Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2020; 26(29): 4302-4315
Published online Aug 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i29.4302
Published online Aug 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i29.4302
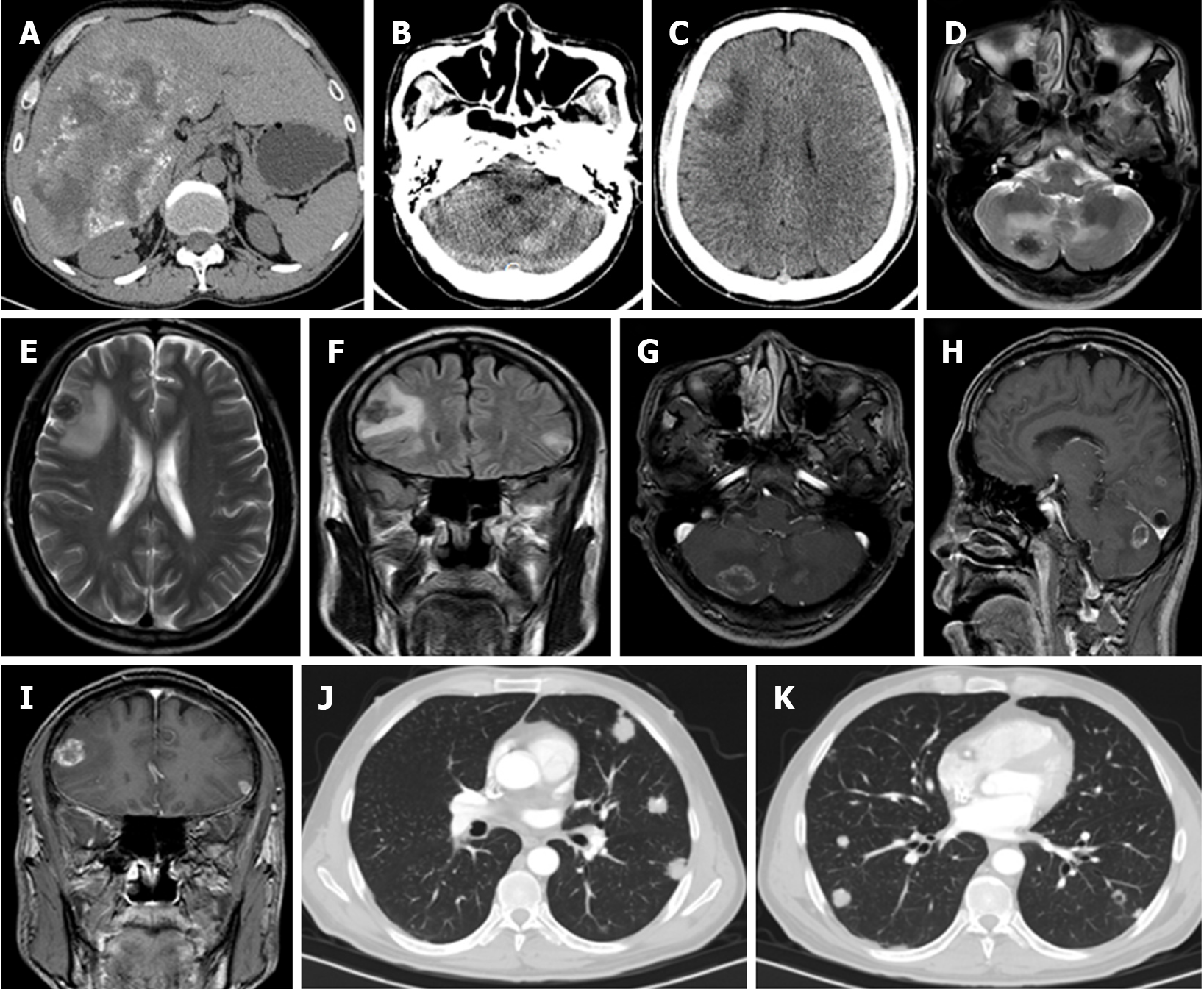
Figure 4 Male, age 52 years, Han Chinese.
A: Abdominal computed tomography (CT) showing the hepatic alveolar echinococcosis lesion in the right liver lobe. echinococcus multilocularis Ulm classification-CT Type IIIb with more solid portions at the edge; B, C: Cranial CT scan showing multiple bilateral cerebellar hemisphere and frontal lobe calcified masses with surrounding edema; D, E: Coronal T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showing multiple lesions with associated edema; F: Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MRI showing two lesions with low signal intensity and surrounding edema; G-I: T1-weighted contrast-enhanced MRI showing nodular enhancement of the lesion; J, K: Chest CT scan showing multiple irregular solid nodules in both lungs and some lesions with “empty bubble sign” .
- Citation: Graeter T, Bao HH, Shi R, Liu WY, Li WX, Jiang Y, Schmidberger J, Brumpt E, Delabrousse E, Kratzer W, the XUUB Consortium. Evaluation of intrahepatic manifestation and distant extrahepatic disease in alveolar echinococcosis. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(29): 4302-4315
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i29/4302.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i29.4302