Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2020; 26(38): 5822-5835
Published online Oct 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i38.5822
Published online Oct 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i38.5822
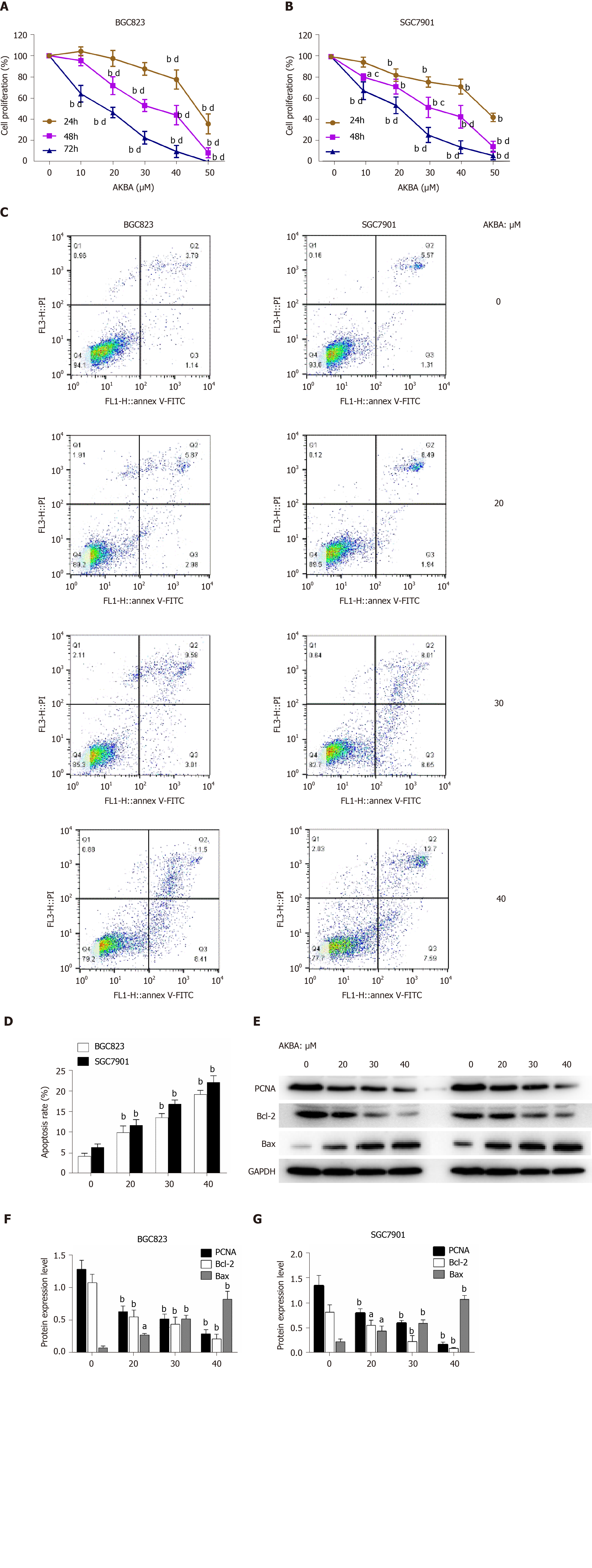
Figure 2 Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid inhibits the proliferation and induces the apoptosis of gastric cancer cells.
A and B: Dose- and time-dependent effects of acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (AKBA) on BGC823 and SGC7901 cell proliferation; C: Flow cytometry-based annexin V-FITC/PI labeling of apoptotic cells; D: Histogram showing apoptosis rates; E: Expression levels of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), Bcl-2, and Bax in BGC823 and SGC7901 cells measured via Western blot analysis after AKBA treatment; F and G: Histograms showing the relative expression levels of PCNA, Bcl-2, and Bax compared with GAPDH in BGC823 and SGC7901 cells. Each data point represents the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control (0 µM). cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs control (24 h). AKBA: Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid; PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- Citation: Sun MX, He XP, Huang PY, Qi Q, Sun WH, Liu GS, Hua J. Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer cells through the phosphatase and tensin homolog /Akt/ cyclooxygenase-2 signaling pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(38): 5822-5835
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i38/5822.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i38.5822