Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2020; 26(34): 5101-5117
Published online Sep 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i34.5101
Published online Sep 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i34.5101
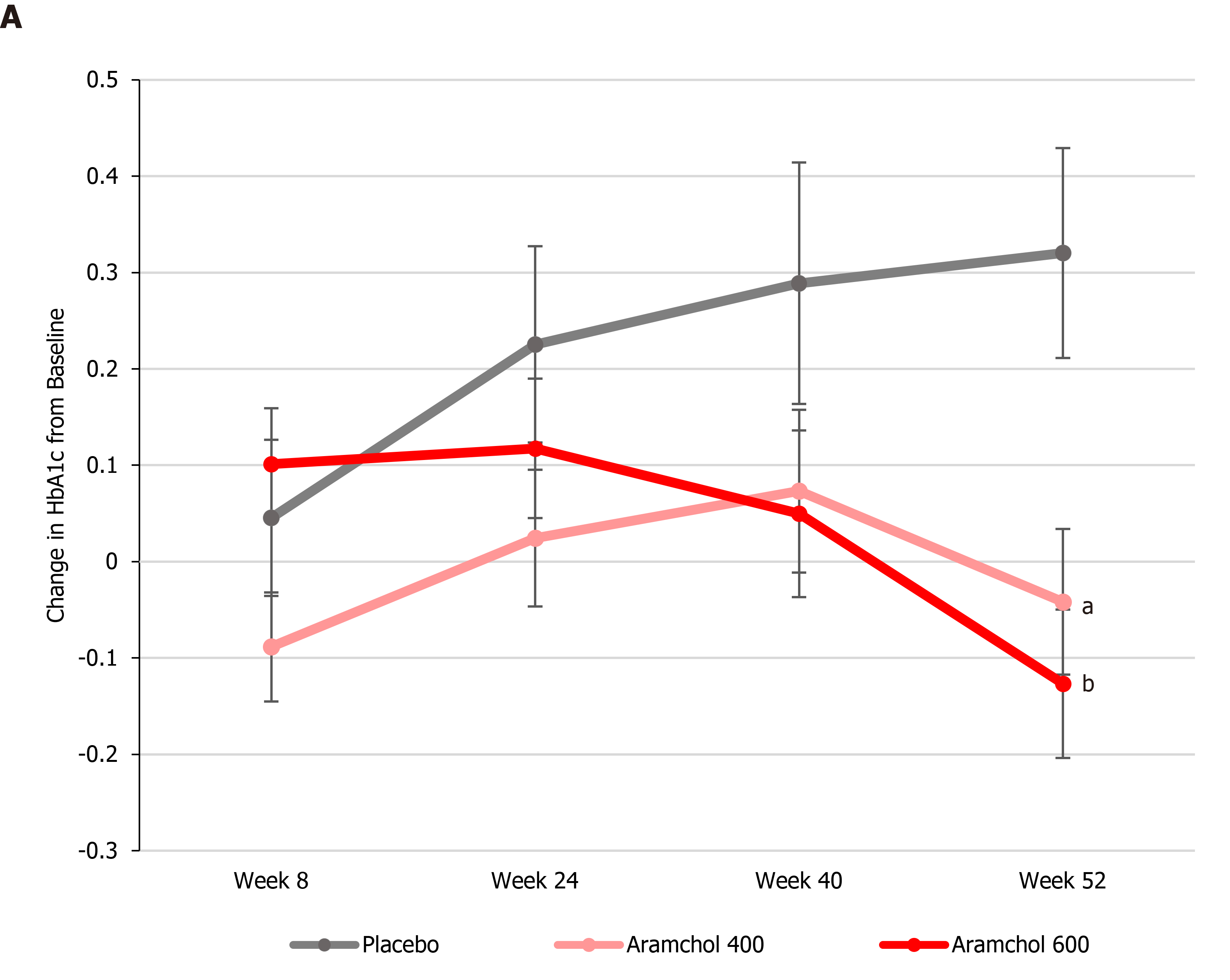
Figure 1 Arachidyl amido cholanoic acid improves glycemic control in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis patients.
ARREST is a multicenter, placebo-controlled study designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of two arachidyl amido cholanoic acid (Aramchol) doses (400 and 600 mg tablets/d) and placebo tablets in subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, confirmed by liver biopsy, who were overweight or obese, and had prediabetes or type II diabetes. Blood hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) content was determined at baseline and weeks 8, 24, 40, and 52. At week 52, both Aramchol doses resulted in a decrease in HbA1c, while NASH patients on the placebo arm showed an increase. The differences from placebo were statistically significant (aP = 0.0061 and bP = 0.0008 for Aramchol 400 mg vs placebo and 600 mg vs placebo, respectively).
- Citation: Fernández-Ramos D, Lopitz-Otsoa F, Delacruz-Villar L, Bilbao J, Pagano M, Mosca L, Bizkarguenaga M, Serrano-Macia M, Azkargorta M, Iruarrizaga-Lejarreta M, Sot J, Tsvirkun D, van Liempd SM, Goni FM, Alonso C, Martínez-Chantar ML, Elortza F, Hayardeny L, Lu SC, Mato JM. Arachidyl amido cholanoic acid improves liver glucose and lipid homeostasis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis via AMPK and mTOR regulation. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(34): 5101-5117
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i34/5101.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i34.5101