Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2020; 26(39): 5997-6014
Published online Oct 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i39.5997
Published online Oct 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i39.5997
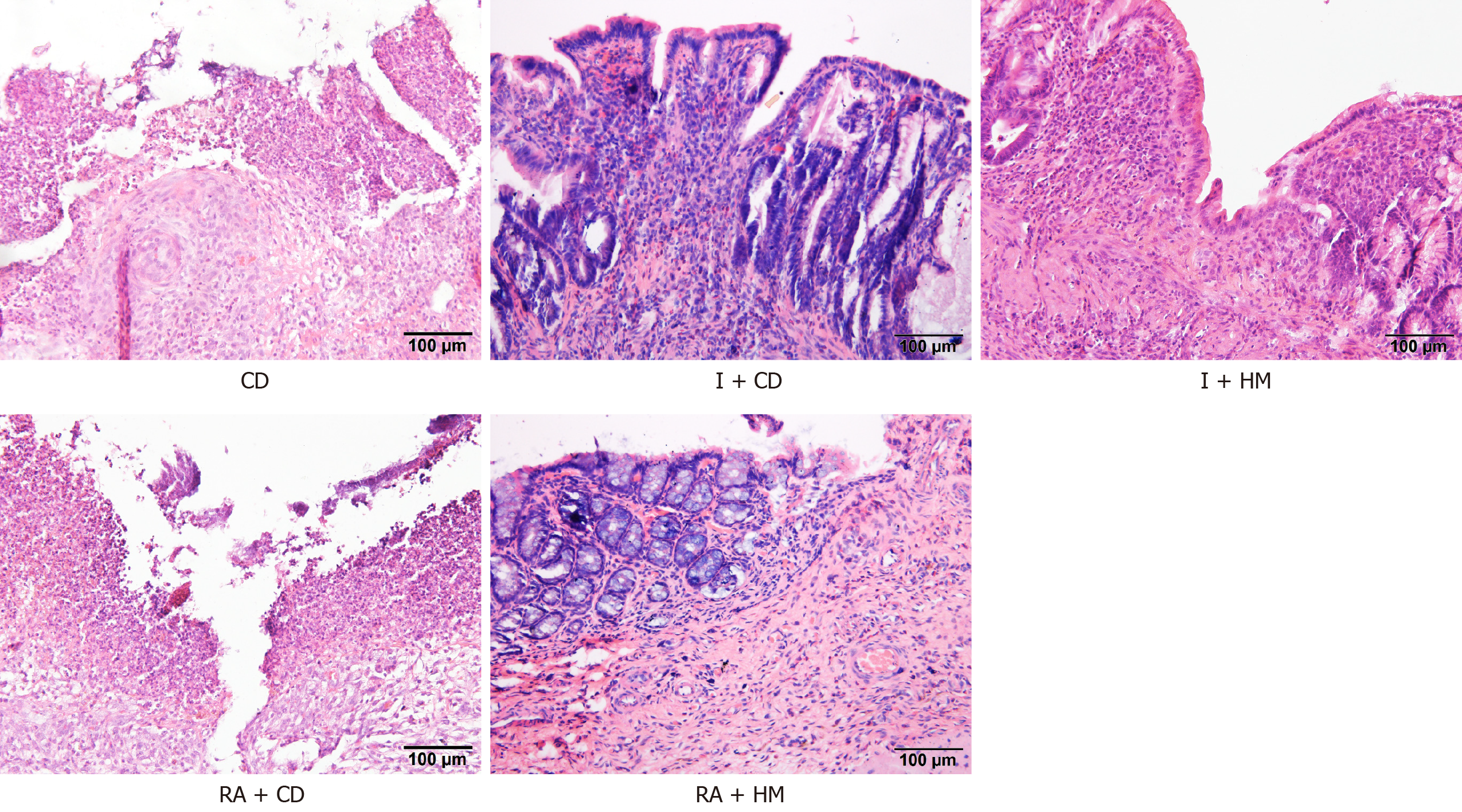
Figure 4 Histopathological observations of colon tissue from each group by hematoxylin and eosin staining.
Scale bar: 100 μm. CD: Crohn’s disease; I + CD: Insulin + Crohn’s disease; I + HM: Insulin + herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion; RA + CD: Rapamycin + Crohn’s disease; RA + HM: Rapamycin + herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion.
- Citation: Wang SY, Zhao JM, Zhou CL, Zheng HD, Huang Y, Zhao M, Zhang ZY, Wu LY, Wu HG, Liu HR. Herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion inhibits colonic autophagy in Crohn’s disease via signaling involving distinct classes of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(39): 5997-6014
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i39/5997.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i39.5997