Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2020; 26(42): 6599-6613
Published online Nov 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i42.6599
Published online Nov 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i42.6599
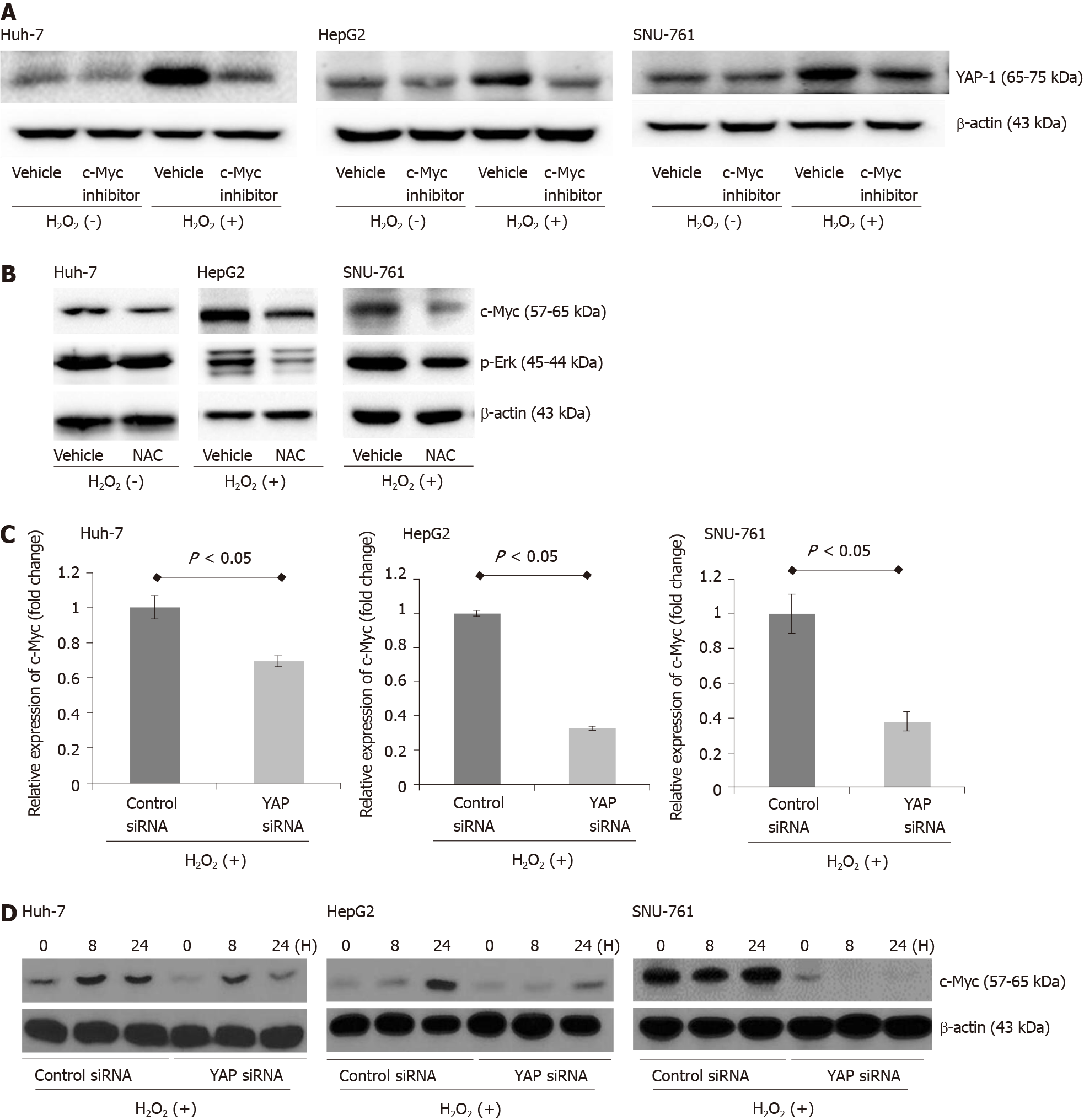
Figure 5 Up-regulation of the c-Myc pathway was dependent on yes-associated protein-1 expressions in reactive oxygen species-exposed hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
A: A c-Myc inhibitor (10058-F4, 60 μmol/L) significantly decreased the protein expression of yes-associated protein-1 (YAP-1) in reactive oxygen species (ROS)-exposed hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. The experiment was repeated three times; B: N-acetylcysteine treatment downregulated c-Myc protein expression in ROS-exposed HCC cell lines. The experiment was repeated three times; C: YAP-1 small interfering RNA (siRNA) transfection significantly suppressed c-Myc mRNA expression compared to control siRNA transfection in ROS-exposed HCC cells (all P < 0.05). The c-Myc mRNA expression was quantified using quantitative PCR and normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase mRNA expression. The data are expressed as the mean ± SD. The experiment was repeated three times; D: Immunoblot analyses of c-Myc were performed in ROS-exposed HCC cells transfected with YAP-1 siRNA or control siRNA. The experiment was repeated three times. YAP: Yes-associated protein; siRNA: Small interfering RNA; NAC: N-acetylcysteine.
- Citation: Cho Y, Park MJ, Kim K, Kim SW, Kim W, Oh S, Lee JH. Reactive oxygen species-induced activation of Yes-associated protein-1 through the c-Myc pathway is a therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(42): 6599-6613
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i42/6599.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i42.6599