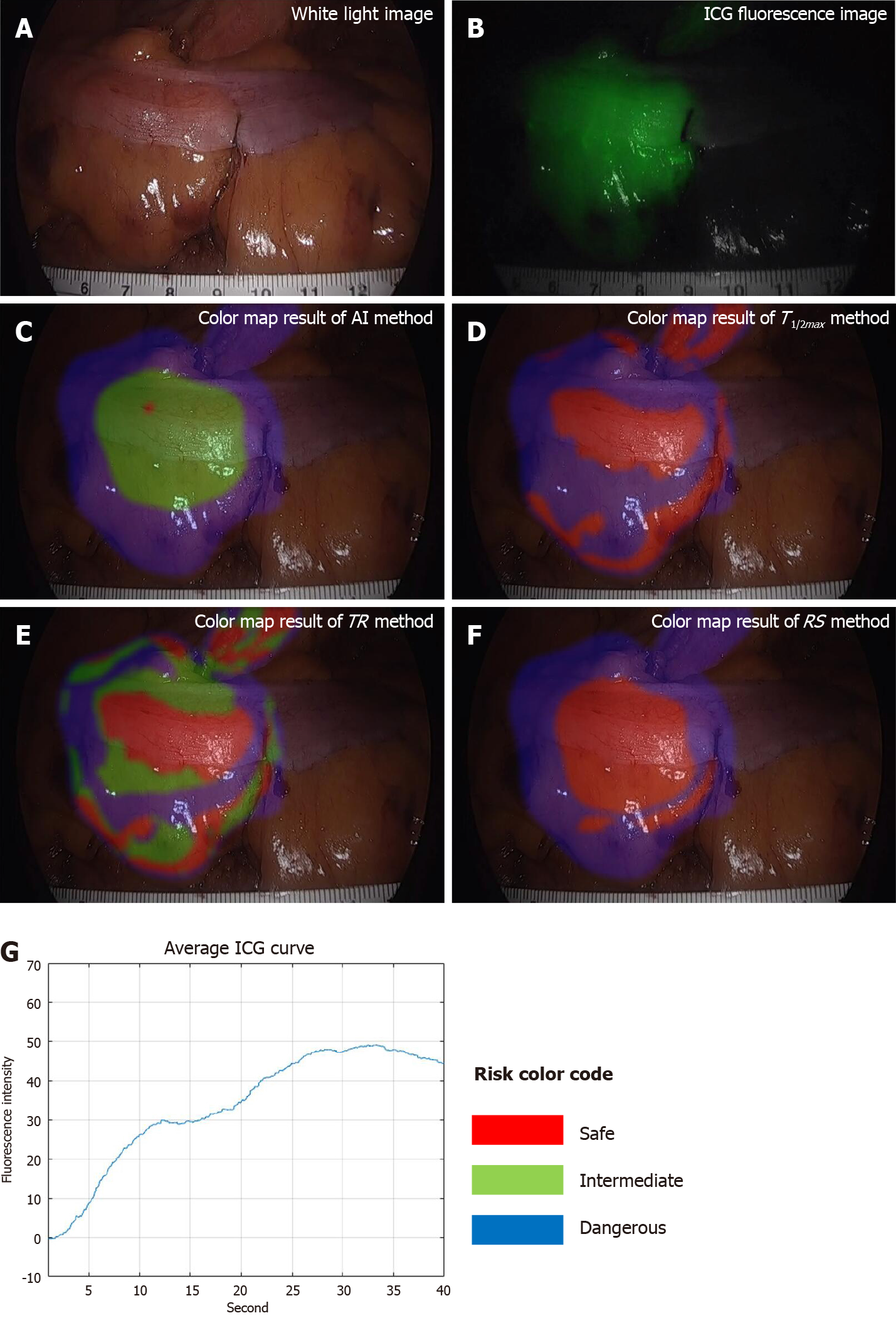
Figure 5 Results of moderate perfusion patient with large Tmax and Fmax, and stepped indocyanine green curve.
A: White light image; B: Indocyanine green (ICG) fluorescence image; C: Color map result of artificial intelligence (AI) method; D: Color map result of T1/2max method; E: Color map result of time ratio (TR) method; F: Color map result of rising slope (RS) method; G: Average ICG curve. The result of AI method was analyzed as risk-intermediate in the middle and risk-dangerous in the outside. The result of T1/2max method was mixed up with risk-safe and risk-dangerous, and the result of TR was mixed up with all risk status. The result of RS method was analyzed as risk-safe in the middle and risk-dangerous in the outside. TR: Time ratio; RS: Rising slope; ICG: Indocyanine green; AI: Artificial intelligence.
- Citation: Park SH, Park HM, Baek KR, Ahn HM, Lee IY, Son GM. Artificial intelligence based real-time microcirculation analysis system for laparoscopic colorectal surgery. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(44): 6945-6962
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i44/6945.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i44.6945