Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2020; 26(40): 6207-6223
Published online Oct 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i40.6207
Published online Oct 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i40.6207
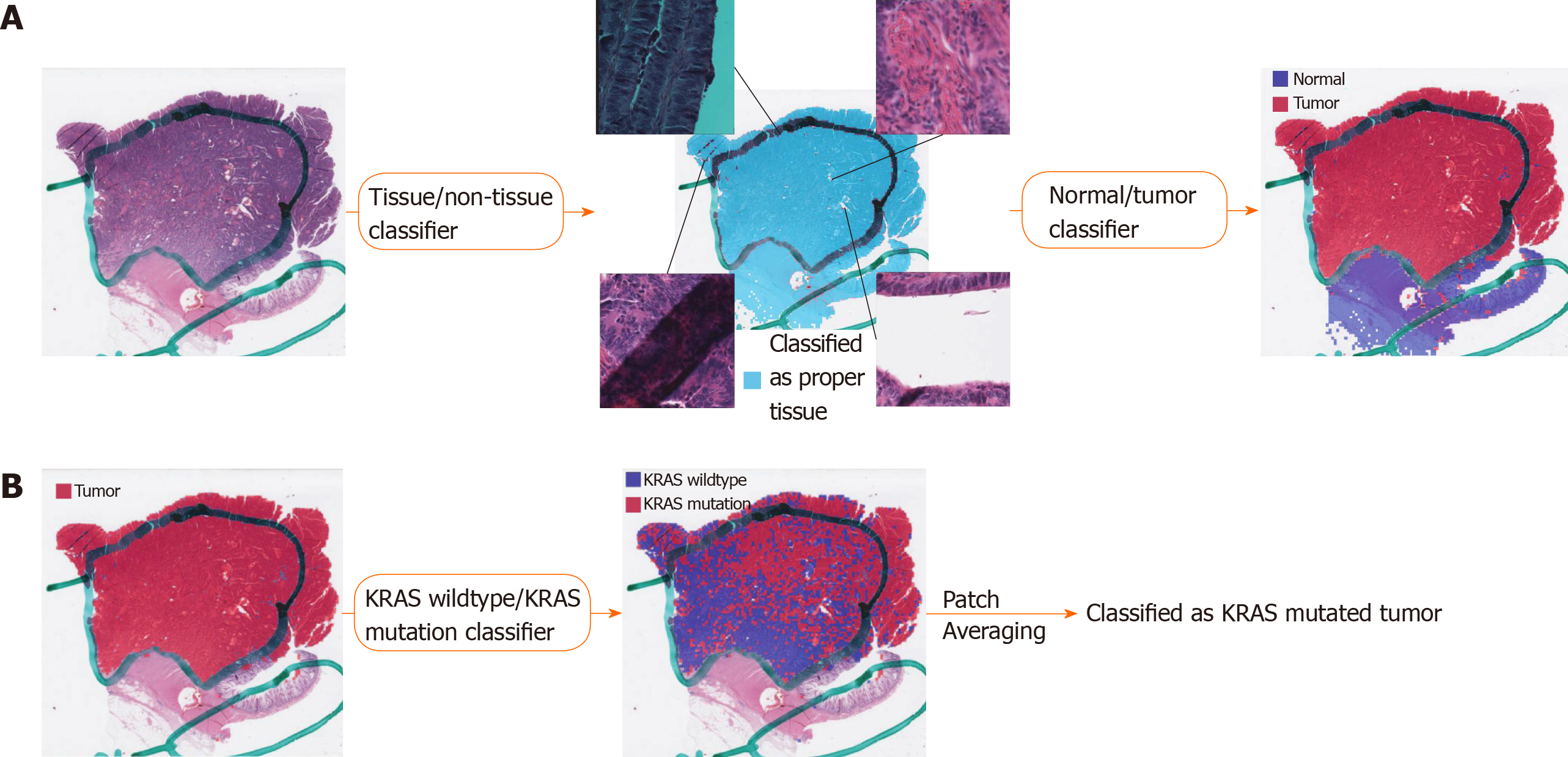
Figure 1 Fully automated prediction of mutation with three consecutive classifiers.
A: Proper tissue patches can be selected by the tissue/non-tissue classifier. The four insets in the middle panel demonstrated the tissue patches representing pen marking, blurry scanned area, background rich region, and tissue folding, clockwise from top left, all removed by the tissue/non-tissue classifiers. Then, the normal/tumor classifier delineates the tumor patches among the proper tissue patches; B: The wild-type/mutation classifiers are applied only for patches with tumor probability higher than 0.9. The patch-level probabilities of mutation are averaged to yield the slide-level probability.
- Citation: Jang HJ, Lee A, Kang J, Song IH, Lee SH. Prediction of clinically actionable genetic alterations from colorectal cancer histopathology images using deep learning. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(40): 6207-6223
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i40/6207.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i40.6207