Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2020; 26(39): 5983-5996
Published online Oct 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i39.5983
Published online Oct 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i39.5983
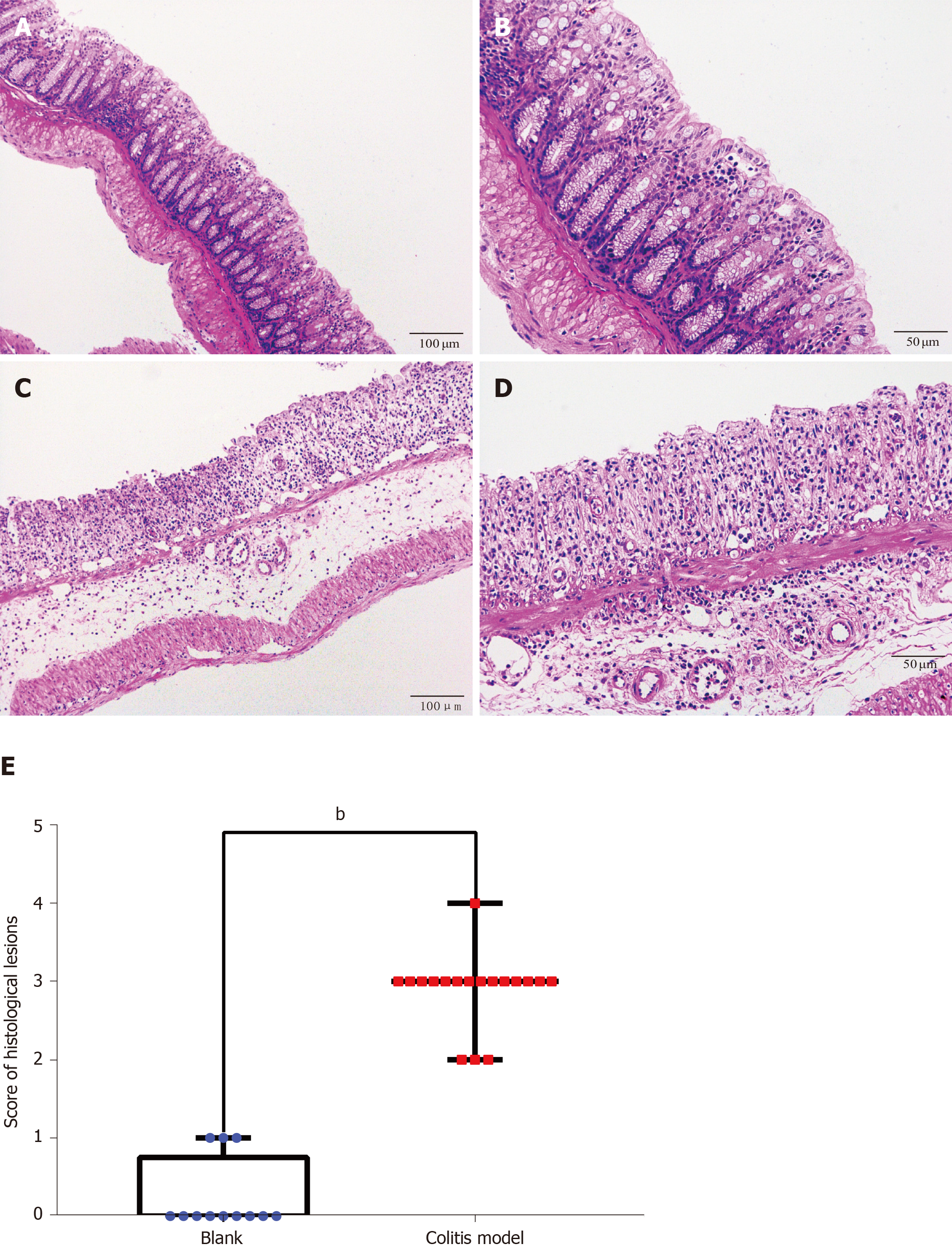
Figure 3 Hematoxylin-eosin staining and histological lesion score of colon tissues.
Hematoxylin-eosin staining of colon tissues from the control and dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis model mice. A: Control mice (× 100); B: Control mice (× 200); C: Colitis mice (× 100); D: Colitis mice (× 200); E: Histological lesion scores of colon tissues. Numerous neutrophils infiltrated and the crypts, goblet cells and normal four-layer structure of colon disappeared in the colitis model mice. Compared to the score of the control group (n = 4, 12 pieces), the score of the model group (n = 6, 18 pieces) increased significantly (P < 0.01).
- Citation: Shi L, Han X, Li JX, Liao YT, Kou FS, Wang ZB, Shi R, Zhao XJ, Sun ZM, Hao Y. Identification of differentially expressed genes in ulcerative colitis and verification in a colitis mouse model by bioinformatics analyses. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(39): 5983-5996
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i39/5983.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i39.5983