Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2020; 26(41): 6346-6360
Published online Nov 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i41.6346
Published online Nov 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i41.6346
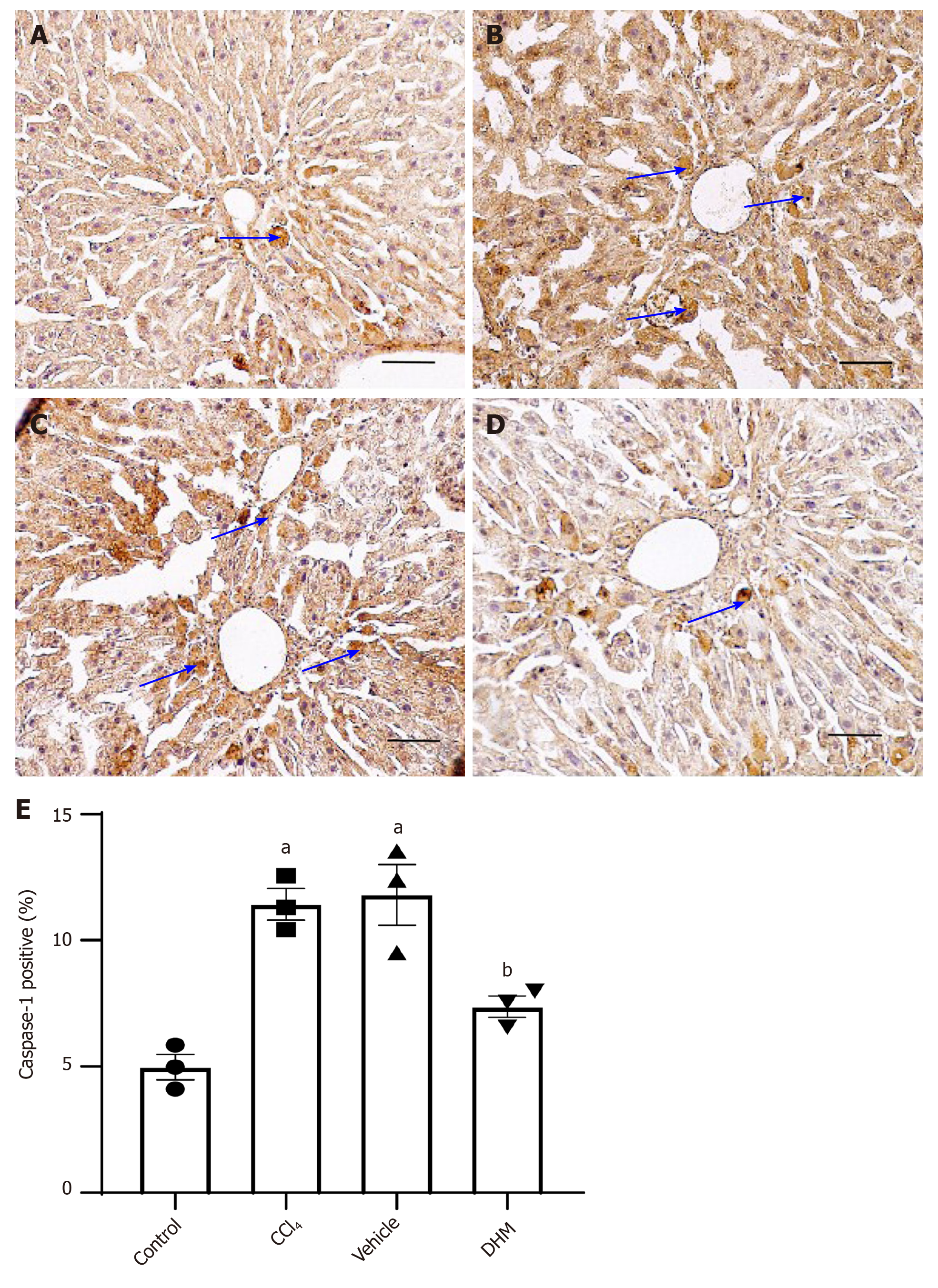
Figure 4 Changes in the expression of caspase-1, the core protein of pyroptosis, were observed by immunohistochemistry.
A-D: The immunohistochemical results of caspase-1 in the control, CCl4, vehicle and dihydromyricetin groups, respectively; E: Statistical graph of the immunohistochemical results of caspase-1 in the above four groups. There was very little caspase-1 in the control group; while in the CCl4 and vehicle groups, a large amount of caspase-1 was observed; but caspase-1 was significantly decreased in the dihydromyricetin group. The scale bar refers to 100 μm. aP < 0.01 vs control group; bP < 0.05 vs vehicle group; n = 3. DHM: Dihydromyricetin.
- Citation: Cheng QC, Fan J, Deng XW, Liu HC, Ding HR, Fang X, Wang JW, Chen CH, Zhang WG. Dihydromyricetin ameliorates chronic liver injury by reducing pyroptosis. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(41): 6346-6360
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i41/6346.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i41.6346