Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2020; 26(39): 5997-6014
Published online Oct 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i39.5997
Published online Oct 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i39.5997
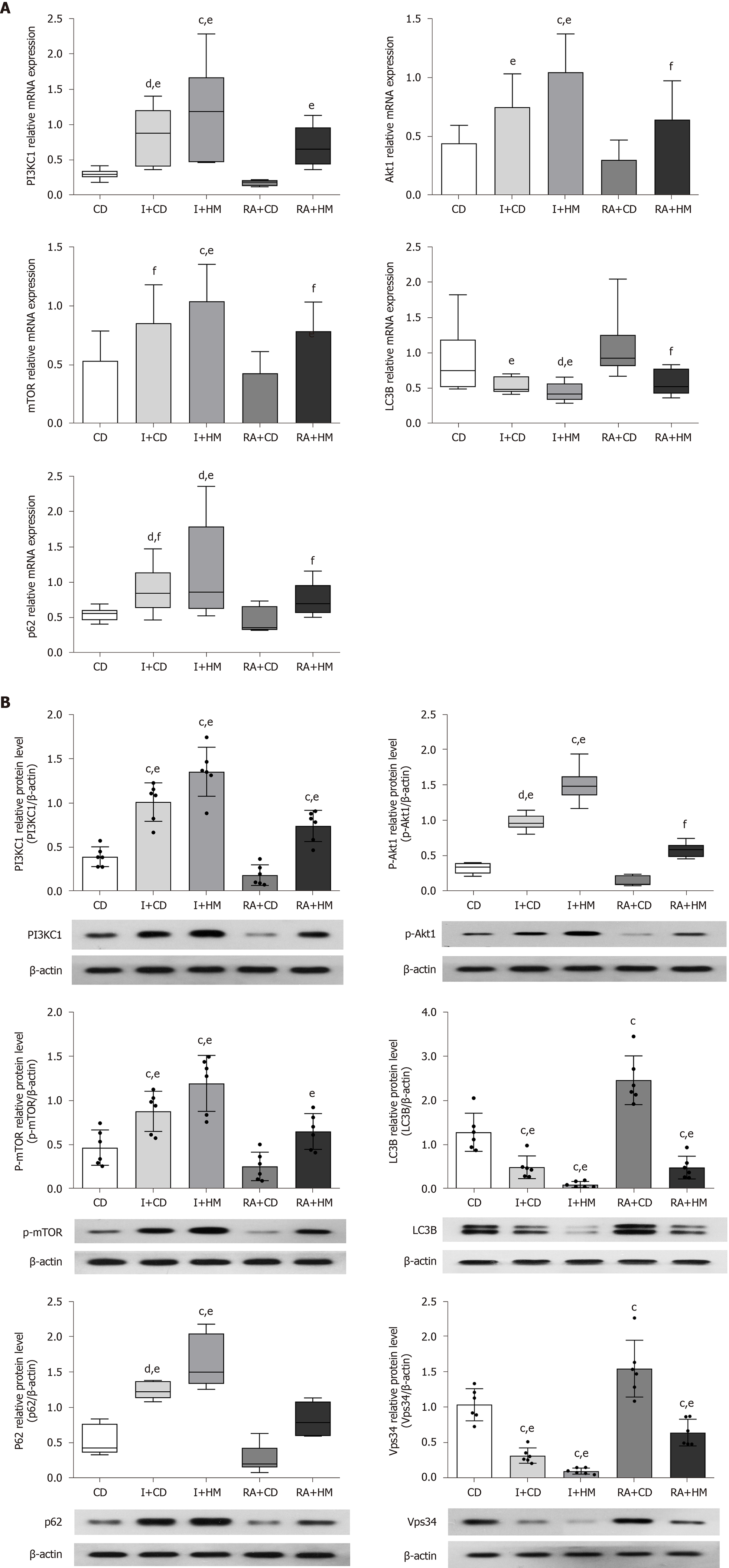
Figure 6 Herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion at the Qihai (CV6) and bilateral Tianshu (ST25) acupoints regulates the mRNA and protein expression of PI3KC signaling-related molecules in the colon tissues of Crohn’s disease rats.
A: The mRNA levels of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase class I (PI3KC1), Akt1, mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 beta (LC3B), and sequestosome 1 (p62) were determined by real-time PCR; B: Expression changes of the PI3KC1, p-Akt1, mTOR, LC3B, p62, and class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase proteins evaluated by Western blot. Six independent experiments were analyzed, and the data are presented as the mean ± SD or medians (P25, P75). cP < 0.01, dP < 0.05 vs CD group; eP < 0.01, fP < 0.05 vs RA+CD group. CD: Crohn’s disease; I + CD: Insulin + Crohn’s disease; I + HM: Insulin + herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion; RA+CD: Rapamycin + Crohn’s disease; RA + HM: Rapamycin + herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion; PI3KC1: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase class I; Akt1: Protein kinase B akt-1; p-Akt1: Phospho-protein kinase B akt-1; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; p-mTOR: Phospho-mammalian target of rapamycin; LC3B: Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 beta; p62: Sequestosome 1; Vps34: Class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.
- Citation: Wang SY, Zhao JM, Zhou CL, Zheng HD, Huang Y, Zhao M, Zhang ZY, Wu LY, Wu HG, Liu HR. Herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion inhibits colonic autophagy in Crohn’s disease via signaling involving distinct classes of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(39): 5997-6014
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i39/5997.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i39.5997