Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2020; 26(3): 291-306
Published online Jan 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i3.291
Published online Jan 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i3.291
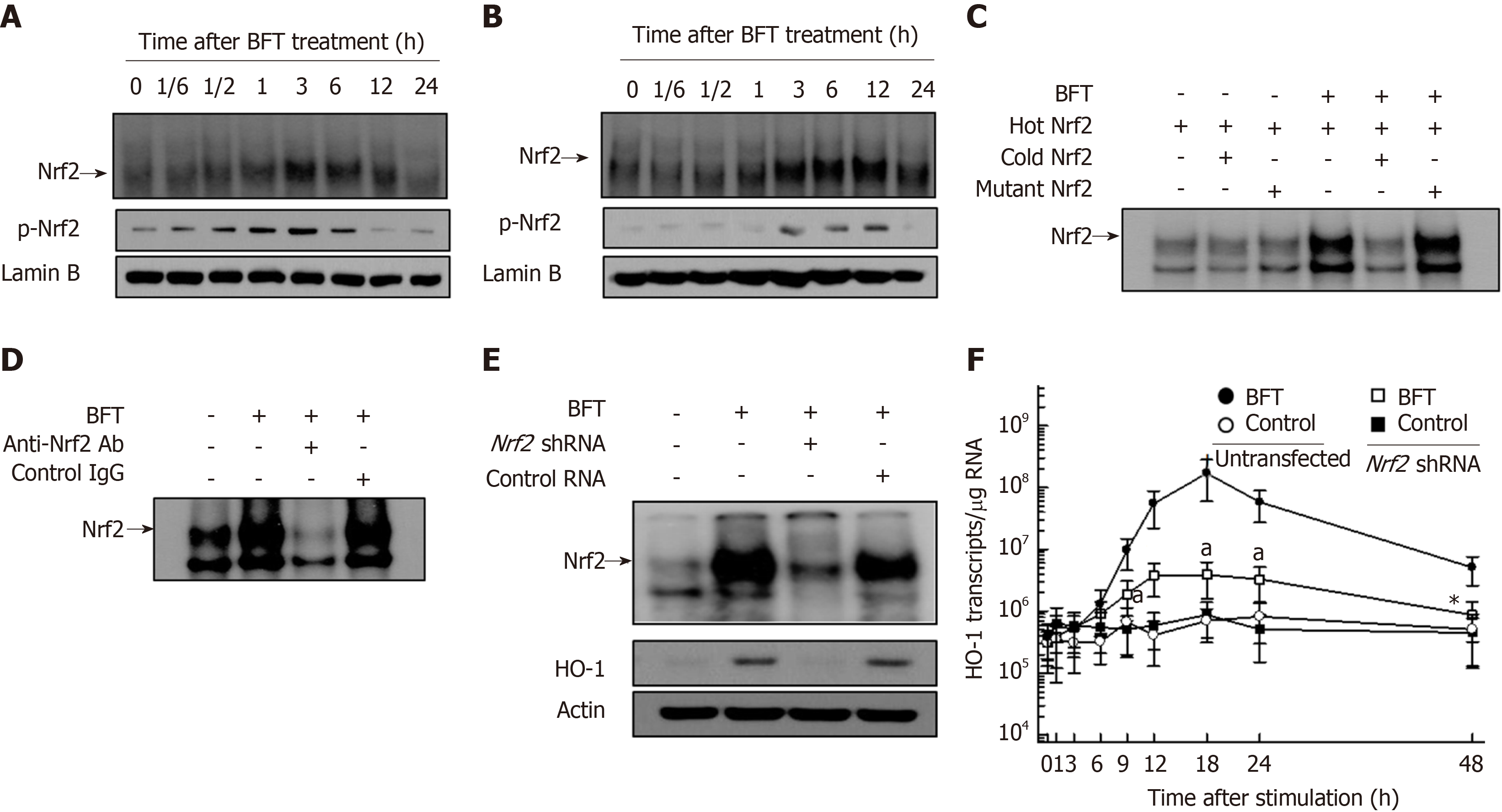
Figure 5 Activation of Nrf2 in dendritic cells stimulated with Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin.
A and B: Bone marrow (BM)-derived dendritic cells (DCs) (A) and DC2.4 cells (B) were treated with BFT (100 ng/mL) for the indicated periods. Nrf2 DNA binding activity was assessed by EMSA. Immunoblot results for concurrent phospho-Nrf2 and lamin B in nuclear extracts are provided beneath the EMSA. C and D: Competition and supershift assays for Nrf2 signals. C: BM-derived DCs were treated with BFT (100 ng/mL) for 6 h and nuclear extracts were then prepared. The competition assay for Nrf2 signals was performed by adding a 100-fold excess of the unlabeled probe (“cold” probe) before the addition of the radiolabeled probe (“hot” probe) or a mutant probe to the reaction (top panel). D: Supershift assays using nuclear extracts were performed using anti-Nrf2 Ab and IgG isotype control Ab (bottom panel). Results are representative of more than three independent experiments. E: DC2.4 cells were transfected with Nrf2-specific shRNA or control RNA. Transfected cells were combined with BFT (100 ng/mL) for 12 h. Nrf2 binding activity was assayed by EMSA (top panel). Transfected cells were treated with BFT (100 ng/mL) for 24 h and the expression of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and actin was analyzed by immunoblot (bottom panel). F: DC2.4 cells were treated with BFT (100 ng/mL) for the indicated periods. The levels of HO-1 mRNA were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR using a standard RNA. The values are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 5). β-actin mRNA levels in each group remained relatively constant throughout the same periods (approximately 106 transcripts/μg total RNA). aP < 0.05 vs untransfected cells treated with BFT. HO-1: Heme oxygenase-1; BFT: Bacteroides fragilis toxin.
- Citation: Ko SH, Jeon JI, Woo HA, Kim JM. Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin upregulates heme oxygenase-1 in dendritic cells via reactive oxygen species-, mitogen-activated protein kinase-, and Nrf2-dependent pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(3): 291-306
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i3/291.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i3.291