Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2020; 26(38): 5759-5783
Published online Oct 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i38.5759
Published online Oct 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i38.5759
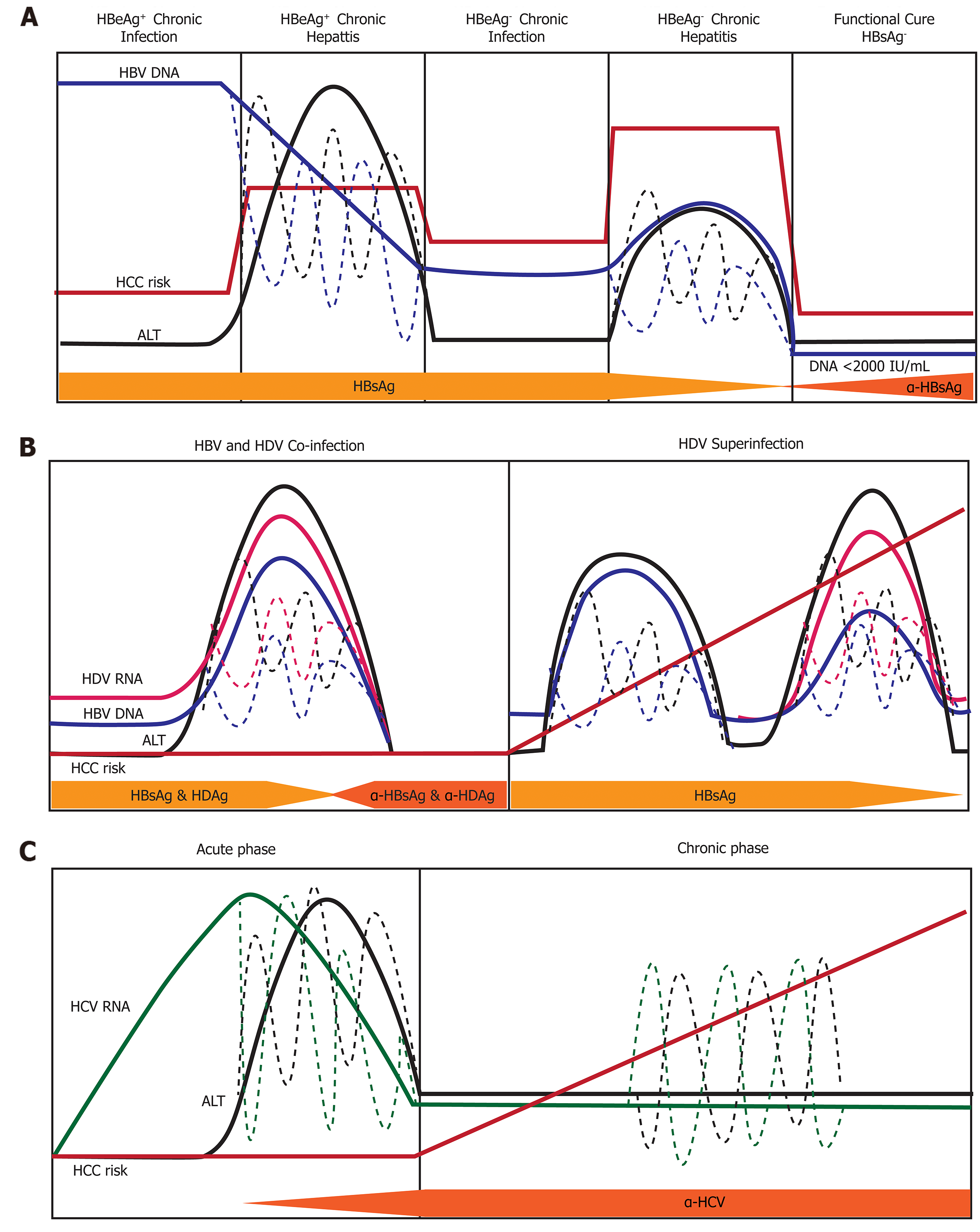
Figure 6 Natural history of infection with hepatitis B, delta, or C virus.
Variations in hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA, hepatitis C virus RNA, hepatitis delta virus (HDV) RNA, and ALT levels indicated by dashed lines. A: Natural history of chronic Hepatitis B virus infection. There are five phases of infection HBeAg+ chronic infection, HBeAg+ chronic hepatitis, HBeAg- chronic infection, and HBeAg- phase. Each clinical phase is defined by a host immune response with respect to HBV viral activity; B: Natural history of HDV infection in either HBV co-infection or HDV superinfection when the individual is a chronic carrier of HBV; and C: Natural history of Hepatitis C virus infection. There are two main phases of infection acute infection and chronic infection. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; HDV: Hepatitis delta virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
- Citation: D'souza S, Lau KCK, Coffin CS, Patel TR. Molecular mechanisms of viral hepatitis induced hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(38): 5759-5783
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i38/5759.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i38.5759