Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2020; 26(40): 6224-6240
Published online Oct 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i40.6224
Published online Oct 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i40.6224
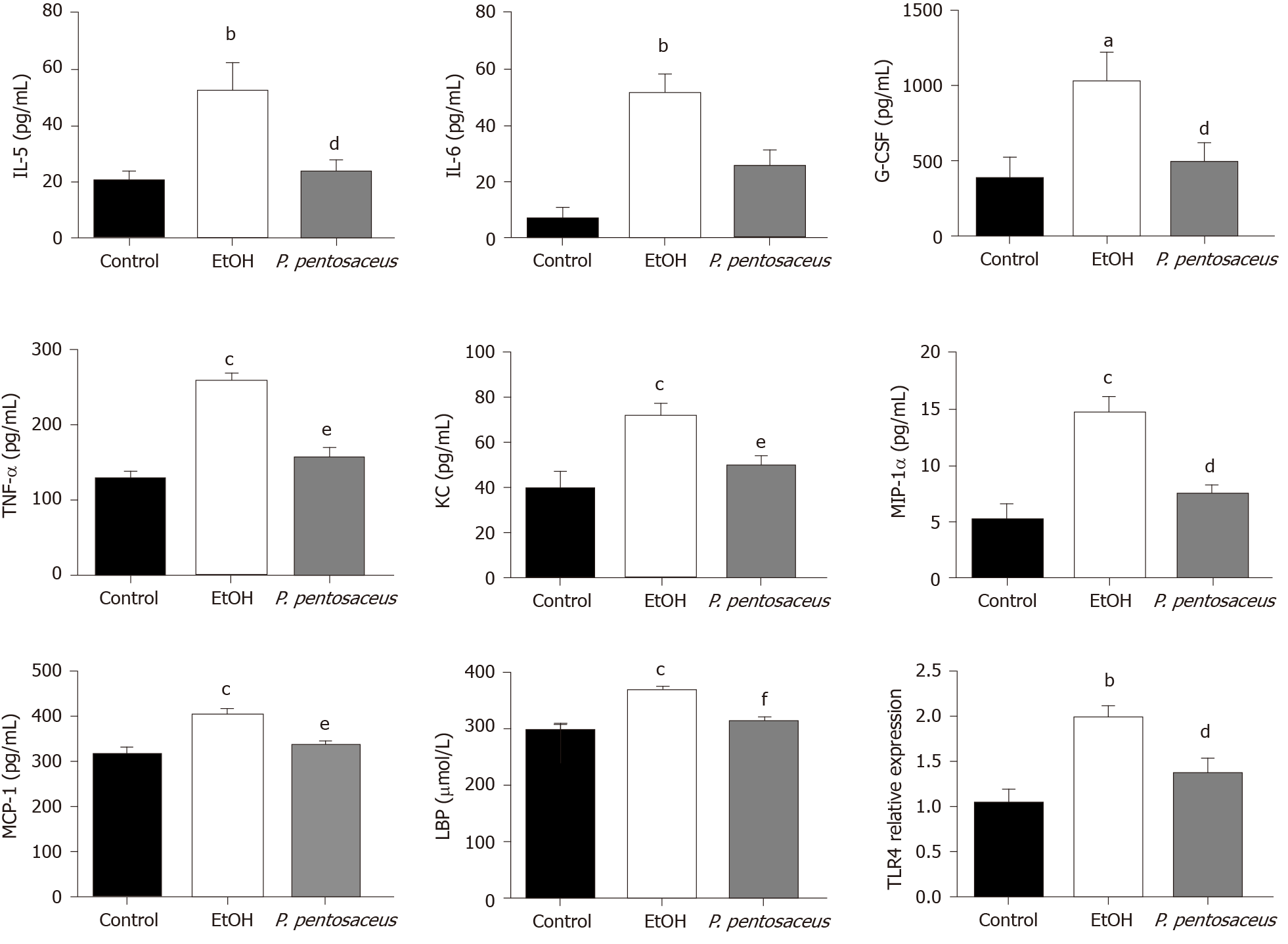
Figure 2 Effects of the Pediococcus pentosaceus treatment on lipopolysaccharide-binding protein and proinflammatory cytokine levels during ethanol-induced liver injury.
The serum levels of interleukin (IL)-5, IL-6, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, tumor necrosis factor-α, keratinocyte-derived protein chemokine, macrophage inflammatory protein-1α, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and lipopolysaccharide-binding protein and expression of the Toll-like receptor 4 mRNA in the liver. All data are presented as means ± SE. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs the Control group. dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 vs the EtOH group. P. pentosaceus: Pediococcus pentosaceus; IL: Interleukin; G-CSF: Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; KC: Keratinocyte-derived protein chemokine; MIP-1α: Macrophage inflammatory protein-1α; MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; LBP: Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4.
- Citation: Jiang XW, Li YT, Ye JZ, Lv LX, Yang LY, Bian XY, Wu WR, Wu JJ, Shi D, Wang Q, Fang DQ, Wang KC, Wang QQ, Lu YM, Xie JJ, Li LJ. New strain of Pediococcus pentosaceus alleviates ethanol-induced liver injury by modulating the gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acid metabolism. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(40): 6224-6240
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i40/6224.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i40.6224