Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2020; 26(39): 5997-6014
Published online Oct 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i39.5997
Published online Oct 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i39.5997
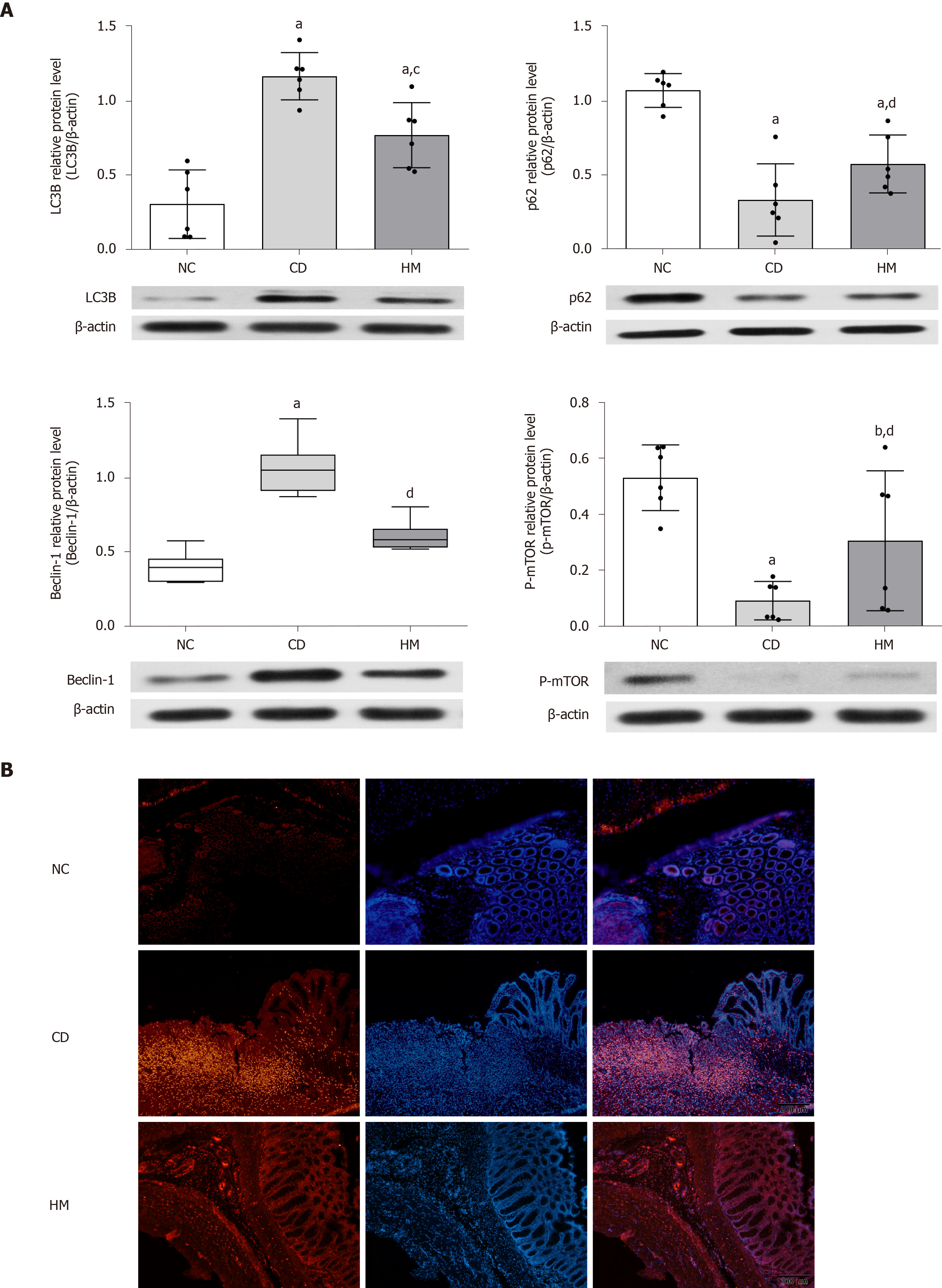
Figure 3 Herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion at the Qihai (CV6) and bilateral Tianshu (ST25) acupoints regulates the expression of autophagy proteins in the colon tissues of Crohn’s disease rats.
A: Expression changes of the microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 beta, sequestosome 1, coiled-coil myosin-like BCL2-interacting protein, and phospho-mammalian target of rapamycin proteins evaluated by Western blot. Six independent experiments were analyzed, and the data are presented as the mean ± SD or medians (P25, P75). aP < 0.01, bP < 0.05 vs NC group; cP < 0.01, dP < 0.05 vs CD group; B: Immunofluorescence images for LC3B (Red) in each group. Scale bar: 200 μm. NC: Normal control; CD: Crohn’s disease; HM: Herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion; LC3B: Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 beta; p62: Sequestosome 1; Beclin-1: Coiled-coil myosin-like BCL2-interacting protein; p-mTOR: Phospho-mammalian target of rapamycin.
- Citation: Wang SY, Zhao JM, Zhou CL, Zheng HD, Huang Y, Zhao M, Zhang ZY, Wu LY, Wu HG, Liu HR. Herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion inhibits colonic autophagy in Crohn’s disease via signaling involving distinct classes of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(39): 5997-6014
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i39/5997.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i39.5997