Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2020; 26(42): 6582-6598
Published online Nov 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i42.6582
Published online Nov 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i42.6582
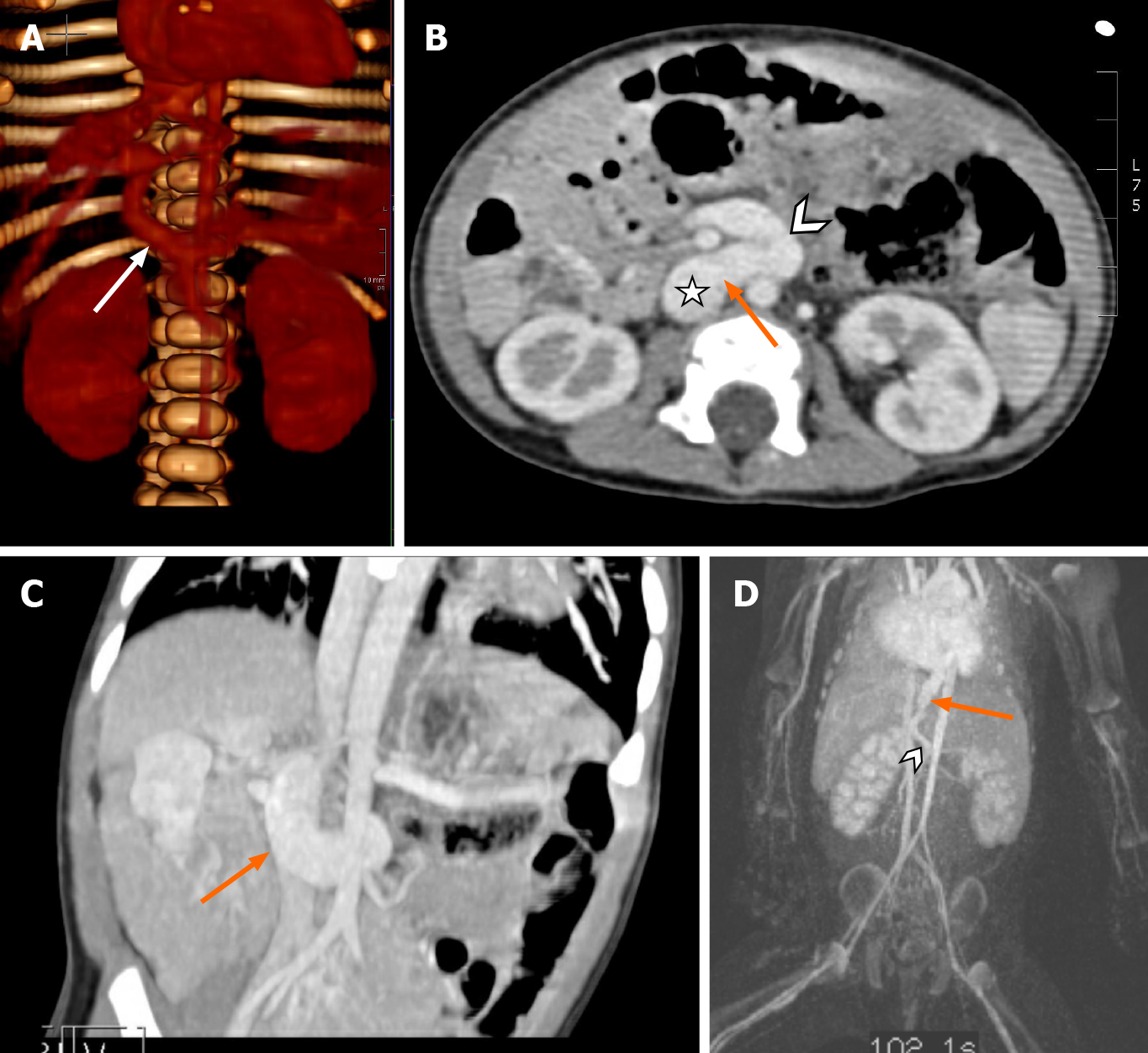
Figure 4 Examples of congenital extrahepatic portosystemic shunts.
A: Nineteen-month-old with congenital extrahepatic porto-systemic shunts (CEPSS) Type II. Connection (arrow) of portal vein to inferior vena cava (IVC). Reconstruction 3D rendering of a computed tomography scan; B and C: One year old with a history of heterotaxia, intestinal malrotation, pulmonary arteriovenous malformations and CEPSS Type II (orange arrow), portal vein (chevron) to IVC (star); D: Type II extrahepatic shunt superior mesenteric vein (chevron) and shunt (arrow) draining directly into the right atrium.
- Citation: Schmalz MJ, Radhakrishnan K. Vascular anomalies associated with hepatic shunting. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(42): 6582-6598
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i42/6582.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i42.6582