Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2020; 26(30): 4501-4522
Published online Aug 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i30.4501
Published online Aug 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i30.4501
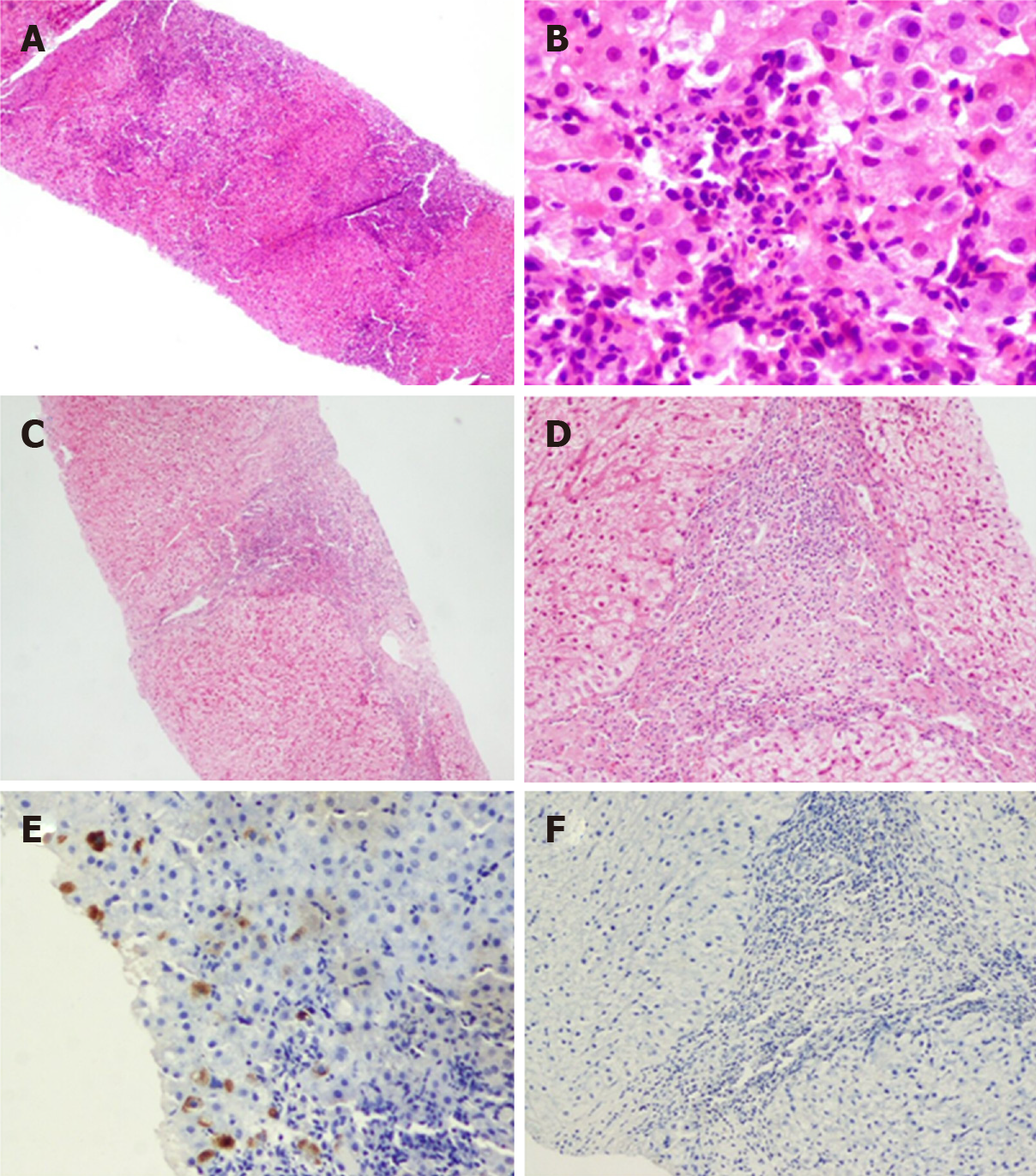
Figure 6 Typical case 2 (pathology No.
liver 0178). A: Extensive necrosis involving multiple lobules and bridging necrosis at low magnification (G4); B: Necrotic cellular debris at high magnification (G4); C: Limited fusion necrosis in two immunohistochemistry assays of liver at low magnification (G3); D: Limited fusion necrosis in two immunohistochemistry assays of liver at high magnification (G3); E: Hepatitis B virus surface antigen (+) in one immunohistochemistry assay of liver; F: Hepatitis B virus surface antigen (-) in two immunohistochemistry assays of liver.
- Citation: Xing YF, Wei CS, Zhou TR, Huang DP, Zhong WC, Chen B, Jin H, Hu XY, Yang ZY, He Q, Jiang KP, Jiang JM, Hu ZB, Deng X, Yang F, Li FY, Zhao G, Wang LC, Mi YQ, Gong ZJ, Guo P, Wu JH, Shi WQ, Yang HZ, Zhou DQ, Tong GD. Efficacy of a Chinese herbal formula on hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B patients. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(30): 4501-4522
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i30/4501.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i30.4501