Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2020; 26(33): 4900-4918
Published online Sep 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i33.4900
Published online Sep 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i33.4900
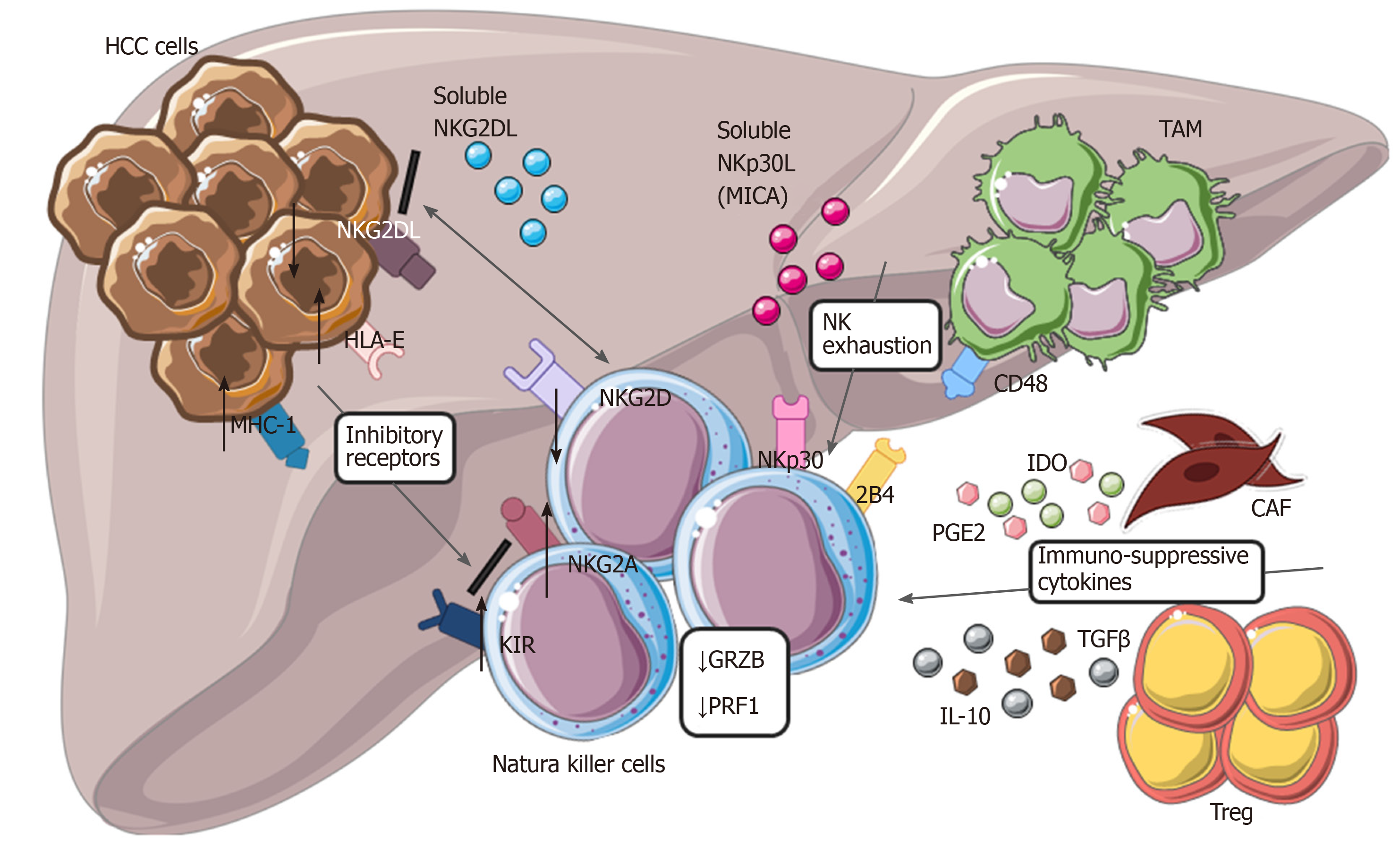
Figure 3 Modulation of natural killer cells cytotoxic activity in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Tumor cells with tumor-associated macrophages and other cells within tumor microenvironment are involved in dysfunctional activity of natural killer cells (NK), reducing their ability to recognize and eliminate malignant cells. Down regulation of NKG2D, up-regulation of different inhibitory receptors, secretion of cytokines from cancer-associated fibroblasts and Treg, interaction of CD48/2B4 are the main mechanisms involved in NK exhaustion. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; NK: Natural killer cells; CAF: Cancer-associated fibroblasts; TAM: Tumor-associated macrophages; IL-10: Interleukin-10; MHC-1: major histocompatibility complex class I; KIR: Killer Ig-like receptors.
- Citation: Polidoro MA, Mikulak J, Cazzetta V, Lleo A, Mavilio D, Torzilli G, Donadon M. Tumor microenvironment in primary liver tumors: A challenging role of natural killer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(33): 4900-4918
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i33/4900.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i33.4900