Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2020; 26(35): 5314-5327
Published online Sep 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i35.5314
Published online Sep 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i35.5314
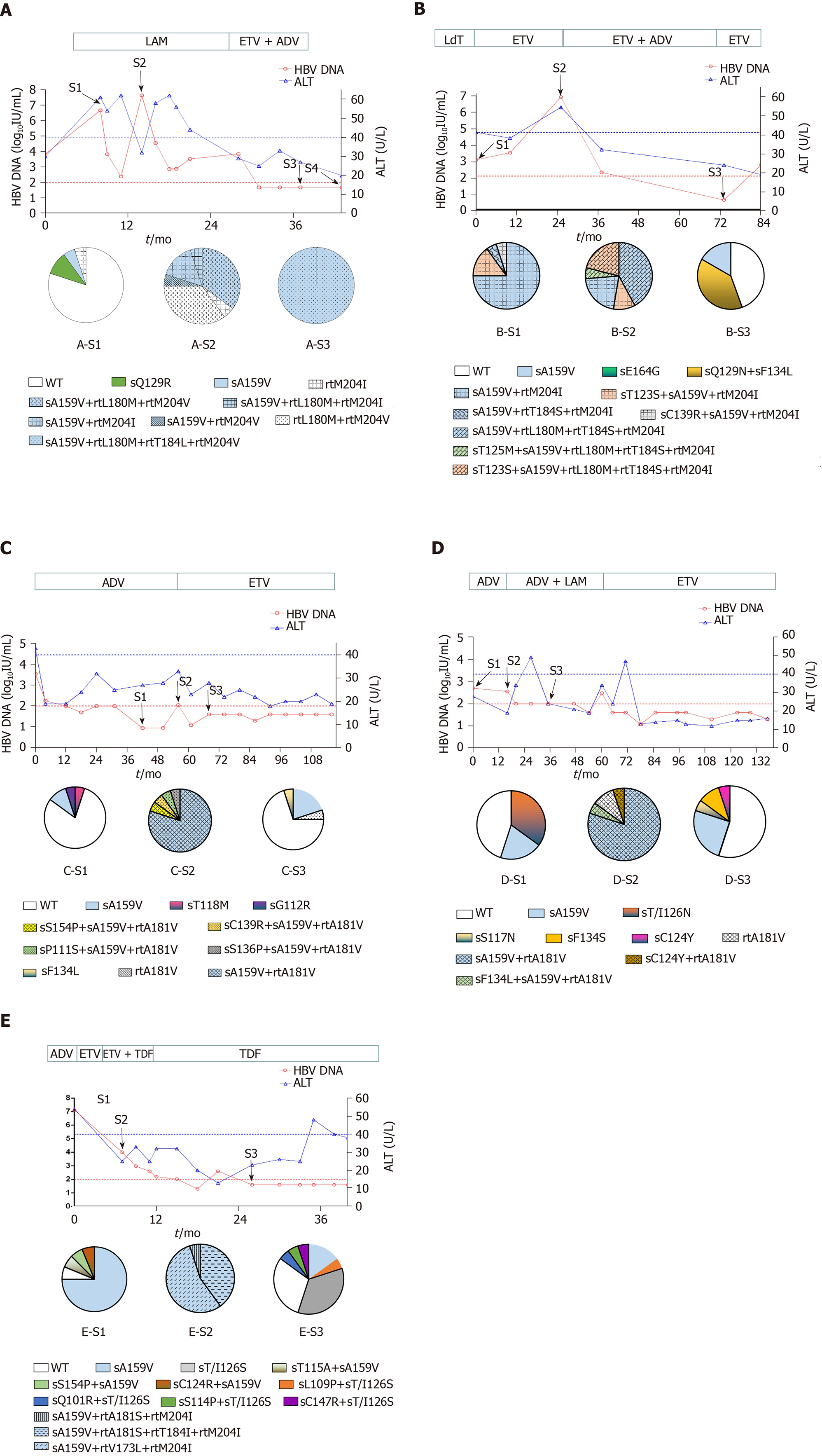
Figure 1 Evolution of drug-resistant hepatitis B virus strains and clinical responses during antiviral therapy in five representative patients.
Dynamic changes in serum hepatitis B virus deoxyribonucleic acid (HBV DNA) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels are shown along with antiviral therapies. The duration (months) of antiviral therapy is represented by bars above the graph, and the serum samples from the patient for cloning are indicated by arrows. Two dashed lines show the lower detection limit of HBV DNA (100 IU/mL) and normal ALT levels (40 U/L). Proportions of wild-type and mutant HBV reverse transcriptase from each sample are depicted by a series of pie charts. A: Evolution of drug-resistant hepatitis B virus strains and clinical responses during antiviral therapy in patient A; B:Evolution of drug-resistant hepatitis B virus strains and clinical responses during antiviral therapy in patient B; C:Evolution of drug-resistant hepatitis B virus strains and clinical responses during antiviral therapy in patient C; D:Evolution of drug-resistant hepatitis B virus strains and clinical responses during antiviral therapy in patient D; E:Evolution of drug-resistant hepatitis B virus strains and clinical responses during antiviral therapy in patient E.
- Citation: Huang BX, Liu Y, Fan ZP, Si LL, Chen RJ, Wang J, Luo D, Wang FS, Xu DP, Liu XG. Investigation of immune escape-associated mutations of hepatitis B virus in patients harboring hepatitis B virus drug-resistance mutations. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(35): 5314-5327
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i35/5314.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i35.5314