Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2020; 26(34): 5101-5117
Published online Sep 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i34.5101
Published online Sep 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i34.5101
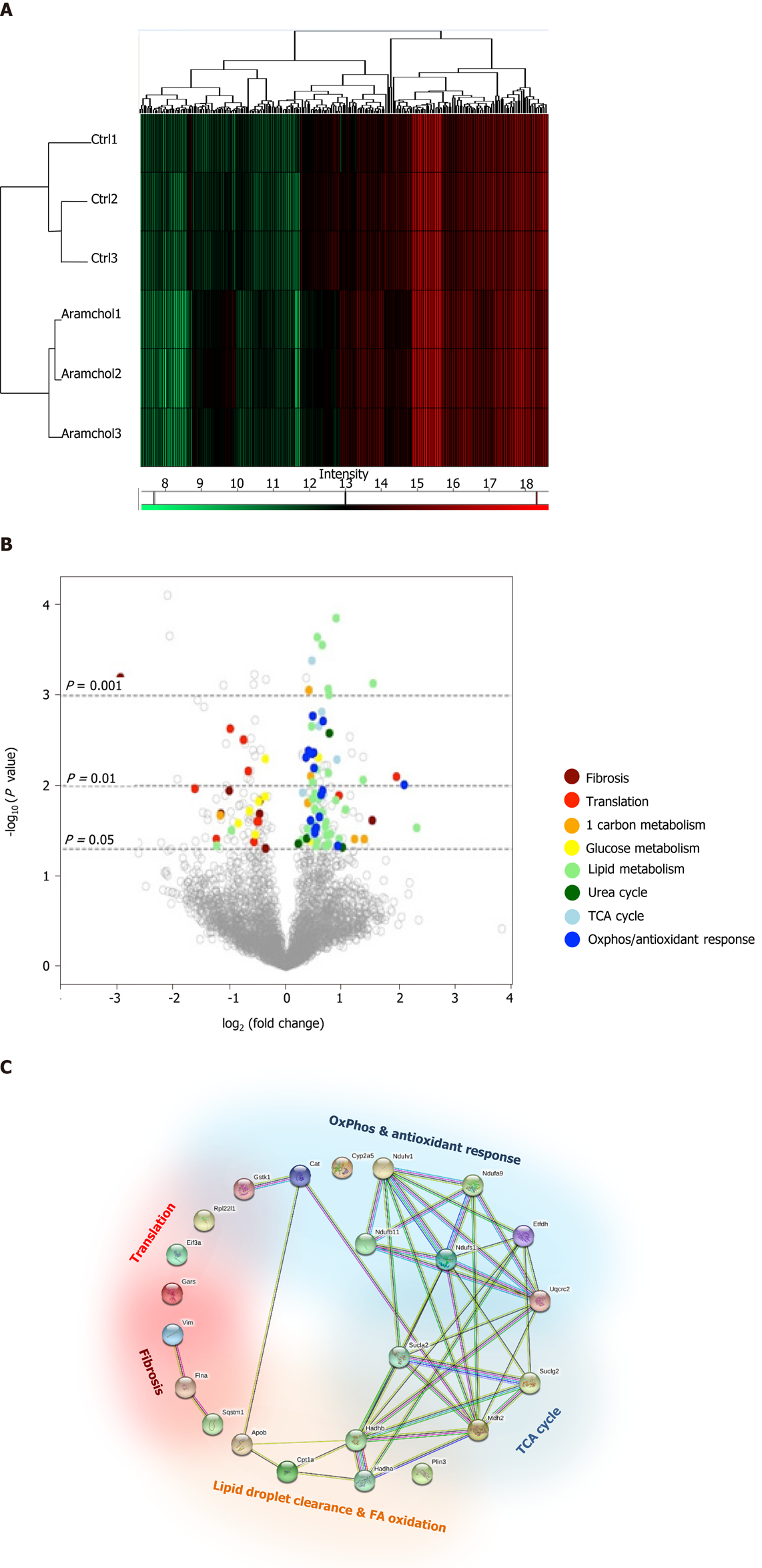
Figure 3 Effect of Arachidyl amido cholanoic acid on the proteome of cultured mouse hepatocytes.
A total of 3220 proteins were identified by proteomics analysis, of which the contents of 219 changed significantly (6.80%, P < 0.05) between the two experimental groups [vehicle vs arachidyl amido cholanoic acid (Aramchol) 20 µmol/L]. A: Hierarchical clustering showing classification of the samples into two differentiated groups: Control and Aramchol treated; B: The differentially expressed proteins according to the up- or down-regulation were classified with colors in a volcano plot depending on their biological functions; C: Classification of the selected differentially expressed proteins in key biological functions. STRING software was used for the analysis.
- Citation: Fernández-Ramos D, Lopitz-Otsoa F, Delacruz-Villar L, Bilbao J, Pagano M, Mosca L, Bizkarguenaga M, Serrano-Macia M, Azkargorta M, Iruarrizaga-Lejarreta M, Sot J, Tsvirkun D, van Liempd SM, Goni FM, Alonso C, Martínez-Chantar ML, Elortza F, Hayardeny L, Lu SC, Mato JM. Arachidyl amido cholanoic acid improves liver glucose and lipid homeostasis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis via AMPK and mTOR regulation. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(34): 5101-5117
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i34/5101.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i34.5101