Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2020; 26(37): 5673-5681
Published online Oct 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i37.5673
Published online Oct 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i37.5673
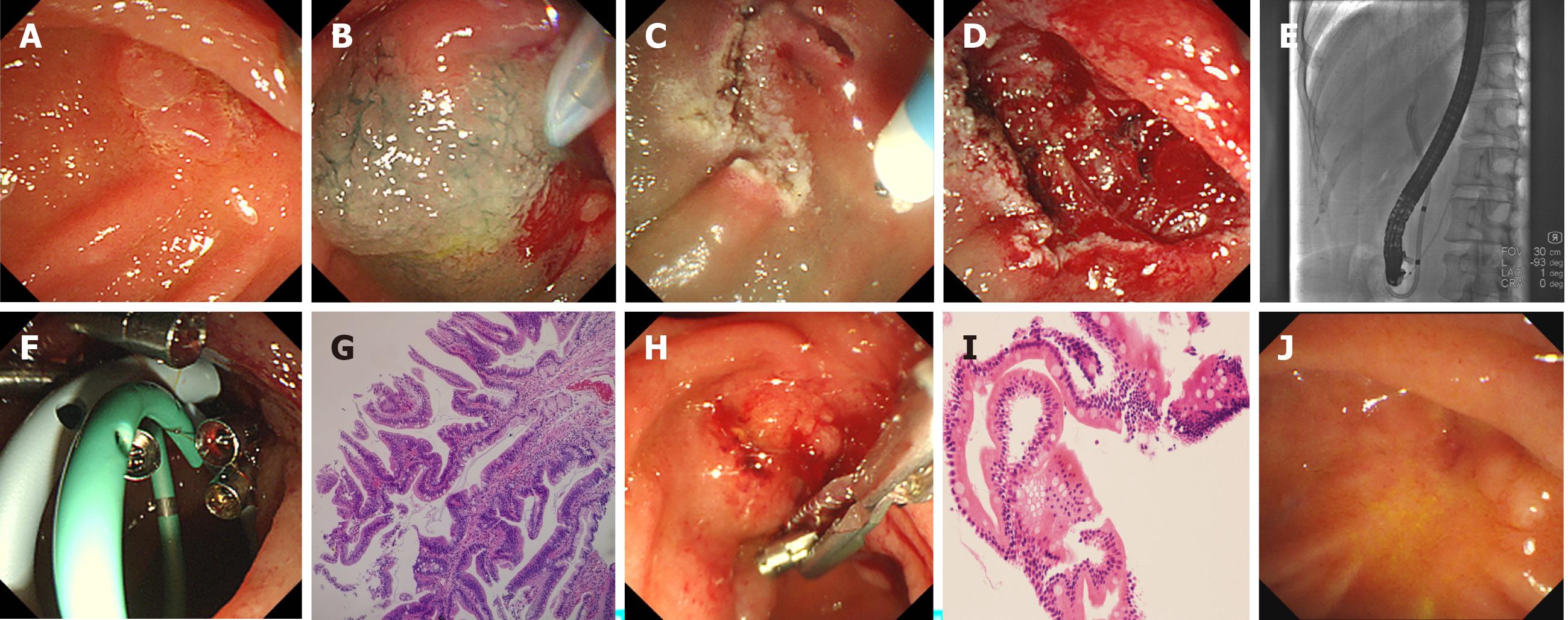
Figure 2 Endoscopic and pathological characteristics of case 2.
A: Red and protuberant laterally spreading lesion was seen in the mucosa around the opening of the pancreaticobiliary duct; B-D: Hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) such as submucosal injection and submucosal dissection are shown, and the artificial ulcer was created; E and F: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography showed the normal bile and pancreatic ducts, biliary and pancreatic stents were implanted, and close incision was performed by endoscopic clips; G: Hematoxylin and eosin-stained resected specimen showing tubulovillous adenoma with clean cutting edge, 4 ×; H: Endoscopic follow-up 3 mo after hybrid ESD showed that the pancreatic stent disappeared, and the biliary stent and clips were removed; I: Histological follow-up of biopsy specimen revealed chronic and acute inflammation of small intestinal mucosa, 20 ×; J: Endoscopic follow-up 38 mo after hybrid ESD with no recurrence.
- Citation: Wang ZK, Liu F, Wang Y, Wang XD, Tang P, Li W. Preliminary experience of hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection by duodenoscope for recurrent laterally spreading papillary lesions. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(37): 5673-5681
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i37/5673.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i37.5673