Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2020; 26(39): 6074-6086
Published online Oct 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i39.6074
Published online Oct 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i39.6074
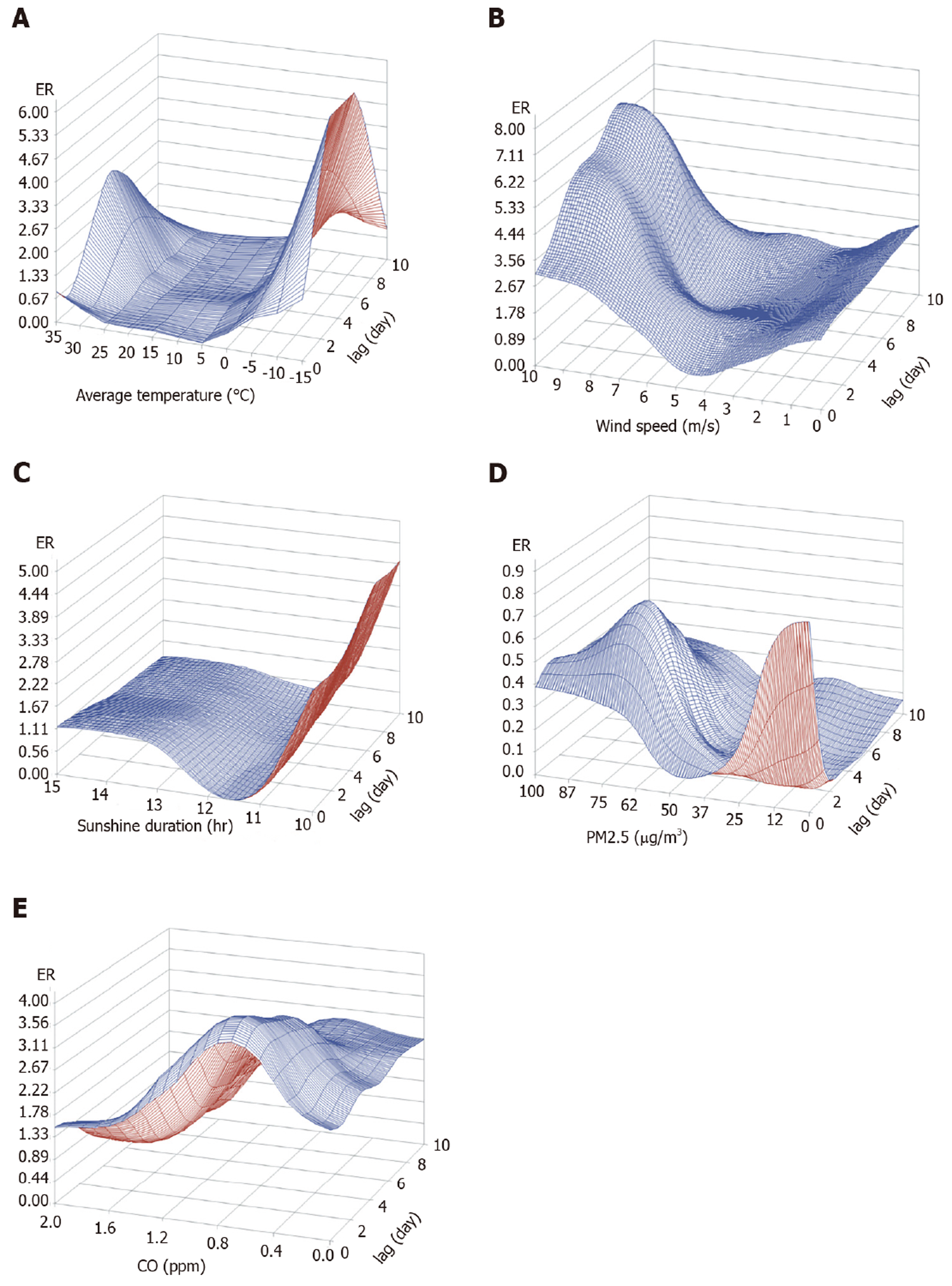
Figure 4 Three-dimensional graph of the prediction model.
Each graph shows excess risk according to factor and time lag. A: Average temperature; B: Wind speed; C: Sunshine duration; D: Particulate matter with a diameter ≤ 2.5 µm; E: Carbon monoxide. CO: Carbon monoxide; PM2.5: Particulate matter with a diameter ≤ 2.5 µm; ppm: Parts-per-million.
- Citation: Seo HS, Hong J, Jung J. Relationship of meteorological factors and air pollutants with medical care utilization for gastroesophageal reflux disease in urban area. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(39): 6074-6086
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i39/6074.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i39.6074