Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2020; 26(33): 4900-4918
Published online Sep 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i33.4900
Published online Sep 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i33.4900
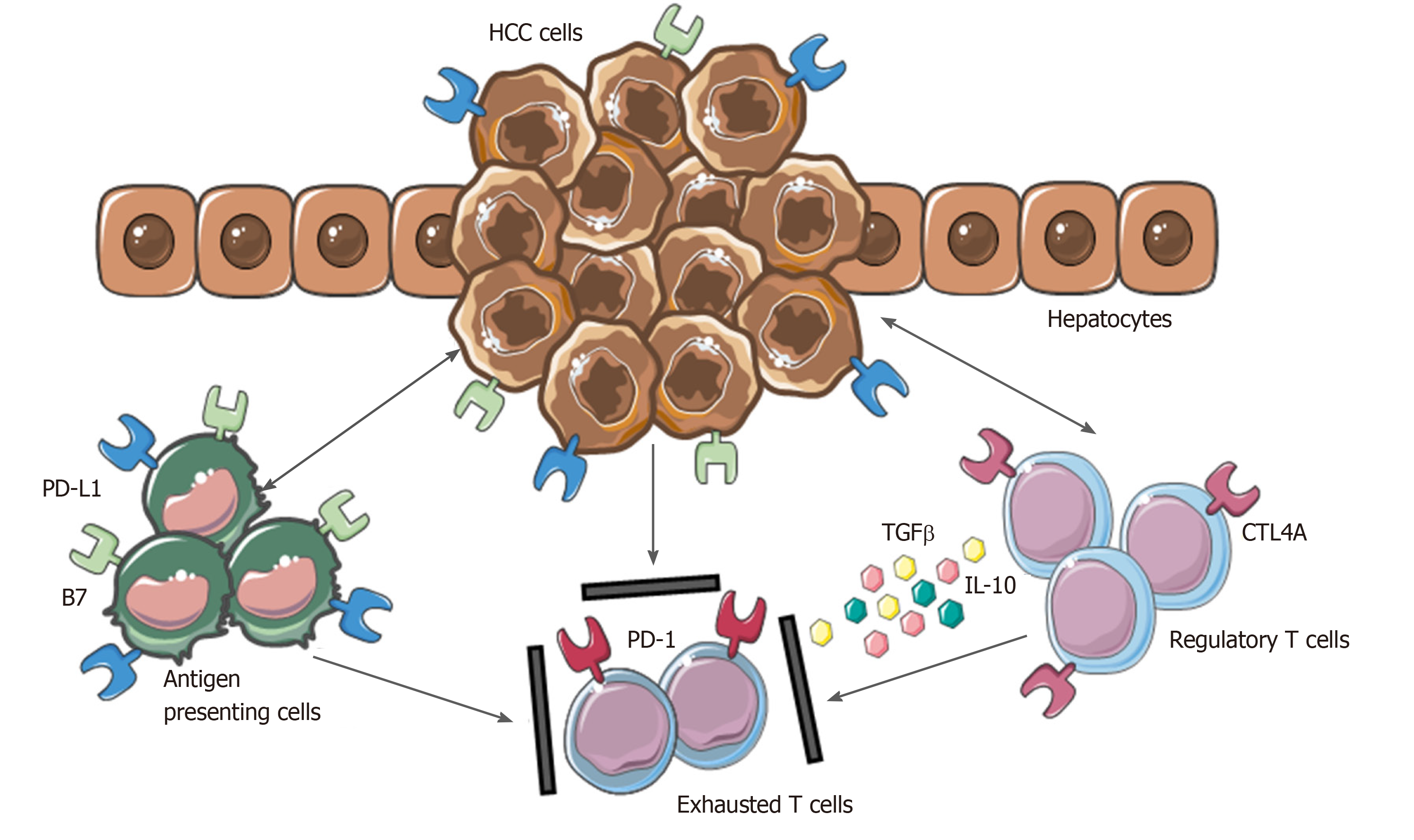
Figure 2 Mechanisms involved in hepatocellular carcinoma immune evasion.
In physiological conditions, liver has the ability to induce immunotolerance against antigen from gastrointestinal tract. These mechanisms have a detrimental role during hepatocellular carcinoma development and progression. Upregulation of inhibitory programmed death-ligand 1 molecule from tumor cells, Kupffer cells, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and antigen presenting cells, together with the release of interleukin-10 and transforming growth factor beta, lead to an exhausted phenotype of CD8+ cells and prevent tumor cells from immune damage. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; PD-L1: Programmed death-ligand 1; CTL4A: Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4; PD-1: Programmed cell death protein 1; TGFβ: Transforming growth factor beta; IL-10: Interleukin-10.
- Citation: Polidoro MA, Mikulak J, Cazzetta V, Lleo A, Mavilio D, Torzilli G, Donadon M. Tumor microenvironment in primary liver tumors: A challenging role of natural killer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(33): 4900-4918
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i33/4900.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i33.4900