Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2020; 26(35): 5314-5327
Published online Sep 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i35.5314
Published online Sep 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i35.5314
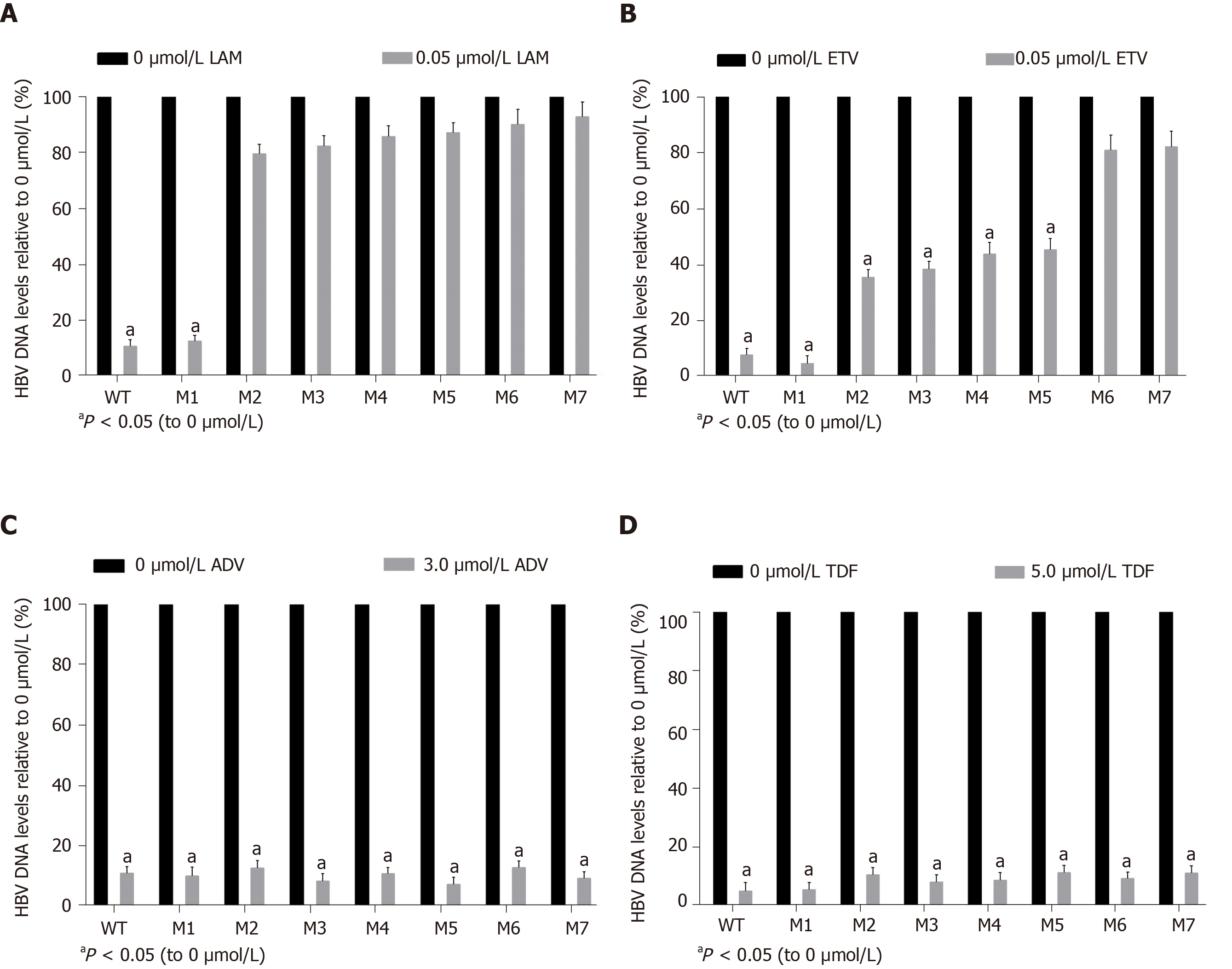
Figure 5 Assessment of drug-induced viral inhibition.
Human hepatocellular carcinomas cells were transiently transfected with wild-type or individual viral vectors and cultured with or without one of the following four drugs: (A) 0.05 μmol/L lamivudine, (B) 0.05 μmol/L entecavir, (C) 3.0 μmol/L adefovir, and (D) 5.0 μmol/L tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. Viral inhibition was evaluated as the relative hepatitis B virus deoxyribonucleic acid level of samples with the drug to that without the drug. M1, sA159V; M2, rtM204I; M3, sA159V+rtM204I; M4, rtL180M+rtM204V; M5, sA159V+tL180M+rtM204V; M6, rtL180M+rtT184L+rtM204V; M7, sA159V+rtL180M+rtT184L+rtM204V. aP < 0.05.
- Citation: Huang BX, Liu Y, Fan ZP, Si LL, Chen RJ, Wang J, Luo D, Wang FS, Xu DP, Liu XG. Investigation of immune escape-associated mutations of hepatitis B virus in patients harboring hepatitis B virus drug-resistance mutations. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(35): 5314-5327
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i35/5314.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i35.5314